Abstract
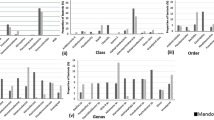
Although it is known that Palk Bay sediments harbor diverse and novel bacteria with important ecological and environmental functions, a comprehensive view of their molecular diversity is still lacking. In the present study, bacterial diversity in Palk Bay sediments was characterized using the molecular method terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphisms (T-RFLP). The bacterial assemblages detected by T-RFLP analysis revealed that the nearshore sediment harbored high number of bacterial count, whereas the 2.5-m sediment harbored diverse and distinct bacterial composition with fine heterogeneity. The major bacterial groups detected in all the three sediment samples were Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria (including alpha (α), gamma (γ), delta (δ), and epsilon (ε)-Proteobacteria), and uncultured bacteria. This is the first study that reveals the presence of Bacteroidetes, delta (δ)- and epsilon (ε)-Proteobacteria, and uncultured bacteria in Palk Bay sediments. The hitherto unexplored wide microbial diversity of Palk Bay coastal area was unraveled in the current study through culture-independent approach. These data suggest that the continued use of cultivation-independent techniques will undoubtedly lead to the discovery of additional bacterial diversity and provide a direct means to learn more about the ecophysiology and biotechnological potential of Palk Bay coastal area.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rees, G. N., Baldwin, D. S., Watson, G. O., Perryman, S., & Nielsen, D. L. (2004). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 86, 339–347.
Amann, R. I., Ludwig, W., & Schleifer, K. H. (1995). Microbiology Reviews, 59, 143–169.
Thies, J. E. (2007). Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71, 579–591.
Handelsman, J., & Smalla, K. (2003). Current Opinion in Microbiology, 6, 271–273.
Avaniss-Aghajani, E., Jones, K., Chapman, D., & Brunk, C. (1994). BioTechniques, 17, 144–149.
Kitts, C. L. (2001). Current Issues in Intestinal Microbiology, 2, 17–25.
Liu, W. T., Marsh, T. L., Cheng, H., & Forney, L. J. (1997). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 4516–4522.
Hiraishi, A., Iwasaki, M., & Shinjo, H. (2000). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 90, 148–156.
Dang, H., Li, J., Chen, M., Li, T., Zeng, Z., & Yin, X. (2009). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25, 179–188.
Ludemann, H., Arth, I., & Liesack, W. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 754–762.
Flynn, S. J., Löffler, F. E., & Tiedje, J. M. (2000). Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1056–1061.
Lukow, T., Dunfield, P. F., & Liesack, W. (2000). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 32, 241–247.
Sakamoto, M., Takeuchi, Y., Umeda, M., Ishikawa, I., & Benno, Y. (2003). Journal of Medical Microbiology, 52, 79–89.
Gong, J., Si, W., Forster, R. J., Huang, R., Yu, H., Yin, Y., Yang, C., & Han, Y. (2007). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 59, 147–157.
Sait, L., Galic, M., Strugnell, R. A., & Janssen, P. H. (2003). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 2100–2109.
Luna, G. M., Dell’Anno, A., Corinaldesi, C., Armeni, M., & Danovaro, R. (2009). International Microbiology, 12, 153–159.
Jørgensen, B. B., & Boetius, A. (2007). Nature Reviews Microbiology, 5, 770–781.
Teske, A. P. (2006). Geomicrobiology Journal, 23, 357–368.
D’Hondt, S., Rutherford, S., & Spivack, A. J. (2002). Science, 295, 2067–2070.
Whitman, W. B., Coleman, D. C., & Wiebe, W. J. (1998). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 6578–6583.
Dhillon, A., Teske, A., Dillon, J., Stahl, D. A., & Sogin, M. L. (2003). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 2765–2772.
Marchesi, J. R., Weightman, A. J., Cragg, B. A., Parkes, R. J., & Fry, J. C. (2001). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 34, 221–228.
Gontang, E. A., Fenical, W., & Jensen, P. R. (2007). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 3272–3282.
Kormas, K. A., Smith, D. C., Edgcomb, V., & Teske, A. (2003). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 45, 115–125.
Newberry, C. J., Webster, G., Cragg, B. A., Parkes, R. J., Weightman, A. J., & Fry, J. C. (2004). Environmental Microbiology, 6, 274–287.
Tankéré, S. P. C., Bourne, D. G., Muller, F. L. L., & Torsvik, V. (2002). Environmental Microbiology, 4, 97–105.
Nithya, C., Aravindraja, C., & Pandian, S. K. (2010). Research in Microbiology, 161, 293–304.
Nithya, C., Begum, M. F., & Pandian, S. K. (2010). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 88, 341–358.
Nithya, C., & Pandian, S. (2010). Archives of Microbiology, 192, 843–854.
