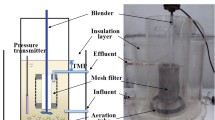
Abstract
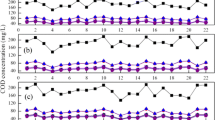
In enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) process, phosphorus (P) in wastewater is removed via wasted sludge without actual recovery. A novel approach to realize phosphorus recovery with special external chemical oxygen demand (COD) addition in EBPR process was proposed. During the new operating approach period, it was found that (1) no phosphorus was detected in the effluent; (2) with an external addition of 10 % of influent COD amount, 79 % phosphorus in the wastewater influent was recovered; (3) without wasted sludge, the MLVSS concentration in the system increased from 2,010 to 3,400 mg/L and kept stable after day 11 during 24-day operating period. This demonstrates that the novel approach is feasible to realize phosphorus recovery with no wasted sludge discharge in EBPR process. Furthermore, this approach decouples P removal and sludge age, which may enhance the application of membrane bioreactor for P removal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann, R. I., Krumholz, L., & Stahl, D. A. (1990). Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental-studies in microbiology. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 762–770.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Burns, R. T., Moody, L. B., Celen, I., & Buchanan, J. R. (2003). Optimization of phosphorus precipitation from swine manure slurries to enhance recovery. Water Science and Technology, 48, 139–146.
Comeau, Y., Hall, K. J., Hancock, R. E. W., & Oldham, W. K. (1986). Biochemical-model for enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Water Research, 20, 1511–1521.
Cordell, D., Drangert, J. O., & White, S. (2009). The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 19, 292–305.
Crocetti, G. R., Banfield, J. F., Keller, J., Bond, P. L., & Blackall, L. L. (2002). Glycogen-accumulating organisms in laboratory-scale and full-scale wastewater treatment processes. Microbiol-Sgm, 148, 3353–3364.
Crocetti, G. R., Hugenholtz, P., Bond, P. L., Schuler, A., Keller, J., Jenkins, D., et al. (2000). Identification of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and design of 16S rRNA-directed probes for their detection and quantitation. Appl Environ Microb, 66, 1175–1182.
Elser, J., & Bennett, E. (2011). A broken biogeochemical cycle. Nature, 478, 29–31.
Isaacs, S. H., & Henze, M. (1995). Controlled carbon source addition to an alternating nitrification denitrification waste-water treatment process including biological p-removal. Water Research, 29, 77–89.
Li, H. J., & Chen, Y. G. (2011). Research on polyhydroxyalkanoates and glycogen transformations: key aspects to biologic nitrogen and phosphorus removal in low dissolved oxygen systems. Front Environ Sci En, 5, 283–290.
Li, J., Xing, X. H., & Wang, B. Z. (2003). Characteristics of phosphorus removal from wastewater by biofilm sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 16, 279–285.
Li, X., Gao, D. W., Liang, H., Liu, L., & Fu, Y. (2012). Phosphorus removal characteristics of granular and flocculent sludge in SBR. Appl Microbiol Biot, 94, 231–236.
Lin, Y. M., Liu, Y., & Tay, J. H. (2003). Development and characteristics of phosphorus-accumulating microbial granules in sequencing batch reactors. Appl Microbiol Biot, 62, 430–435.
Lopez, C., Pons, M. N., & Morgenroth, E. (2006). Endogenous processes during long-term starvation in activated sludge performing enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Water Research, 40, 1519–1530.
Lu, H. B., Oehmen, A., Virdis, B., Keller, J., & Yuan, Z. G. (2006). Obtaining highly enriched cultures of Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphates through alternating carbon sources. Water Research, 40, 3838–3848.
Majed, N., Chernenko, T., Diem, M., & Gu, A. Z. (2012). Identification of functionally relevant populations in enhanced biological phosphorus removal processes based on intracellular polymers profiles and insights into the metabolic diversity and heterogeneity. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 5010–5017.
Monclus, H., Sipma, J., Ferrero, G., Rodriguez-Roda, I., & Comas, J. (2010). Biological nutrient removal in an MBR treating municipal wastewater with special focus on biological phosphorus removal. Bioresource Technology, 101, 3984–3991.
Oehmen, A., Keller-Lehmann, B., Zeng, R. J., Yuan, Z. G., & Keller, E. (2005). Optimisation of poly-beta-hydroxyalkanoate analysis using gas chromatography for enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1070, 131–136.
Smolders, G. J. F., Vandermeij, J., Vanloosdrecht, M. C. M., & Heijnen, J. J. (1994). Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process—stoichiometry and Ph influence. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 43, 461–470.
Soejima, K., Matsumoto, S., Ohgushi, S., Naraki, K., Terada, A., Tsuneda, S., et al. (2008). Modeling and experimental study on the anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic process for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal: the effect of acetate addition. Process Biochemistry, 43, 605–614.
Thomas, M., Wright, P., Blackall, L., Urbain, V., & Keller, J. (2003). Optimisation of Noosa BNR plant to improve performance and reduce operating costs. Water Science and Technology, 47, 141–148.
Wei, Y. S., Van Houten, R. T., Borger, A. R., Eikelboom, D. H., & Fan, Y. B. (2003). Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Water Research, 37, 4453–4467.
Wu, G. X., & Rodgers, M. (2010). Dynamics and function of intracellular carbohydrate in activated sludge performing enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 49, 271–276.
Yang, S., Yang, F. L., Fu, Z. M., & Lei, R. B. (2009). Comparison between a moving bed membrane bioreactor and a conventional membrane bioreactor on organic carbon and nitrogen removal. Bioresource Technol, 100, 2369–2374.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of Hundred-Talent Program of CAS, Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. WK2060190007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, CW., Ma, YJ., Zhang, F. et al. A Novel Approach for Phosphorus Recovery and No Wasted Sludge in Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Process with External COD Addition. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 820–828 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0575-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0575-6