Abstract
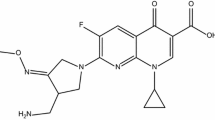
Nanohybrid of cefuroxime (CFO) with layered double hydroxide (LDH) has been prepared, and the rate of dissolution and bioavailability of CFO using nanohybrid as a drug delivery system has been broadly studied. The intercalation process was confirmed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. The CFO contents were found to be 19.0 wt% in the nanohybrid. The release mechanism of CFO was investigated with respect to anion and pH of the dissolution media such as gastric, intestinal and blood simulated media. The effect of pH was evaluated on the release of CFO from nanohybrid, and the dissolution of CFO from the nanohybrid was found to be a slow process at pH 4.0, 6.8, and 7.4. Further the addition of Cl ion and PAM in release media did not affect the release rate of drug at pH 4.0 and 6.8, while at pH 7.4, Cl ion and PAM have significant role on the drug release. At pH 1.2, the release study shows that LDH dissolved in the acidic medium and CFO released in its molecular form. The release behavior suggests two mechanisms that are responsible for the release of CFO from nanohybrid: weathering (dependent on the pH) and ion exchange (highly dependent on the anions). Surface reactions mediated by solid weathering ruled the release in gastric fluid, whereas anion exchange determined CFO release in lysosomal, intestinal, and blood medium. In order to evaluate the drug release mechanism, the released data were fitted by mathematical models describing various kinetic.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prestwich, G. D., & Luo, Y. (2001). Expert Opinion Therapeutics Patent, 11, 1395–1410.
Ahmed, A., Bonner, C., & Desai, T. A. (2002). Journal of Controlled Release, 81, 291–306.
Ambrogi, V., Fardella, G., & Grandolini, G. (2001). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 220, 23–32.
Ambrogi, V., Fardella, G., Grandolini, G., Nochetti, M., & Perioli, L. (2003). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 92, 1407–1418.
Biswick, T., Park, D. H., Shul, Y. G., & Choy, J. H. (2010). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 71, 647–649.
Berger, J., Reist, M., Mayer, J. M., Felt, O., Peppas, N. A., & Gurny, R. (2001). European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 57, 19–34.
Oh, J. M., et al. (2006). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 67, 1024–1027.
Bondesson, L., Mikkelsen, K. V., Garberg, P., & Ågren, H. (2007). Spectrochimica Acta A, 66, 213–224.
Ladewig, K., Xu, Z. P., & Lu, G. Q. (2009). Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 6, 907–922.
Chakraborty, J., Roychowdhury, S., Sengupta, S., & Ghosh, S. (2013). Materials Science Engineering C Materials Biological Applications, 33, 2168–2174.
Bugatti, V., Gorras, G., Montanari, F., Nocchetti, M., Tammaro, L., & Vittoria, V. (2011). Applied Clay Science, 52, 34–40.
Choi, S.-J., Oh, J.-M., & Choy, J.-H. (2008). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69, 1528–1532.
Choy, J. H., Kimb, Y. K., Sona, Y. H., Choy, Y. B., Oha, J. M., Jung, H., & Hwang, S. J. (2008). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69, 1547–1551.
Choy, J.-H., Choi, S.-J., Oh, J.-M., & Park, T. (2007). Applied Clay Science, 36, 122–132.
Paek, S. M., Jang, J. U., Hwang, S. J., & Choy, J. H. (2006). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 67, 1020–1023.
Perioli, L., Ambrogi, V., di Nauta, L., Nochetti, M., & Rossi, C. (2011). Applied Clay Science, 51, 407–413.
Park, J. K., Choy, Y. B., Oh, J. M., Kim, J. Y., Hwang, S. J., & Choy, J. H. (2008). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 359, 198–204.
Del Arco, M., Fernández, A., Martín, C., & Rives, V. (2009). Applied Clay Science, 42, 538–544.
Choi, G., Lee, J. H., Oha, Y. J., Choy, Y. B., Park, M. C., Chang, H. C., & Choy, J. H. (2010). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 402, 117–122.
Del Hoyo, C. (2007). Applied Clay Science, 36, 103–121.
Ryu, S. J., Jung, H., Oh, J. M., Lee, J. K., & Choy, J. H. (2010). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 71, 685–688.
Khan, S. B., Liu, C., Jang, E. S., Akhtar, K., & Han, H. (2011). Materials Letters, 65, 2923–2926.
Xu, Z. P., & Lu, G. Q. (2006). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 78, 1771–1779.
Franz, J. (1975). Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 67, 190–196.
Gordijo, C. R., Barbosa, C. A. S., Ferreira, A. M. D. C., & Constantino, V. R. L. (2005). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 94, 1135–1148.
Woo, M. A., Kim, T. W., Paek, M. J., Ha, H. W., Choy, J. H., & Hwang, S. J. (2011). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 184, 171–176.
Aisawa, S., Higashiyama, N., Takahashi, S., Hirahara, H., Ikematsu, D., Kondo, H., Nakayama, H., & Narita, E. (2007). Applied Clay Science, 35, 146–154.
Gunawan, P., & Xu, R. (2008). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 97, 4367–4378.
Jinno, J., Kamada, N., Miyake, M., Yamada, K., Mukai, T., Mukai, T., Odomi, M., Toguchi, H., Liversidge, G. G., Higaki, H., & Kimura, T. (2006). Journal of Controlled Release, 111, 56–64.
Choy, J. H., Junga, J. S., Oha, J. M., Parka, M., Jeong, J., Kang, Y. K., & Han, O. J. (2004). Biomaterials, 25, 3059–3064.
