Abstract
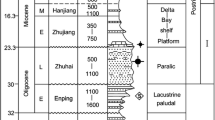
The alkane fraction of 11 biodegraded oils and five non-biodegraded oils from the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China, were analyzed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry to investigate the biomarker alteration caused by biodegradation. Results indicated that the concentration of 25-norhopanes was correlated with increased biodegradation. The oil samples showed an increase in the C31 and C32 hopane 22S/(22S + 22R), C29 sterane C2920S/(20S + 20R), and C29ββ/(ββ + αα) thermal maturity parameters in the heavily biodegraded oils. Oleanane was preferentially biodegraded compared with C3017α-hopane, which was preferentially biodegraded compared with C2917α, 21β-norhopane, C30 moretane, and C29 25-norhopane. The selective depletion of C27–C29 steranes followed the order ααα 20R > ααα 20S + αββ 20R > αββ 20S and C27 > C29 > C28, and the diasteranes and C20–C21 steranes were much more resistant to biodegradation than regular C27–C29 steranes. The steranes were generally preferentially biodegraded compared with the hopanes in this study.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ourisson, G., Albrecht, P., & Rohmer, M. (1984). The microbial origin of fossil fuels. Scientific American, 251, 44–51.
Prince, R. C. (1987). Hopanoids: the world’s most abundant biomolecules?. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 12, 455–456.
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1991). Effects of source, thermal maturity, and biodegradation on the distribution and isomerization of homohopanes in petroleum. Organic Geochemistry, 17, 47–61.
Lewan, M. D., Bjorǿy, M., & Dolcater, D. L. (1986). Effects of thermal maturation on steroid hydrocarbons as determined by hydrous pyrolysis of Phosphoria Retort Shale. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 50, 1977–1987.
Lu, S. T., Ruth, E., & Kaplan, I. R. (1989). Pyrolysis of kerogens in the absence and presence of montmorillonite. I. The generation, degradation and isomerization of steranes and triterpanes at 200 and 300 °C. Organic Geochemistry, 14, 491–499.
Peters, K. E., Moldowan, J. M., & Sundararaman, P. (1990). Effects of hydrous pyrolysis on biomarker thermal maturity parameters: Monterey phosphatic and siliceous members. Organic Geochemistry, 15, 249–265.
Mackenzie, A. S., Patience, R. L., Maxwell, J. R., Vandenbroucke, M., & Durand, B. (1980). Molecular parameters of maturation in the Toarcian shales, Paris Basin, France I. Changes in the configurations of the acyclic isoprenoid alkanes, steranes and triterpanes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 44, 1709–1721.
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1993). The biomarker guide: interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Wang, Z. D., Fingas, M., Blenkinsopp, S., Sergya, G., Landriaulta,M., Sigouin, L., Foght,J., Semple, K., & Westlake, D.W.S. (1998). Comparison of oil composition changes due to biodegradation and physical weathering in different oils. Journal of Chromatography A, 809, 89–107.
Ross, A. S., Farrimond, P., Erdmann, & M. Larter, S.R. (2010). Geochemical compositional gradients in a mixed oil reservoir indicative of ongoing biodegradation. Organic Geochemistry, 41, 307–320.
López, L., Mónaco, S. L. & Volkman, J. K. (2015). Evidence for mixed and biodegraded crude oils in the Socororo field, Eastern Venezuela Basin. Organic Geochemistry, 82,12–21.
Petsch, S. T., Berner, R. A., & Eglinton, T.I. (2000). A field study of the chemical weathering of ancient sedimentary organic matter. Organic Geochemistry, 31, 475–487.
Petsch, S. T., Edwards, K. J., & Eglinton T. I. (2005). Microbial transformations of organic matter in black shales and implications for global biogeochemical cycles. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 219, 157–170.
Marynowski, L., & Wyszomirski, P. (2008). Organic geochemical evidence diagenetic oxidation of the terrestrial organic matter during the Triass semi arid climatic conditions. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 2612–2618.
Marynowski, L., Kurkiewicz, S., Rakociński, M., & Simoneit, B.R.T. (2011). Effects of weathering on organic matter: I. Changes in molecular composition of extractable organic compounds caused by paleoweathering of a Lower Carboniferous (Tournaisian) marine black shale. Chemical Geology, 285, 144–156.
Clayton, J. L., & King, J. D. (1987). Effects of weathering on biological marker and aromatic hydrocarbon composition of organic matter in Phosphoria shale outcrop. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51, 2153–2157.
