Abstract
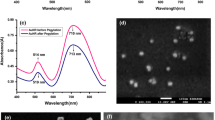
Gold nanoparticles exhibit unique spectral properties that make them ideal for biosensing, imaging, drug delivery, and other therapeutic applications. Interaction of gold nanoparticles within biological environments is dependent on surface characteristics, which may rely on particular capping agents. In this study, gold nanospheres (GNS) synthesized with different capping agents—specifically citric acid (CA) and tannic acid (TA)—were compared for serum protein adsorption and cellular uptake into a lung epithelial cell line (A549). Both GNS samples exhibited noticeable protein adsorption based on surface charge data after exposure to serum proteins. Light scattering measurements revealed that GNS-CA-protein composites were smaller and less dense compared to GNS-TA-protein composites. The cell uptake characteristics of these nanoparticles were also different. GNS-CA formed large clusters and elicited high uptake, while GNS-TA were taken up as discrete particles, possibly through nonendosomal mechanisms. These results indicate that the capping agents used for GNS synthesis result in unique biological interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, A., Huang, S. W., O'Donnel, M., et al. (2007). Journal of Applied Physics, 102, 064701.
El-Sayed, I. H., Huang, X., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2005). Nano Letters, 5, 829.
Quian, X., Peng, X. H., Ansari, D. O., et al. (2008). Nature Biotechnology, 26, 83.
Lukianova-Hleb, E. Y., Oginsky, A. O., Shenefelt, D. L., et al. (2011). Journal of Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology, 2, 1000104.
Wang, X., Quian, X., Beitler, J. J., et al. (2011). Cancer Research, 71, 1526.
Tuncagil, S., Ozdemir, C., Demirkol, D. O., et al. (2011). Food Chemistry, 127, 1317.
Sanvicens, N., Mannelli, I., Salvador, J. P., et al. (2011). Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 30, 541.
Hao, R. Z., Song, H. B., Zuo, G. M., et al. (2011). Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26, 3398.
Han, G., Ghosh, P., De, M., & Rotello, V. M. (2007). Nanobiotechnology, 3, 40.
Stobiecka, M., & Hepel, M. (2011). Biomaterials, 32, 3312.
Venkatpurwar, V., Shiras, A., & Pokharkar, V. (2011). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 314–320, 409.
Lynch, I., Cedervall, T., Lundqvist, M., et al. (2007). Advances in Colloid Interfaces, 134–135, 167.
Cedervall, T., Lynch, I., Lindman, S., et al. (2050). Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 2007, 104.
Nel, A. E., Madler, L., Velegol, D., et al. (2009). Nature Materials, 8, 543.
Alkilany, A. M., & Murphy, C. J. (2010). Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 12, 2313.
Yuan, J., Guo, Q. Q., He, X. Z., & Liu, Y. P. (2011). Advances in Materials Research, 194–196, 462.
Neal, H. C., Stolnik, S., Schacht, E., Keawy, E. R., Garnett, M. C., Davis, S. S., & Illum, L. J. (1998). Pharmaceutical Sciences, 87, 1242.
Ehrenberg, M. S., Friedman, A. E., Finkelstein, J. N., et al. (2009). Biomaterials, 30, 603.
Chithrani, B. D., Ghazani, A. A., & Chan, W. C. W. (2006). Nano Letters, 6, 662.
Brewer, S. H., Glomm, W. H., Johnson, M. C., et al. (2005). Langmuir, 21, 9303.
Shang, L., Wang, Y., Jiang, J., & Dong, S. (2007). Langmuir, 23, 2714.
Kaufman, E. D., Belyea, J., Johnson, M. C., et al. (2007). Langmuir, 23, 6053.
Chaudhuri, A., Battaglia, G., & Golestanian, R. (2011). Physical Biology, 8, 046002.
Lee, O. S., Schatz, G. C., & Hurst, S. J. (2011). Biomedical nanotechnology: methods and protocols (Vol. 726, p. 283). New York: Springer.
Jiang, W., Kim, B. Y. S., Rutka, J. T., & Chan, W. C. W. (2008). Nature Nanotechnology, 3, 145.
Heister, E., Neves, V., Silva, S. R. P., et al. (2011). In R. Klingeler & R. B. Sim (Eds.), Carbon nanotubes for biomedical applications (p. 223). Heidelberg: Springer.
Chèvre, R., Bihan, O. L., Beilvert, F., et al. (2011). Nucleic Acids Research, 39, 1610.
Liu, B. R., Huang, Y. W., Winiarz, J. G., et al. (2011). Biomaterials, 32, 3520.
Febvay, S., Marini, D. M., Belcher, A. M., & Clapham, D. E. (2010). Nano Letters, 10, 2211.
Pittella, F., Zhang, M., Lee, Y., et al. (2011). Biomaterials, 32, 3106.
Nakase, I., Kogure, K., & Harashima, H. (2011). In S. Futaki & U. Langel (Eds.), Cell-penetrating peptides: methods and protocols. New York: Springer, 683, 525.
Tkachenko, A. G., Xie, H., Coleman, D., et al. (2003). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125, 4700.
de la Fuente, J. M., & Berry, C. C. (2005). Bioconjugate Chemistry, 16, 1176.
Murdock, R. C., Braydich-Stolle, L., Schrand, A. A., et al. (2008). Toxicological Sciences, 101, 239.
Raper, J. A., & Amal, R. (1993). Particle and Particle Systems Characterization, 10, 239.
Lui, J., Shih, W. Y., Sarikaya, M., & Aksay, I. A. (1990). Physical Review A, 41, 3206.
Saleh, N. B., Pfefferle, L. D., & Elimelech, M. (2010) Influence of Biomacromolecules and Humic Acid on the Aggregation Kinetics of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 2412–2418.
Taylor, U., Klein, S., Petersen, S., et al. (2010). Cytometry Part A, 77A, 439.
Aelenei, N., Popa, M. I., Novac, O., et al. (2009). Journal of Materials Science, 20, 1095.
Chung, K. T., Wong, T. Y., Wei, C. I., et al. (1998). Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 38, 421.
Goodman, C. M., McCusker, C. D., Yilmaz, T., & Rotello, V. M. (2004). Bioconjugate Chemistry, 15, 897.
Arnida, Malugin, A., & Ghandehari, H. (2010). Journal of Applied Toxicology, 30, 212.
Wang, S., Lu, W., Tovmachenko, O., et al. (2008). Chemical Physics Letters, 463, 145.
Acknowledgments
Ms. Mukhopadhyay was supported through the Wright Scholar program. This research was supported in part by an appointment to the Postgraduate Research Participation Program at the US Air Force Research Laboratory administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the US Department of Energy and USAFRL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC. 153 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, A., Grabinski, C., Afrooz, A.R.M.N. et al. Effect of Gold Nanosphere Surface Chemistry on Protein Adsorption and Cell Uptake In Vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 327–337 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9666-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9666-z