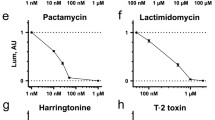
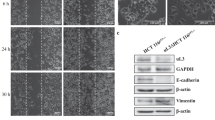
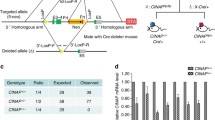
Abstract
Apoptotic cell death is a fundamental process in the development and physiological homeostasis of multicellular organisms. It is associated with control of cell numbers in tissues and organs during development, with cell turnover, and with response to infection. Molecules that trigger this process in continuously proliferating cancer cells can be used as chemotherapeutic agents. Ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs) that inhibit translation in a cell by depurinating (N-glycosidase activity) the 28S rRNA are known to serve as apoptosis inducers. However, the role of depurination activity of the RIPs in apoptosis induction is still controversial. Presently, there are three different hypotheses which propose that depurination is: (1) essential, (2) essential but not the sole factor, or (3) not essential for apoptosis induction. This article reviews various experimental outcomes on the importance of N-glycosidase activity of RIPs in the induction of apoptosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elmore, S. (2007). Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicologic Pathology, 35, 495–516.
Fink and Cookson. (2005). Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infection and Immunity, 74, 1907–1916.
Gerl, R., & Vaux, D. L. (2005). Apoptosis in the development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis, 26, 263–270.
Schindaowski, K., Leutner, S., Muller, W. E., & Eckert, A. (2000). Age related changes in apoptotic cells of human lymphocytes. Neurobiology Age, 21, 661–670.
Shi, Y.-B. (1999). Amphibian metamorphogenesis; from morphology to molecular biology. USA: Wiley.
Hartley, M. R., & Lord, J. M. (2004). Genetics of ribosome inactivating proteins. Mini Reviews in Medical Chemistry, 4, 487–492.
Motto, M., & Lupotto, E. (2004). The genetics and properties of cereal ribosome-inactivating proteins. Mini Reviews in Medical Chemistry, 4, 493–503.
Frigerio, L., & Roberts, L. M. (1998). The enemy within: ricin and plant cells. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49, 1473–1480.
Mishra, V., Bilgrami, S., Sharma, R. S., Kaur, P., Yadav, S., Krauspenhaar, R., Betzel, C., Voelter, W., Babu, C. R., & Singh, T. P. (2005). Crystal structure of Himalayan mistletoe ribosome inactivating protein reveals the presence of a natural inhibitor and a new functionally active sugar-binding site. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 20712–20721.
Mishra, V., Sharma, R. S., Yadav, S., Babu, C. R., & Singh, T. P. (2004). Purification and characterization of four isoforms of Himalayan mistletoe ribosome-inactivating protein from Viscum album having unique sugar affinity. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 423, 288–301.
Mishra, V., Sharma, R. S., Paramsivam, M., Bilgrami, S., Yadav, S., Betzel, C., Babu, C. R., & Singh, T. P. (2005). cDNA cloning and characterization of ribosome-inactivating protein of a hemi-parasitic plant (Viscum album L.) from northwestern Himalayas (India). Plant Science, 168, 615–625.
Mishra, V., Ethayathullah, A. S., Sharma, R. S., Yadav, S., Krauspenhaar, R., Betzel, C., Babu, C. R., & Singh, T. P. (2004). Structure of novel ribosome-inactivating protein from hemi-parasitic plant inhabiting the northwestern Himalayas. Acta Crystallographica, D60, 2295–2304.
Olsnes, S., & Pihl, A. (1973). Isolation and properties of abrin: a toxic protein inhibiting protein synthesis. Evidence for different biological functions of its two constituent peptide chains. European Journal of Biochemistry, 35, 179–185.
Olsnes, S., & Pihl, A. (1973). Different biological properties of the two constituent chains of ricin, a toxic protein inhibiting protein. Biochemistry, 12, 3121–3126.
Griffiths, G. D., Leek, M. D., & Gee, D. J. (1987). The toxic plant proteins ricin and abrin induce apoptotic changes in mammalian lymphoid tissues and intestine. The Journal of Pathology, 151, 221–229.
Sandvig, K., & van Deurs, B. (1992). Pathways followed by ricin and Shiga toxin into cells. Experimental Cell Research, 200, 253–262.
Bussing, A. (1996). Induction of apoptosis by the mistletoe lectins: a review on the mechanisms of cytotoxicity mediated by Viscum album. L Apopt, 1, 25–32.
Bolognesi, A., Tazzari, P. L., Olivieri, F., Polito, L., Falini, B., & Stirpe, F. (1996). Induction of apoptosis by ribosome-inactivating proteins and related immunotoxins. International Journal of Cancer, 68, 349–355.
