Abstract
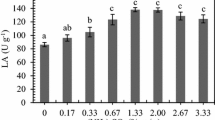
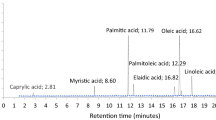
Two-phase olive mill waste (TPOMW) is presently the major waste produced by the olive mill industry. This waste has potential to be used as substrate for solid state fermentation (SSF) despite of its high concentration of phenolic compounds and low nitrogen content. In this work, it is demonstrated that mixtures of TPOMW with winery wastes support the production of lipase by Aspergillus spp. By agar plate screening, Aspergillus niger MUM 03.58, Aspergillus ibericus MUM 03.49, and Aspergillus uvarum MUM 08.01 were chosen for lipase production by SSF. Plackett–Burman experimental design was employed to evaluate the effect of substrate composition and time on lipase production. The highest amounts of lipase were produced by A. ibericus on a mixture of TPOMW, urea, and exhausted grape mark (EGM). Urea was found to be the most influent factor for the lipase production. Further optimization of lipase production by A. ibericus using a full factorial design (32) conducted to optimal conditions of substrate composition (0.073 g urea/g and 25 % of EGM) achieve 18.67 U/g of lipolytic activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morillo, J. A., Antizar-Ladislao, B., Monteoliva-Sánchez, M., Ramos-Cormenzana, A., & Russell, N. J. (2009). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 25–39.
Assas, N., Ayed, L., Marouani, L., & Hamdi, M. (2002). Process Biochemistry, 38, 361–365.
Haagensen, F., Skiadas, I. V., Gavala, H. N., & Ahring, B. K. (2009). Biomass and Bioenergy, 33, 1643–1651.
Abrunhosa, L., Oliveira, F., Dantas, D., Gonçalves, C., & Belo, I. (2013). Bioprocess and Biosyst Eng, 36, 285–291.
de la Casa, J. A., Romero, I., Jiménez, J., & Castro, E. (2012). Ceramics Int., 38, 5027–5037.
Bustamante, M. A., Moral, R., Paredes, C., Pérez-Espinosa, A., Moreno-Caselles, J., & Pérez-Murcia, M. D. (2008). Waste manage, 28, 372–380.
Eusébio, A., Mateus, M., Baeta-Hall, L., Almeida-Vara, E., & Duarte, J. C. (2005). Water Science and Technology, 51, 107–112.
Pandey, A. (2003). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 13, 81–84.
Chakradhar, D., Javeed, S., & Sattur, A. P. (2009). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot., 36, 1179–1187.
Pérez-Guerra, N., Torrado-Agrasar, A., López-Macias, C., & Pastrana, L. (2003). Electronic Journal of Agricultural Food chemistry, 2, 343–350.
Gutarra, M. L. E., Cavalcanti, E. D. C., Castilho, L. R., Freire, D. M. G., & Santanna, G. L., Jr. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121–124, 105–116.
Chen, L., Yang, X., Raza, W., Luo, J., Zhang, F., & Shen, Q. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 3900–3910.
Cordova, J., Nemmaoui, M., Ismaı̈li-Alaoui, M., Morin, A., Roussos, S., Raimbault, M., & Benjilali, B. (1998). J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym, 5, 75–78.
Moftah, O. A. S., Grbavčić, S., Zuža, M., Luković, N., Bezbradica, D., & Knežević-Jugović, Z. (2012). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 348–364.
Hegedus, D. D., & Khachatourians, G. G. (1988). Biotechnology Letters, 10, 637–642.
Aloui, F., Abid, N., Roussos, S., & Sayadi, S. (2007). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 35, 120–125.
Giannoutsou, E. P., Katsifas, E. A., Geli, A., & Karagouni, A. D. (2012). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 849–856.
Vishwanatha, K. S., Apu-Rao, A. G., & Singh, S. A. (2010). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 37, 129–138.
Perrone, G., Varga, J., Susca, A., Frisvad, J. C., Stea, G., Kocsubé, S., Tóth, B., Kozakiewicz, Z., & Samson, R. A. (2008). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58, 1032–1039.
Delabona, P. S., Pirota, R. D. P. B., Codima, C. A., Tremacoldi, C. R., Rodrigues, A., & Farinas, C. S. (2013). Ind Crops Prod, 42, 236–242.
Gopinath, S. C. B., Anbu, P., & Hilda, A. (2005). Mycoscience, 46, 119–126.
Serra, R., Cabañes, F. J., Perrone, G., Castellá, G., Venâncio, A., Mulè, G., & Kozakiewicz, Z. (2006). Mycologia, 98, 295–306.
Kouker, G., & Jaeger, K. (1987). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 53, 211–213.
Gomes, N., Gonçalves, C., García-Román, M., Teixeira, J. A., & Belo, I. (2011). Analytical Methods, 3, 1008–1013.
Charney, J., & Tomarelli, M. (1947). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 171, 501–505.
Mar, S., Morales, H., Ramos, A. J., & Sanchis, V. (2006). Society, 1474, 1468–1474.
Jarvis, G. N., & Thiele, J. H. (1997). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 29, 41–47.
Kim, J. T., Kang, S. G., Woo, J. H., Lee, J. H., Jeong, B. C., & Kim, S. J. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 74, 820–828.
Vassilev, N., Baca, M. T., Vassileva, M., Franco, I., & Azcon, R. (1995). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 44, 546–549.
Cayuela, M. L., Sánchez-Monedero, M. A., & Roig, A. (2010). Biodegradation, 21, 465–473.
Falony, G., Armas, J. C., Mendoza, J. C. D., & Hernández, J. L. M. (2006). Food Technology and Biotechnology, 44, 235–240.
Ali, S., & Rafi, H. (2010). Engineering in Life Science, 10, 465–473.
Crognale, S., D’Annibale, A., Federici, F., Fenice, M., Quaratino, D., & Petruccioli, M. (2006). Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 81, 1547–1555.
Rodríguez-Couto, S. (2008). Biotechnology Journal, 3, 859–870.
Han, J. R., An, C. H., & Yuan, J. M. (2005). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99, 910–915.
Acknowledgments
José Manuel Salgado is grateful for Postdoctoral fellowship (EX-2010-0402) of Education Ministry of Spanish Government. Luís Abrunhosa was supported by the grant SFRH/BPD/43922/2008 from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia—FCT, Portugal. Authors thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) for financial support through the project FCT Pest-OE/EQB/LA0023/2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salgado, J.M., Abrunhosa, L., Venâncio, A. et al. Integrated Use of Residues from Olive Mill and Winery for Lipase Production by Solid State Fermentation with Aspergillus sp.. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 1832–1845 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0613-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0613-4