Abstract
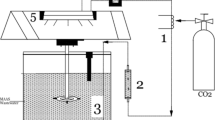
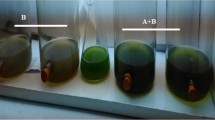
In this work, capability of the green microalga (MA), Chlorella vulgaris, in treating synthetic anaerobic effluent of municipal wastewater was investigated. While pure C. vulgaris (100 % MA) provided maximum soluble chemical oxygen demand (sCOD) and N − NH +4 removal efficiencies of 27 and 72 % respectively, addition of activated sludge (AS) to MA in different mass ratios (91, 80, 66.7, 9 % MA) improved wastewater treatment efficiency. Thus giving maximum sCOD and N − NH +4 removal efficiencies 85 and 86.3 % (for MA/AS = 10/1), respectively. Utilizing AS without C. vulgaris, for treating the synthetic wastewater resulted in 87 % maximum sCOD and 42 % maximum N − NH +4 removal efficiencies. Furthermore, algal growth and specific growth rates were measured in the systems with microalga as the dominant cellular population. As a result, faster algal growth was observed in mixed systems. Specific growth rate of C. vulgaris was 0.14 (day−1) in 100 % MA and 0.39 (day−1) in 80 % MA. Finally, data gathered by online measurement of dissolved oxygen indicate that algae-activated sludge mixture improves photosynthetic activity of examined microalga strain during anaerobic effluent treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Activated Sludge
- C. vulgaris :
-
Chlorella vulgaris
- DO:
-
Dissolved Oxygen
- MA:
-
Microalgae
- μ:
-
Microalgal Specific Growth Rate
- sCOD:
-
Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand
- t:
-
Operational Time
- WWT:
-
Wastewater Treatment
References
de-Godos, I., Vargas, V. A., Blanco, S., García González, M. C., Soto, R., García-Encina, P. A., et al. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 5150–5158.
Di Termini, I., Prassone, A., Cattaneo, C., & Rovatti, M. (2011). Ecological Engineering, 37, 976–980.
Munoz, R., & Guieysse, B. (2006). Water Research, 40, 2799–2815.
Medina, M., & Neis, U. (2007). Water Science Technology, 55, 165–171.
Rawat, I., Ranjith Kumar, R., Mutanda, T., & Bux, F. (2011). Applied Energy, 88, 411–3424.
Munoz, R., Kollner, C., Guieysse, B., & Mattiasson, B. (2004). Biotechnology Bioengineering, 6, 797–803.
Chen, C., Yeh, K., Aisyah, R., Lee, D., & Chang, J. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 71–81.
Chisti, Y. (2007). Biotechnology Advances, 25, 294–306.
Perez-Garcia, O., Escalante, F. M., De-Bashan, L. E., & Bashan, Y. (2011). Water Research, 45, 11–36.
Wang, L., Min, M., Li, Y., Chen, P., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 1174–1186.
McGinn, P. J., Dickinson, K. E., Park, K. C., Whitney, C. G., MacQuarrie, S. P., Black, F. J., et al. (2012). Algal Research, 1, 155–165.
Kim, J., Lingaraju, B., Rheaume, R., Lee, J., & Siddiqui, K. (2010). Tsinghua Science and Technology, 15, 391–396.
Aslan, S., & Kapdan, I. (2006). Ecological Engineering, 28, 64–70.
Borowitzka, M. A. (1988). In M. A. Borowitzka & L. J. Borowitzka (Eds.), Micro-algal Biotechnology, (456–465): algal growth media and sources of algal cultures (pp. 456–465). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Martinez-Sosa, D., Helmreich, B., & Horn, H. (2012). Process Biochemistry, 47, 792–798.
Riahi, K., Mammou, A. B., & Thayer, B. B. (2009). Journal of Hazardous Material, 161, 608–613.
Akila, G., & Chandra, T. S. (2007). Process Biochemistry, 42, 466–471.
Tawfik, A., Sobhey, M., & Badawy, M. (2008). Desalination, 227, 167–177.
Prieto, A.L. (2011), PhD thesis, University of South Florida, South Florida, USA.
Kassab, G., Halalsheh, M., Klapwijk, A. F., & van Lier, J. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 3299–3310.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). New York: American Public Health Association.
Travieso Córdoba, L. Domínguez Bocanegra, A.R. Rincón Llorente, B. Sánchez Hernández, E. Benítez Echegoyen, F. Borja, R. Raposo Bejines, F. and Colmenarejo Morcillo, M.F. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology [online]. 15 April 2008, vol. 11, no. 2 [cited date]. Available from Internet: http://www.ejbiotechnology.cl/content/vol11/issue2/full/1/index.html. ISSN 0717–3458. DOI: 10.2225/vol11-issue2-fulltext-1.
González-Fernández, C., Molinuevo-Salces, B., & García-González, M. C. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 960–966.
Gonzalez, L. E., Canizares, R. O., & Baena, S. (1997). Bioresource Technology, 60, 259–262.
Ruiz-Marin, A., Mendoza-Espinosa, L., & Stephenson, T. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 58–64.
Shi, J., Podola, B., & Melkonian, M. (2007). Journal of Applied Phycology, 5, 417–423.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roudsari, F.P., Mehrnia, M.R., Asadi, A. et al. Effect of Microalgae/Activated Sludge Ratio on Cooperative Treatment of Anaerobic Effluent of Municipal Wastewater. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 131–140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0480-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0480-z