Narayanan, S., Surendranath, K., Bora, N., Surolia, A., & Anjali, A. K. (2005). Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. FEBS Letters, 579, 1324–1331.
Sikriwal, D., & Batra, J. K. (2010). Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. In J. M. Lord & M. R. Hartley (Eds.), Plant cell monographs (Toxic plant proteins, Vol. 18, pp. 107–132). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Habeck, M. (2003). Mistletoe compound enters clinical trials. Drug Dicovery Today, 8, 52–53.
Barbieri, L., Ciani, M., Girbes, T., Liuc, W.-Y., Van Damme, E. J. M., Peumans, W. J., & Stirpe, F. (2004). Enzymatic activity of toxic and non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. FEBS Letters, 563, 219–222.
Das, M. K., Sharma, R. S., & Mishra, V. (2011). A cytotoxic type-2 ribosome inactivating protein (from leafless mistletoe) lacking sugar affinity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 49, 1096–1103.
Battelli, M. G. (2004). Cytotoxicity and toxicity to animals and humans of ribosome inactivating proteins. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 4, 513–521.
Martin, S. J., Lennon, S. V., Bonham, A. M., & Cotter, T. G. (1990). Induction of apoptosis (programmed cell death) in human leukemic HL-60 cells by inhibition of RNA or protein synthesis. Journal of Immunology, 145, 1859–1867.
Kageyama, A., Kusano, I., Tamura, T., Oda, T., & Muramatsu, T. (2002). Comparison of the apoptosis-inducing abilities of various protein synthesis inhibitors in U937 cells. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 66, 835–839.
Olmo, N., Turnay, J., González, de Buitrago, G., López de Silanes, I., Gavilanes, J. G., & Lizarbe, M. A. (2001). Cytotoxic mechanism of the ribotoxin α-sarcin: induction of cell death via apoptosis. European Journal of Biochemistry, 268, 2113–2123.
Ghosh, P., & Batra, J. K. (2006). The differential catalytic activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins saporin 5 and 6 is due to a single substitution at position 162. Biochemistry Journal, 400, 99–104.
Langer, M., Mockel, B., Eck, J., Zinke, H., & Lentzen, H. (1999). Site-specific mutagenesis of mistletoe lectin: the role of RIP activity in apoptosis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication, 264, 944–948.
Vervecken, W., Kleca, S., Pfuller, U., & Bussing, A. (2000). Induction of apoptosis by mistletoe lectin I and its subunits. No evidence for cytotoxic effects caused by isolated A- and B-chains. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 32, 317–326.
Irodanov, M. S., Pribnow, D., Magun, J. L., Dinh, T.-H., Pearson, J. A., Chen, S. L.-Y., & Magun, B. E. (1997). Ribotoxic stress response: activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 17, 3373–3381.
Smith, W. E., Kane, A. V., Campbell, S. T., Acheson, D. W., Cochran, B. H., & Thorpe, C. M. (2003). Shiga toxin 1 triggers a ribotoxic stress response leading to p38 and JNK activation and induction of apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Infections and Immunity, 71, 1497–1504.
Hur, Y., Hwang, D. J., Zoubenko, O., Coetzer, C., Uckun, F. H., & Tumer, N. E. (1995). Isolation and characterization of pokeweed antiviral protein mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of residues important for toxicity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 92, 8448–8452.
Hudak, K. A., Wang, P., & Tumer, N. E. (2000). Pokeweed antiviral protein inhibits translation of capped RNAs independently of ribosome depurination by acting directly on the RNA template. RNA, 6, 369–380.
Li, X.-P., Baricevic, M., Saidasan, H., & Tumer, N. E. (2007). Ribosome depurination is not sufficient for ricin-mediated cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Infection and Immunity, 75, 417–428.
Di, R., Kyu, E., Shete, V., Saidasan, H., Kahn, P. C., & Tumer, N. E. (2011). Identification of amino acids critical for the cytotoxicity of Shiga toxin 1 and 2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicon, 57, 525–539.
Martin, S. J. (1993). Apoptosis: suicide, execution or murder? Trends in Cell Biology, 3, 141–144.
Soler-Rodríguez, A.-M., Ghetie, M.-A., Oppenheimer-Marks, N., Uhr, J. W., & Vitetta, E. S. (1993). Ricin A-chain and ricin A-chain immunotoxins rapidly damage human endothelial cells: implications for vascular leak syndrome. Experimental Cell Research, 206, 223–234.
Brigotti, M., Alfieri, R., Sestili, P., Bonelli, M., Petronini, P. G., Guidarelli, A., Barbieri, L., Stirpe, F., & Sperti, S. (2002). Damage to nuclear DNA induced by Shiga toxin 1 andricin in human endothelial cells. The FASEB Journal, 16, 365–372.