Nithya, C., & Pandian, S. K. (2010). Microbiological Research, 165, 578–593.
Nithya, C., Devi, M. G., & Pandian, S. K. (2011). Biofouling, 27, 519–528.
Nithya, C., & Pandian, S. K. (2011). Marine Environmental Research, 71, 283–294.
Thajuddin, N., & Subramanian, G. (2005). Current Science, 89, 47–57.
Vijayakumar, R., Muthukumar, C., Thajuddin, N., Panneerselvam, A., & Saravanamuthu, R. (2007). Actinomycetologica, 21, 59–65.
Weisburg, W. G., Barns, S. M., Pelletier, D. A., & Lane, D. J. (1991). Journal of Bacteriology, 173, 697–703.
Moyer, C. L., Tiedje, J. M., Dobbs, F. C., & Karl, D. M. (1996). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 2501–2507.
Michel, F.C. Jr., Sciarini, S. (2003). Abstr. N-289. Abstr. 103rd Gen. Meet. American Society Microbiology American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.31 2003.
Scupham, A. J. (2007). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 60, 136–147.
Zhu, X. Y., Zhong, T., Pandya, Y., & Joerger, R. D. (2006). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 124–137.
Zhang, R., Thiyagarajan, V., & Qian, P. Y. (2008). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 65, 169–178.
Clarke, K. R., & Warwick, R. M. (2001). Changes in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Plymouth, UK: Primer-E.
Kruskal, J. B. (1964). Psychometrika, 29, 1–27.
Denaro, R., D’Auria, G., Di Marco, G., Genovese, M., Troussellier, M., Yakimov, M. M., & Giuliano, L. (2005). Environmental Microbiology, 7, 78–87.
Bernbom, N., Nørrung, B., Saadbye, P., Mølbak, L., Vogensen, F. K., & Licht, T. R. (2006). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 66, 87–95.
Dunbar, J., Ticknor, L. O., & Kuske, C. R. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 2943–2950.
Hartmann, M., Frey, B., Kölliker, R., & Widmer, F. (2005). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 61, 349–360.
Lueders, T., & Friedrich, M. W. (2003). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 320–326.
Frey, J. C., Angert, E. R., & Pell, A. N. (2006). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 67, 9–19.
Dunbar, J., Ticknor, L. O., & Kuske, C. R. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 190–197.
Osborn, A. M., Moore, E. R. B., & Timmis, K. N. (2000). Environmental Microbiology, 2, 39–50.
Marsh, T. L., Saxman, P., Cole, J., & Tiedje, J. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 3616–3620.
Gray, J. P., & Herwig, R. P. (1996). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 4049–4059.
Jensen, P. R., Mincer, T. J., Williams, P. G., & Fenical, W. (2005). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 43–48.
Stach, E. M., & Bull, A. T. (2005). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 3–9.
Köchling, T., Lara-Martín, P., González-Mazo, E., Amils, R., & Sanz, J. L. (2011). International Microbiology, 14, 143–154.
Castle, D., & Kirchman, D. L. (2004). Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2, 303–314.
Dobretsov, S., Dahms, H. U., & Qian, P. I. Y. (2006). Biofouling, 22, 43–54.
Eccleston, G. P., Brooks, P. R., & Kurtböke, D. I. (2008). Marine Drugs, 6, 243–261.
El-Gendy, M. M. A., Hawas, U. W., & Jaspars, M. (2000). The Journal of Antibiotics, 61, 379–386.
Hong, K., Gao, A. H., Xie, Q. Y., Gao, H., Zhuang, L., Lin, H. P., Yu, H. P., Li, J., Yao, X. S., & Goodfellow, M. (2009). Marine Drugs, 7, 24–44.
Imada, C. (2005). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 59–63.
MikhaÄlov, V. V., Kuznetsova, T. A., & Eliakov, G. B. (1995). Bioorganicheskaia Khimiia, 21, 3–8.
Selvin, J., Shanmughapriya, S., Gandhimathi, R., Seghal Kiran, G., Rajeetha Ravji, T., Natarajaseenivasan, K., & Hema, T. A. (2009). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 83, 435–445.
Solanki, R., Khanna, M., & Lal, R. (2008). Indian Journal of Microbiology, 48, 410–431.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research grant from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India (GOI) (Grant No. BT/PR11994/ndb/52/134/2009). The authors gratefully acknowledge the computational and bioinformatics facility provided by the Alagappa University Bioinformatics Infrastructure Facility (funded by DBT, GOI; Grant No. BT/BI/25/001/2006). Financial support provided to Chari Nithya by Alagappa University in the form of Research Fellowship is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, C., Pandian, S.K. Evaluation of Bacterial Diversity in Palk Bay Sediments Using Terminal-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (T-RFLP). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 1763–1777 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9578-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9578-y