Abstract
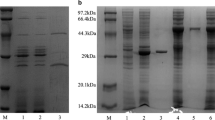
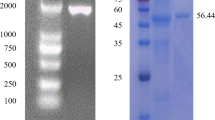
Bacterial cellulases have taken on satisfactory application performance and economic value in detergent industry. Neutral endoglucanase (EG1) gene was cloned from Bacillus subtilis and expressed Pichia pastoris in our previous study. Redesigned endoglucanases enhanced cellulase domain, added and deleted carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), named EG2, EG3, and EG4, respectively, were constructed in this study. The redesigned EG genes were expressed in P. pastoris, and their characters were also discussed. The optimal temperature and pH value of the all EGs was 65 °C and 6.0, respectively, where their enzymatic activities in P. pastoris cultivation supernatant reached 867, 651, 966, and 881 U/mL. EG2 showed 24.9 % enzymatic activity loss compared to natural endoglucanase. EG4 showed specific activity 30 % loss and thermostability decrease compared to EG1, which suggested CBM played an important role in improving the catalytic power and heat stability of cellulase family which attached. The specific activity of EG2 and EG3 showed similar to EG1, which suggested neither enhancement of CD nor CBM to endoglucanase can improve its catalytic power, which might rest with its intact topologic structure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarvis, M. (2003). Nature, 426(6967), 611–612.
Lynd, L. R., & Zhang, Y. (2002). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 77(4), 467–475.
Marchessault, R. H., Sundarajan, P. R. (1993). New York: Academic Press, 11–95
Schmoll, M., & Kubicek, C. P. (2003). Acta Microbiologica Et Immunologica Hungarica, 50(2–3), 125–145.
Beguin, P., Millet, J., Chauvaux, S., Salamitou, S., Tokatlidis, K., Navas, J., et al. (1992). Biochemical Society Transactions, 20(1), 42–46.
Davies, G., & Henrissat, B. (1995). Structure, 3(9), 853–859.
Linder, M., Nevanen, T., Soderholm, L., Bengs, O., & Teeri, T. T. (1998). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 60(5), 642–647.
Bae, H. J., Turcotte, G., Chamberland, H., Karita, S., & Vezina, L. P. (2003). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 227(2), 175–181.
Black, G. W., Rixon, J. E., Clarke, J. H., Hazlewood, G. P., Theodorou, M. K., Morris, P., et al. (1996). Biochemical Journal, 319(Pt 2), 515–520.
Meissner, K., Wassenberg, D., & Liebl, W. (2000). Molecular Microbiology, 36(4), 898–912.
Sunna, A., Gibbs, M. D., & Bergquist, P. L. (2000). Biochemical Journal, 346(Pt 3), 583–586.
Guan, X. Y., Wu, Q., Xu, B., & Chen, H. (2009). Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 3, 68–72.
Wu, Z. F., Zeng, M., & Wu, Q. (2009). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 17(3), 529–535.
Mandels, M., Andreotti, R., Roche, C. (1976). Biotechnology and Bioengineering Symposium, (6), 21–33.
Chen, H., Liao, J. H., Guan, X. Y., & Wu, Q. (2008). Hereditas, 30(5), 649–654.
Liu, G., Tian, S. L., Deng, X., & Xing, M. (2006). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22(12), 1301–1305.
Cornell, W., & Nam, K. (2009). Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 9(9), 844–853.
Zhang, Y. Z., Gao, P. J., Ma, L. P., Shi, D. X., & Pang, S. J. (1998). Applied Physics A: Materials Science and Processing, 67(4), 83–85.
Xiao, Z. Z., Qu, Y. B., & Wang, T. H. (2001). Biotechnology Letters, 23(9), 711–715.
Yan, B. X., & Sun, Y. (1997). Journal of Protein Chemistry, 16(1), 59–66.
Zhuang, S., Li, Y. H., Ding, G. J., & Zhao, F. K. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 1327–1334.
Nakamura, A., Fukumori, F., Horinouchi, S., Masaki, H., Kudo, T., Uozumi, T., et al. (1991). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266(3), 1579–1583.
Wolfgang, D. E., & Wilson, D. B. (1999). Biochemistry, 38(30), 9746–9751.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support for this work from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30671530).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zi-Zhong, T., Zhen-Fang, W., Hui, C. et al. Characterization of Novel EGs Reconstructed from Bacillus subtilis Endoglucanase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 1764–1773 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0111-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0111-8