Horrix, C., Raviv, Z., Flescher, E., Voss, C., & Berger, M. R. (2011). Plant ribosome-inactivating proteins type II induce the unfolded protein response in human cancer cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 68, 1269–1281.
Li, J., Xia, X., Ke, Y., Smith, M., & Zhu, X. (2007). Trichosanthin induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells via mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling pathways. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1770, 1169–1180.
Shih, S.-F., Wu, Y.-H., Hung, C. H., Yang, H.-Y., & Lin, H.-Y. (2001). Abrin triggers cell death by inactivating a thiol-specific antioxidant protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 21870–21877.
Sikriwal, D., Ghosh, P., & Batra, J. K. (2008). Ribosome inactivating protein saporin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial cascade, independent of translation inhibition. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 40, 2880–2888.
Baluna, R., Coleman, E., Jones, C., Ghetie, V., & Vitetta, E. S. (2000). The effect of a monoclonal antibody coupled to ricin A chain-derived peptides on endothelial cells in vitro: insights into toxin-mediated vascular damage. Experimental Cell Research, 258, 417–424.
Fryxell, D. K., Gawlak, S. L., Dodge, R. W., & Siegall, C. B. (1998). Identification of a specific tyrosine residue in Bryodin 1 distinct from the active site but required for full catalytic and cytotoxic activity. Protein Science, 7, 318–324.
Peumans, W. J., Hao, Q., & van Damme, E. J. M. (2001). Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: more than RNA N-glycosidases? The FASEB Journal, 15, 1493–1506.
Day, P. J., Lord, J. M., & Roberts, L. M. (1998). The deoxyribonuclease activity attributed to ribosome-inactivating proteins is due to contamination. European Journal of Biochemistry, 258, 540–545.
Nicolas, E., Goodyer, I. D., & Theodore, F. (1997). An additional mechanism of ribosome-inactivating protein cytotoxicity: degradation of extrachromosomal DNA. Biochemistry Journal, 327, 413–417.
Bagga, S., Seth, D., & Batra, J. K. (2003). The cytotoxic activity of ribosome-inactivating protein Saporin-6 is attributed to its rRNA N-glycosidase and internucleosomal DNA fragmentation activities. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 27, 4813–4820.
Eck, J., Langer, M., Möckel, B., Baur, A., Rothe, M., Zinke, H., & Lentzen, H. (1999). Cloning of the mistletoe lectin gene and characterization of the recombinant A-chain. European Journal of Biochemistry, 264, 775–784.
Hsu, D. K., Yang, R. Y., & Liu, F. T. (2006). Galectins in apoptosis. Methods in Enzymology, 417, 256–73.
Hajto, T., Hostanska, K., Frei, K., Rordorf, C., & Gabius, H. J. (1990). Increased secretion of tumor necrosis factors alpha, interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 by human mononuclear cells exposed to beta-galactoside-specific lectin from clinically applied mistletoe extract. Cancer Research, 50, 3322–3326.
Hasegawa, N., Kimura, Y., Oda, T., Komatsu, N., & Muramatsu, T. (2000). Isolated ricin B-chain-mediated apoptosis in U937 cells. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 64, 1422–1429.
Shahidi-Noghabi, S., van Damme, E. J. M., Iga, M., & Smagghe, G. (2010). Exposure of insect midgut cells to Sambucus nigra L. agglutinins I and II causes cell death via caspase-dependent apoptosis. Journal of Insect Physiology, 56, 1101–1107.
Walzel, H., Blach, M., Neels, P., Schulz, U., Wollenhaupt, K., & Brock, J. T. (2001). The B-chain of mistletoe lectin I efficiently stimulates calcium signaling in human Jurkat T-cells. Immunology Letters, 78, 57–66.
Zhang, C., Gong, Y., Ma, H., An, C., Chen, D., & Chen, Z. L. (2001). Reactive oxygen species involved in trichosanthin-induced apoptosis of human choriocarcinoma cells. Biochemistry Journal, 355, 653–661.
Liu, B., Bian, B. H.-J., & Bao, J.-K. (2010). Plant lectins: potential antineoplastic drugs from bench to clinic. Cancer Letters, 287, 1–12.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Anne Kathryn Marie Kauffman, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA (USA), for critical reading, constructive suggestions and editing the MS; the Department of Biotechnology (Govt. of India) and the University of Delhi for financial support to VM and RSS. MKD received CSIR-JRF for PhD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, M.K., Sharma, R.S. & Mishra, V. Induction of Apoptosis by Ribosome Inactivating Proteins. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 1552–1561 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9550-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9550-x