Kong, X., Jin, L., Wei, M., & Duan, X. (2010). Applied Clay Science, 49, 324–329.
Li, B., He, J., Evans, D. G., & Duan, X. (2004). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 287, 89–95.
Li, A., Qin, L., Wang, W., Zhu, R., Yongchun, Y., Liu, H., & Wang, S. (2011). Biomaterials, 32, 469–477.
Palazzo, B., Sidoti, M. C., Roveri, N., Tampieri, A., Sandri, M., Bertolazzi, L., Galbusera, F., Dubini, G., Vena, P., & Contro, R. (2005). Materials Science and Engineering C, 25, 207–213.
Neu, H. C., & Fu, K. P. (1978). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotheraphy, 13, 657–664.
Rojas, R., Palena, M. C., Jimenez-Kairuz, A. F., Manzo, R. H., & Giacomelli, C. E. (2012). Applied Clay Science, 62–63, 15–20.
Sahoo, S., Chakraborti, C. K., & Behera, P. K. (2012). Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 2268–2284.
Debi Prasanna Mohanty, Yogesh Panditrao Palve, Debasish Sahoo and P.L.Nayak, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 1 (2012) 52–62.
Singhvi, G., & Singh, M. (2011). International Journal Pharmaceutical Studies Research, 2, 77–84.
San Román, M. S., Holgado, M. J., Salinas, B., & Rives, V. (2012). Applied Clay Science, 158–163.
Belskaya, O. B., Gulyaeva, T. I., Leont’eva, N. N., Zaikovskii, V. I., Larina, T. V., Kireeva, T. V., Doronin, V. P., & Likholobov, V. A. (2011). Kinetics and Catalysis, 876–885.
Gao, X., Lei, L., O'Hare, D., Xie, J., Gao, P., & Chang, T. (2013). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 174–180.
San Román, M. S., Holgado, M. J., Salinas, B., & Rives, V. (2013). Applied Clay Science, 1–7.
Raki, L., Beaudoin, J. J., & Mitchell, L. (2004). Cement and Concrete Research, 1717–1724.
Chakraborty, J., Roychowdhury, S., Sengupta, S., & Ghosh, S. (2013). Materials Science and Engineering C 2168–2174.
Carja, G., Lehutu, G., Dartu, L., Mertens, M., & Cool, P. (2012). Applied Clay Science, 37–42.
Choy, J. H., Oh, J. M., & Choi, S. J. (2011). Elsevier Ltd.
Kima, M. H., Park, D.-H., Yang, J.-H., Choy, Y. B., & Choy, J.-H. (2013). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 120–127.
Liu, C., Hou, W., Li, L., Li, Y., Liu, S. (2008). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1792–1797.
bin Hussein, M. Z., Zainal, Z. , Yahaya, A. H., & Foo, D. W. V. (2002). Journal of Controlled Release, 417–427.
Ambrogi, V., Fardella, G., Grandolini, G., Nocchetti, M., & Perioli, L. (2003). Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1407-1418.
Parello, M. L., Rojas, R., & Giacomelli, C. E. (2010). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 134–139.
del Arco, M., Fernández, A., Martín, C., & Rives, V. (2010). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 3002–3009.
Ni, Z., Xing, F., Wang, P., & Cao, G. (2008). Applied Clay Science, 72–80.
Qin, L., Wang, M., Zhu, R., You, S., Zhou, P., & Wang, S. (2013). International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2053–2064.
Perioli, L., Ambrogi, V., di Nauta, L., Nocchetti, M., & Rossi, C. (2011). Applied Clay Science, 407–413.
Ambrogi, V., Perioli, L., Ciarnelli, V., Nocchetti, M., & Rossi, C. (2009). European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 285–291.
Perioli, L., Posati, T., Nocchetti, M., Bellezza, F., Costantino, U., Cipiciani, A. (2011). Applied Clay Science, 374–378.
Ambrogi, V., Fardella, G., Grandolini, G., Perioli, L., & Tiralti, M. C. (2002). AAPS PharmSciTech, 1–6.
Lima, E., Flores, J., Cruz, A. S., Leyva-Gomez, G., & Krotzsch, E. (2013). Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 1–7.
Gasser, M. S. (2009). Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 103–109.
Silion, M., Hritcu, D., Lisa, G., & Popa, M. I. (2012). Journal of Porous Materials, 267–276.
Kurenkov, V. F., Hartan, H.-G., & Lobanov, F. I. (2001). Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 543–554.
Hussein, M. Z., Hashim, N., Yahaya, A. Hj., Zainal, Z. (2011). SainsMalaysiana, 887–896.
Li, B., He, J., Evans, D. G., & Duan, X. (2004). Applied Clay Science, 199–207.
Abdul Latip A. F., Hussein, M. Z., Stanslas, J., Wong, C. C., & Adnan, R. (2013). Chemistry Central Journal, 1–11.
Zhang, H., Pan, D., & Duan, X. (2009). Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 12140–12148.
Zhang, H., Zou, K., Guo, S., & Duan, X. (2006). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1792–1801.
Qi, F., Zhang, X., & Li, S. (2013). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1101–1108.
Zhang, X.-Q., Zeng, M.-G., Li, S.-P., & Li, X.-D. (2014). Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 98–106.
Rani, G. U., Konreddy, A. K., & Mishra*, S., & Sen, G. (2014). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 375–382.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials Research (CEAMR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under Grant no. (CEAMR-434-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.B., Alamry, K.A., Alyahyawi, N.A. et al. Nanohybrid Based on Antibiotic Encapsulated Layered Double Hydroxide as a Drug Delivery System. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 1412–1428 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1211-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1211-9