Volkman, J. K., Alexander, B., Kagi, R. I., & Woodhouse, G.W. (1983). Demethylated hopanes in crude oils and their application in petroleum geochemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 47, 785–794.
Volkman, J. K., Alexander, R., Kagi, R. I., Rowland, S. F., & Sheppard, P. N. (1984). Biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in crude oils from the Barrow Sub-basin of Western Australia. Organic Geochemistry, 6, 619–631.
Peters,K. E., Moldowan, J.M., McCaffrey, M.A., & Fago, F. J. (1996). Selective biodegradation of extended hopanes to 25-norhopanes in petroleum reservoirs. Insights from molecular mechanics. Organic Geochemistry, 24,765–783.
Wenger, L. M., Davis, C. L., & Isaksen, G. H. (2002). Multiple controls on petroleum biodegradation and impact on oil quality. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 5, 375–383.
Larter, S., Huang, H., Adams, J., Bennett, B., Snowdon, L.R., (2012). A practical biodegradation scale for use in reservoir geochemical studies of biodegraded oils. Organic Geochemistry, 45, 66–76.
Zhu, G. Y., Jin, Q., Zhang, S. C., Dai, J. X., Zhang, L. y., & Li, J. (2004). Combination characteristics of lake facies source rock in the Shahejie Formation, Dongying Depression. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(3), 416–427.
Chen, Z. H., & Zha, M. (2006). Overpressured fluid compartment and hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in Dongying Depression. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24 (4): 607–615.
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., & Moldowan, J. M. (2005). The biomarker guide. In: Biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum exploration and earth history, second ed., vol. 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 475–1155.
Beach, F., Peakman, T., Abbott, G. D., Sleeman, R., & Maxwell, J. R. (1989). Laboratory thermal alteration of triaromatic steroid hydrocarbons. Organic Geochemistry, 14, 109–111.
Reed, W. E. (1977). Molecular compositions of weathered petroleum and comparison with its possible sources. Geochimcia et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 237–247.
Rullkӧtter, J., & Wendisch D. (1982). Microbial alteration of 17α(H)-hopane in Madagascar asphalts: removal of C-10 methyl group and ring opening. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46, 1543–1553.
Requejo, A. G. & Halpern, H. I. (1989). An unusual hopane biodegradation sequence in tar sands from the Pt. Arena (Monterey) Formation. Nature, 342, 70–673.
Trendel, J., Guilhem, J., Grisp, P., Repeta, D., Connan, J., & Albrecht, P. (1990). Identification of two C-10 demethylated C28 hopanes in biodegraded petroleum. Journal of Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 12,424–425.
Bost, F. D., Frontera-Suau, R., McDonald, T. J., Peters, K. E., & Morris, P.J. (2001). Aerobic biodegradation of hopanes and norhopanes in Venezuelan crude oils. Organic Geochemistry, 32, 105–114.
Li, N. X., Huang, H. P., Jiang, W. L., Wu T., & Sun J. J. (2015). Biodegradation of 25-norhopanes in a Liaohe Basin (NE China) oil reservoir. Organic Geochemistry, 78, 33–43.
Alexander, R., Kagi, R., Woodhouse, G. W., & Volkman, J. K. (1983). The geochemistry of some biodegraded Australian oils. Australian Petroleum Exploration Association Journals, 23, 53–63.
Philp, R. P. (1983). Correlation of crude oils fron the San Jorges Basin, Argentina. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 47, 267–275.
Talukdar, S., Gallango, O., & Chin-A-Lien, M. (1986). Generation and migration of hydrocarbons in the Maracaibo Basin, Venezuela: an integrated basin study. Organic Geochemistry, 10, 261–279.
Talukdar, S., Gallango, O., & Ruggiero, A. (1988). Generation and migration of oil in the Maturin Subbasin, Eastern Venezuelan Basin. Organic Geochemistry, 13, 537–547.
Sofer, Z., Zumberge, J. E., & Lay, V. (1986). Stable carbon isotopes and biomarkers as tools in understanding genetic relationship, maturation, biodegradation, and migration in crude oils in the Northern Peruvian Oriente (Maranon) Basin. Organic Geochemistry, 10, 377–389.
Chen, Z. H., Zha, M., & Jin, Q. (2004). Episodic expulsion of hydrocarbons in overpressured systems in Dongying depression. Oil & Gas Geology, 25(4), 444–447.
Moldowan, J. M., & McCaffrey, M. A. (1995). A novel microbial hydrocarbon degradation pathway revealed by hopane demethylation in a petroleum reservoir. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1891–1894.
