Abstract
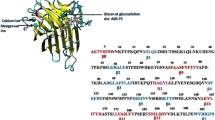
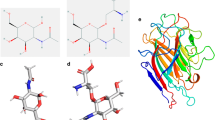
Crystal structure of Butea monosperma seed lectin (BML) was analyzed and the metal ion geometry identified. In order to understand the role of metal ions for the structural stability and ligand binding, studies of demetallized protein were carried out. Binding of different ligands like GalNAc, lactose, and galactose onto native and demetallized protein was studied by isothermal titration calorimetry as well as molecular simulation methods. Molecular dynamics was applied to the structure after removing the coordinates of metal ions, to identify the effect of demetallization in silico. Docking studies of different sugar molecules as well as the fungal α-amylase was carried out and compared the interactions in the native and apo states. It was found that metal ions are important for the ligand binding with increased affinity. However, their absence did not make any alteration to the secondary structure. Though the metal ions were not coordinated to the loops contacting the α-amylase, the absence of metal ions reduced the protein-protein binding strength due to long-range changes in irregular structures of the lectin.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 October 2022
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04192-0
References
Ohba, H., Bakalova, R., Moriwaki, S., & Nakamura, O. (2002). Fractionation of normal and leukemic T-cells by lectin-affinity column chromatography. Cancer Letters, 184, 207–214.
Peumans, W. J., & Van Damme, E. J. (1995). Lectins as plant defense proteins. Plant Physiology, 109, 347–352.
Abhilash, J., Geethanandan, K., Bharath, S. R., Sadasivan, C., & Haridas, M. (2011). Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a galactose-specific lectin from the seeds of Butea monosperma. Acta Crystallographica, Section F: Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications, 67, 524–526.
Abhilash, J., Geethanandan, K., Bharath, S. R., Sabu, A., Sadasivan, C., & Haridas, M. (2015). The crystal structure of a lectin from Butea monosperma: insight into its glycosylation and binding of ligands. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 72, 1376–1383.
Mitra, N., Srinivas, V. R., Ramya, T. N. C., Ahmad, N., Reddy, G. B., & Surolia, A. (2002). Conformational stability of legume lectins reflect their different modes of quaternary association: solvent denaturation studies on concanavalin A and winged bean acidic agglutinin. Biochemistry, 41, 9256–9263.
Imberty, A., Gautier, C., Lescar, J., Pérez, S., Wyns, L. A., & Loris, R. (2000). An unusual carbohydrate binding site revealed by the structures of two Maackia amurensis lectins complexed with sialic acid containing oligosaccharides. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 17541–17548.
Dessen, A., Gupta, D., Sabesan, S., Brewer, C. F., & Sacchettini, J. C. (1995). X-ray crystal structure of the soybean agglutinin cross-linked with a biantennary analog of the blood group I carbohydrate antigen. Biochemistry, 34, 4933–4942.
Hamelryck, T. W., Dao-Thi, M. H., Poortmans, F., Chrispeels, M. J., Wyns, L., & Loris, R. (1996). The crystallographic structure of phytohemagglutinin-L. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 20479–20485.
Buts, L., Dao-Thi, M. H., Loris, R., Wyns, L., Etzler, M., & Hamelryck, T. (2001). Weak protein-protein interactions in lectins: the crystal structure of a vegetative lectin from the legume Dolichos biflorus. Journal of Molecular Biology, 309, 193–201.
Rabijns, A., Verboven, C., Rougé, P., Barre, A., Van Damme, E. J., Peumans, W. J., & De Ranter, C. J. (2001). Structure of a legume lectin from the bark of Robinia pseudoacacia and its complex with Nacetylgalactosamine. Proteins, 44, 470–478.
Naidoo, K. J., & Brady, J. W. (1997). Molecular dynamics simulations of a glycoprotein: the lectin from Erythrina corallodendron. Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, 395, 469–475.
Caffarena, E. R., Grigera, J. R., & Bisch, P. M. (2002). Stochastic molecular dynamics of peanut lectin PNA complex with T-antigen disaccharide. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 21, 227–240.
Praveen, K., & Bernd, N. (2007). Molecular dynamics simulations of pea (Pisum sativum) lectin structure with octyl glucoside detergents: the ligand interactions and dynamics. Biophysical Chemistry, 128, 215–230.
Abhilash, J., Dileep, K. V., Palanimuthu, M., Geethanandan, K., Sadasivan, C., & Haridas, M. (2013). Metal ions in sugar binding, sugar specificity and structural stability of Spatholobus parviflorus seed lectin. Journal of Molecular Modelling, 8, 3271–3278.
Kaushik, S., Mohanty, D., & Surolia, A. (2009). The role of metal ions in substrate recognition and stability of concanavalin A: a molecular dynamics study. Biophysical Journal, 96, 21–34.
Cornell, W. D., Cieplak, P., Bayly, C. I., Gould, I. R., Merz, K. M., Ferguson, D. M., Spellmeyer, D. C., Fox, T., Caldwell, J. W., & Kollman, P. A. (1995). A second generation force field for the simulation of proteins, nucleic acids, and organic molecules. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 117, 5179–5197.
Jorgensen, W. L., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, J. D., Impeyand, R. W., & Klein, M. L. (1983). Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. Journal of Chemical Physics, 79, 926–935.
Sherman, W., Beard, H. S., & Farid, R. (2006). Use of an induced fit receptor structure in virtual screening. Chemical Biology and Drug Design, 67, 83–84.
Friesner, R. A., Murphy, R. B., Repasky, M. P., Frye, L. L., Greenwood, J. R., Halgren, T. A., Sanschagrin, P. C., & Mainz, D. T. (2006). Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure of protein-ligand complexes. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 21, 6177–6196.
Tintu, I., Dileep, K. V., Remya, C., Anu, A., & Sadasivan, C. (2012). 6-Gingerol inhibits fungal alpha amylase: enzyme kinetic and molecular modeling studies. Starch, 8, 607–612.
Ritchie, D. W. (2003). Evaluation of protein docking predictions using Hex 3.1 in CAPRI rounds 1 and 2. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Genetics, 52, 98–106.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Prof. M. Haridas, Department of Biotechnology & Microbiology and Inter University Centre for Bioscience, Kannur University, and holds a Ph.D degree.
J. Abhilash holds a M.Sc degree.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abhilash, J., Haridas, M. Metal Ion Coordination Essential for Specific Molecular Interactions of Butea monosperma Lectin: ITC and MD Simulation Studies. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 277–286 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1573-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1573-7