Abstract
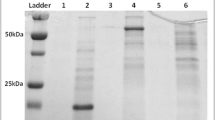
XynX of Clostridium thermocellum is a large, multimodular xylanase of 116 kDa. An Escherichia coli transformant carrying the entire xynX produced three active truncated xylanase species of 105, 85, and 64 kDa intracellularly. The Bacillus subtilis WB700 transformant with the xynX, a strain deficient in seven proteases including Vpr, secreted two active truncated xylanase species of 65 and 44 kDa. The B. subtilis WB800 transformant with xynX, a strain deficient in eight proteases including Vpr and WprA, secreted more active enzymes, 8.46 U ml−1, mostly in the form of 105 and 85 kDa, than the WB700 transformant, 6.93 U ml−1. This indicates that the additional deletion of wprA enabled the WB800 to secrete XynX in its intact form. B. subtilis WB800 produced more total enzyme activity than E. coli (1,692 ± 274 U vs. 141.9 ± 27.1 U), and, more importantly, secreted almost all the enzyme activity. The results suggest the potential use of B. subtilis WB800 as a host system for the production of large multimodular proteins.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminov, R. I., Golovchenko, N. P., & Ohmiya, K. (1995). Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 79, 530–537.
Yang, M. J., Jung, S. H., Shin, E. S., Kim, J., Yun, H. D., Wong, S. L., et al. (2004). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, 430–434.
Wu, S. C., Yeung, J. C., Duan, Y., Ye, R., Szarka, S. J., Habibi, H. R., et al. (2002). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 3261–3269.
Corvey, C., Stein, T., Düsterhus, S., Karas, M., & Entian, K. D. (2003). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 304, 48–54.
Murashima, K., Chen, C. L., Kosugi, A., Tamaru, Y., Doi, R. H., & Wong, S. L. (2002). Journal of Bacteriology, 184, 76–81.
Cho, H. Y., Yukawa, H., Inui, M., Doi, R. H., & Wong, S. L. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 5704–5707.
Westers, L., Dijkstra, D. S., Westers, H., van Dijl, J. M., & Quax, W. J. (2006). Journal of Biotechnology, 123, 211–224.
Lu, Y., Lin, Q., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Bao, W., Lv, F., et al. (2010). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 37, 919–925.
Zhang, W., Lou, K., & Li, G. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1484–1495.
Balat, M., & Balat, H. (2009). Applied Energy, 86, 2273–2282.
Classen, H. L. (1996). Animal Feed Science and Technology, 62, 21–27.
Sun, Y., & Cheng, J. (2002). Bioresource Technology, 83, 1–11.
Demain, A. L., Newcomb, M., & Wu, J. H. (2005). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69, 124–154.
Viikari, L., Kantelinen, A., Sundquist, J., & Linko, M. (1994). FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 13, 335–350.
Jimenez, L., Navarro, E., Ferrer, J. L., Lopez, F., & Ariza, J. (1999). Process Biochemistry, 35, 149–157.
Beg, Q. K., Bhushan, B., Kapoor, M., & Hoondal, G. S. (2000). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 459–466.
Bayer, E. A., Belaich, J. P., Shoham, Y., & Lamed, R. (2004). Annual Review of Microbiology, 58, 521–554.
Kim, H., Jung, K. H., & Pack, M. Y. (2000). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 54, 521–527.
Bayer, E., Shoham, Y., & Lamed, R. (2006). The Prokaryotes, Part 1, 578–617.
Jung, K. H., Lee, K. M., Kim, H., Yoon, K. H., Park, S. H., & Pack, M. Y. (1998). Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International, 44, 283–292.
Shin, E. S., Yang, M. J., Jung, K. H., Kwon, E. J., Jung, J. S., Park, S. K., et al. (2002). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3496–3501.
Selvaraj, T., Kim, S. K., Kim, Y. H., Jeong, Y. S., Kim, Y. J., Phuong, N. D., et al. (2010). The Journal of Microbiology, 48, 856–861.
Jung, K. H., & Pack, M. Y. (1993). Biotechnology Letters, 15, 115–120.
Doi, R. H. (1983). In R. L. Rodriguez & R. C. Tait (Eds.), Recombinant DNA techniques: an introduction (pp. 184–186). Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Lowry, O. H., Bosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randell, R. J. (1951). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
van Leen, R. W., Bakhuis, J. G., van Beckhoven, R. F., Burger, H., Dorssers, L. C., Hommes, R. W., et al. (1991). Biotechnology (New York), 9, 47–52.
Kim, H., Kim, S. F., Ahn, D. H., Lee, J. H., & Pack, M. Y. (1995). Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 5, 26–30.
Kawabata, Y., Kimura, K., & Funane, K. (2012). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1877–1884.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Cooperation Research Program (PJ007449201006), Rural Development Administration, the Basic Research Program of the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation, and partially the 21C Frontier Microbial Genomics and Application Center Program, Ministry of Science and Technology, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nguyen Dinh Phuong and Yu Seok Jeong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phuong, N.D., Jeong, Y.S., Selvaraj, T. et al. Production of XynX, a Large Multimodular Protein of Clostridium thermocellum, by Protease-Deficient Bacillus subtilis Strains. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 375–382 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9781-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9781-x