Abstract
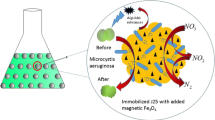
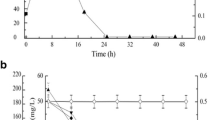
In this study, we investigated the bioremediation of petrochemical wastewater containing BTEX compounds by immobilized Comamonas sp. JB cells. Three kinds of magnetic nanoparticles were evaluated as immobilization supports for strain JB. After comparison with Fe3O4 and a-Fe2O3 nanoparticles, r-Fe2O3 nanoparticle was selected as the optimal immobilization support. The highest biodegradation activity of r-Fe2O3-magnetically immobilized cells was obtained when the concentration of r-Fe2O3 nanoparticle was 120 mg L−1. Additionally, the recycling experiments demonstrated that the degradation activity of r-Fe2O3-magnetically immobilized cells was still high and led to less toxicity than untreated wastewater during the eight recycles. qPCR suggested the concentration of strain JB in r-Fe2O3-magnetically immobilized cells was evidently increased after eight cycles of degradation experiments. These results supported developing efficient biocatalysts using r-Fe2O3-magnetically immobilized cells and provided a promising technique for improving biocatalysts used in the bioremediation of not only petrochemical wastewater but also other hazardous wastewater.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prenafeta-Boldú, F. X., Vervoort, J., Grotenhuis, J. T. C., & van Groenestijn, J. W. (2002). Substrate interactions during the biodegradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) hydrocarbons by the fungus Cladophialophora sp. strain T1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 756–762.
Saeed, T., & Al Mutairi, M. (1999). Chemical composition of the water- soluble fraction of the leaded gasolines in seawater. Environmental International, 25, 117–129.
Littlejohns, J. V., & Daugulis, A. J. (2008). Kinetics and interactions of BTEX compounds during degradation by a bacterial consortium. Process Biochemistry, 43, 1068–1076.
Costa, A. S., Romão, L. P., Araújo, B. R., Lucas, S. C., Maciel, S. T., Wisniewski, A., Jr., & Alexandre, M. R. (2012). Environmental strategies to remove volatile aromatic fractions (BTEX) from petroleum industry wastewater using biomass. Bioresource Technology, 105, 31–39.
Dean, B. J. (1985). Recent findings on the genetic toxicology of benzene, toluene, xylenes and phenols. Mutation Research, 154, 153–181.
Kim, J. M., Le, N. T., Chung, B. S., Park, J. H., Bae, J. W., Madsen, E. L., & Jeon, C. O. (2008). Influence of soil components on the biodegradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and o-, m-, and p-xylenes by the newly isolated bacterium Pseudoxanthomonas spadix BD-a59. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74, 7313–7320.
Chakraborty, R., O’Connor, S. M., Chan, E., & Coates, J. D. (2005). Anaerobic degradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene compounds by Dechloromonas strain RCB. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 8649–8655.
Kim, D., Kim, Y. S., Kim, S. K., Kim, S. W., Zylstra, G. J., Kim, Y. M., & Kim, E. (2002). Monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Rhodococcus sp. strain DK17. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3270–3278.
Shinoda, Y., Sakai, Y., Uenishi, H., Uchihashi, Y., Hiraishi, A., Yukawa, H., Yurimoto, H., & Kato, N. (2004). Aerobic and anaerobic toluene degradation by a newly isolated denitrifying bacterium, Thauera sp. strain DNT-1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 1385–1392.
Zylstra, G. J., & Kim, E. (1997). Aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Sphingomonas yanoikuyae B1. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 408–414.
Jin, H. M., Choi, E. J., & Jeon, C. O. (2013). Isolation of a BTEX-degrading bacterium, Janibacter sp. SB2, from a sea-tidal flat and optimization of biodegradation conditions. Bioresource Technology, 145, 57–64.
Kim, J. M., & Jeon, C. O. (2009). Isolation and characterization of a new benzene, toluene, and ethylbenzene degrading bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. B113. Current Microbiology, 58, 70–75.
Assinder, S. J., & Williams, P. A. (1990). The TOL plasmids: determinants of the catabolism of toluene and the xylenes. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 31, 1–69.
Choi, E. J., Jin, H. M., Lee, S. H., Math, R. K., Madsen, E. L., & Jeon, C. O. (2013). Comparative genomic analysis and benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and o-, m-, and p-xylene (BTEX) degradation pathways of Pseudoxanthomonas spadix BD-a59. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79, 663–671.
Shi, S. N., Qu, Y. Y., Ma, F., & Zhou, J. T. (2014). Bioremediation of coking wastewater containing carbazole, dibenzofuran, dibenzothiphene and naphthalene by a naphthalene-cultivated Arthrobacter sp. W1. Bioresource Technology, 166, 79–86.
Shi, S. N., Qu, Y. Y., Ma, F., & Zhou, J. T. (2014). Bioremediation of coking wastewater containing carbazole, dibenzofuran and dibenzothiphene by immobilized naphthalene-cultivated Arthrobacter sp. W1 in magnetic gellan gum. Bioresource Technology, 164, 28–33.
Dwyer, D. F., Krumme, M. L., Boyd, S. A., & Tiedje, J. M. (1986). Kinetics of phenol biodegradation by an immobilized methanogenic consortium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 52, 345–351.
Lee, S. T., Rhee, S. K., & Lee, G. M. (1994). Biodegradation of pyridine by freely suspended and immobilized Pimelobacter sp. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41, 652–657.
Li, F. L., Xu, P., Feng, J. H., Meng, L., Zheng, Y., Luo, L. L., & Ma, C. Q. (2005). Microbial desulfurization of gasoline in a Mycobacterium goodii X7B immobilized-cell system. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 276–281.
Wang, X., Gai, Z., Yu, B., Feng, J., Xu, C., Yuan, Y., Lin, Z., & Xu, P. (2007). Degradation of carbazole by microbial cells immobilized in magnetic gellan gum gel beads. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 6421–6428.
Fernando Bautista, L., Morales, G., & Sanz, R. (2010). Immobilization strategies for laccase from Trametes versicolor on mesostructured silica materials and the application to the degradation of naphthalene. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8541–8548.
Qiu, H., Lu, L., Huang, X., Zhang, Z., & Qu, Y. (2010). Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on nanoporous copper and its potential applications. Bioresource Technology, 101, 9415–9420.
Liu, Y., Zeng, Z., Zeng, G., Tang, L., Pang, Y., Li, Z., Liu, C., Lei, X., Wu, M., Ren, P., Liu, Z., Chen, M., & Xie, G. (2012). Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of naphthaleneic compounds. Bioresource Technology, 115, 21–26.
Jiang, B., Zhou, Z.C., Dong, Y., Tao, W., Wang, B., Jiang, J.W., & Guan, X.Y., 2014. Biodegradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and o-, m-, and p-xylenes by the newly isolated bacterium Comamonas sp. JB. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Science and Technology Project of Liaoning Province (2014203006), Ocean & Fisheries Project of Liaoning Province (201301), Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (201205012–7), Science and Technology Project of Dalian City (2012J21DW029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 7575 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., Zhou, Z., Dong, Y. et al. Bioremediation of Petrochemical Wastewater Containing BTEX Compounds by a New Immobilized Bacterium Comamonas sp. JB in Magnetic Gellan Gum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 572–581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1596-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1596-0