Chosson, P., Lanau, C., Connan, J., & Dessort, D. (1991). Biodegradation of refractory hydrocarbon biomarkers from petroleum under laboratory conditions. Nature, 351, 640–642.
Munoz, D., Guiliano, M., Dounmenq, P. Jacquot, F., Scherreri, P., & Mille, G. (1997). Long term evolution of petroleum biomarkers in Mangrove soil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 868–874.
Seifert, W. K., Moldowan, J. M., & Demaison G. J. (1984). Source correlation of biodegraded oils. Organic Geochemistry, 6, 633–643.
Hoffmann, C. F., & Strausz O. P. (1986). Bitumen accumulation in Grosmont Platform Complex, Upper Devonian, Albert, Canada. AAPG Bulletin, 70, 1113–1128.
Lin, L. H., Michael, G. H., Kovachev, G. Zhu, H., Philp, R.P., & Lewis, C.A. (1989). Biodegradation of tar-sands bitumens from the Ardmore and Anadarko basins, Carter Country, Oklahoma. Organic Geochemistry, 14, 511–523.
Williams, J. A., Bjorøy, M., Dolcater, D. L., & Winters, J. C. (1986). Biodegradation in South Texas Eocene oils: effects on aromatics and biomarkers. Organic Geochemistry, 10, 451–461.
Walters, C. C., Pierce, S. E., Gormly, J.R., & Rooney, M. A. (1993). Loma Chumico Shale: a super-rich source rock with unusual geochemical characteristics. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 77, 354.
Riva, A., Caccialanza, P. G. & Quagliaroli, F. (1988). Recognition of 18β(H)-oleanane in several crudes and Tertiary-Upper Cretaceous sediments. Definition of a new maturity parameter. Organic Geochemistry, 13, 671–675.
Ekweozor, C. M., & Udo, O. T. (1988). The oleananes: origin, maturation, and limits of occurrence in southern Nigeria sedimentary basin. Organic Geochemistry, 13, 131–140.
Zumber, J. E. (1984). Source Rocks of the La Luna (Upper Cretaceous) in the Middle Magdalena Valley, Colombia. In: Geochemistry and source rock potential of carbonate rocks (J.G.Palacas, ed.), American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, OK, 127–133.
Connan, J., Bouroullec, J., Dessort, D., & Albrecht, P. (1986). The microbial input in carbonate-anhydrite facies of a sabkha palaoenvironment from Guatemala: a molecular approach. Organic Geochemistry, 10, 29–50.
Clark,J. P., & Philp, R. P. (1989). Geochemical characterization of evaporate and carbonate depositional environments and correlation of associated crude oils in Black Creek Basin, Alberta, Canadian Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 37, 401–416.
Brooks, P. W. (1986). Unusual biological marker geochemistry of oils and possible source rocks, offshore Beaufort Mackenzie Delta, Canada. In: Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1985 (D. Leythaeuser and J.Rullötter, eds.), Pregamon Press, Oxford, p, 401–406.
Seifert, W. K., & Moldowan, J. M. (1979). The effect of biodegradation on steranes and terpanes in crude oils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43, 111–126.
Mille, G., Munoz, D., Jacquot, F., Jacquot, F., Rivet, L., & Bertrand, J. C. (1988). The Amoco Cadiz oil spill: evolution of petroleum hydrocarbons in the Ile Grande salt marches (Brittany) after a 13-year period. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 47, 547–559.
Gagni, S., & Cam, D. (2007). Stigmastane and hopanes as conserved biomarkers for estimating oil biodegradation in a former refinery plant-contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 67, 1975–1981.
Brooks, P. W., Fowler, M. G., & Macqueen, R. W. (1988). Biological marker and conventional organic geochemistry of oil sands/heavy oils, Western Canada Basin. Organic Geochemistry, 12, 519–538.
Cao, J., Hu, K., Wang, K., Bian, L. Z., Liu, Y. T., Yang, S. Y., Wang, L. Q., & Chen, Y. (2008). Possible origin of 25-Norhopanes in Jurassic organic poor mudstones from the northern Qaidam Basin (NW China). Organic Geochemistry, 39, 1058–1065.
Acknowledgments
This work was co-funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 41272140), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M571227).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wang, TG. & Yan, D. Changes in Concentration and Distribution of Biomarkers in Biodegraded Oils from Dongying Depression, China. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 177, 713–731 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1775-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1775-z