Abstract
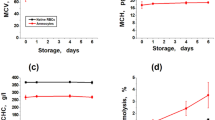
In this work, we describe an optimized procedure based on gradual hemolysis for the isolation of hemoglobin derived from bovine slaughterhouse erythrocytes in a membrane bioreactor. The membrane bioreactor system that provided high yields of hemoglobin (mainly oxyhemoglobin derivate) and its separation from the empty erythrocyte membranes (ghosts) was designed at a pilot scale. Ten different concentrations of hypotonic media were assessed from the aspect of the extent of hemolysis, hematocrit values of the erythrocyte suspensions, cell swelling, and membrane deformations induced by decreased salt concentration. Effective gradual osmotic hemolysis with an extent of hemolysis of 88% was performed using 35 mM Na-phosphate/NaCl buffer of pH 7.2–7.4. Under these conditions most of the cell membranes presented the appearance of the normal ghosts under phase contrast microscope. The hemoglobin purity of >80% was confirmed by SDS-PAGE. Kinetic studies showed that maximal concentration of hemoglobin was reached after 40 min, but the process cycle at which recovery of 83% was achieved lasted for 90 min. The dynamics of both steps, (1) transport through the membrane of erythrocytes during process of hemolysis and (2) transport through the reactor filters, were evaluated.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen, S. M., Medina, F., Winslow, R. W., Snell, S. M., Zegna, A., & Marini, M. A. (1988). Preparation of human hemoglobin Ao for possible use as a blood substitute. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 17, 143–154.
Sakai, H., Takeoka, S., Yokohama, H., Seino, Y., Nishide, H., & Tsuchida, E. (1993). Purification of concentrated hemoglobin using organic solvent and heat treatment. Protein Expression and Purification, 4, 563–569.
Winslow, R. M., & Chapman, K. W. (1994). Pilot-scale preparation of hemoglobin solutions. Methods in Enzymology, 231, 3–16.
Bugarski, B., & Dovezenski, N. (2000). Hemofarm Koncern, Verfahren zur Herstellung von Hemoglobin, Deutsches Patentamt DE 19707508.
Andrade, C. T., Barros, L. A., Lima, M. C., & Azero, E. G. (2004). Purification and characterization of human hemoglobin: effect of the hemolysis conditions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 34, 233–240.
Dimino, M. L., & Palmer, A. F. (2007). Purification of bovine hemoglobin via fast performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 856, 353–357.
Sun, G., & Palmer, A. F. (2008). Preparation of ultrapure bovine and human hemoglobin by anion exchange chromatography. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 867, 1–7.
Danon, D. (1961). Osmotic hemolysis by a gradual decrease in the ionic strength of the surrounding medium. Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology, 57, 111–117.
Hamidi, M., Zarrin, A., Foroozehs, M., & Mohammadi-Samani, S. (2007). Applications of carrier erythrocytes in delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Journal of Controlled Release, 118, 145–160.
Gutiérrez Millán, C., Zarzuelo Castañeda, A., Sayalero Marinero, M. L., & Lanao, J. M. (2004). Factors associated with the performance of carrier erythrocytes obtained by hypotonic dialysis. Blood Cells, Molecules & Diseases, 33, 132–140.
de Olivieira, R. (2002). Humane slaughter of bovine. First Virtual Global Conference on Organic Beef Cattle Production, September 02 to October 15, 2002 (Via Internet).
Jain, N. C. (1993). Essentials of veterinary hematology. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
Martínez Graciá, C., López Martínez, G., Ros Berruezo, G., Vidal Guevara, M. L., & Abellán Ballesta, P. (2000). Use of heme iron concentrate in the fortification of weaning foods. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48, 2930–2936.
Van Assendelft, O.W., Holtz, A.H. and Lewis, S.M. (1984). Recommended method for the determination of the hemoglobin content of blood. I.C.S.H. Publications World Health Organization, 1.4.1.
Palmer, A. F., Sun, G., & Harris, D. R. (2008). Tangential flow filtration of hemoglobin. Biotechnology Progress, 25, 189–199.
Sabine, J. C., & Nickolai, D. J. (1952). A microhematocrit method and its use with citrated blood. Blood, 7, 1128–1131.
Beutler, E. (1983). In W. J. Williams, E. Beutler, A. J. Erslev, & M. A. Lichtman (Eds.), Osmotic fragility, in hematology (pp. 1626–1627). New York: Mc Graw-Hill Book Co.
Vitvitsky, V. M., Frolova, E. V., Martinov, M. V., Komarova, S. V., & Ataullakhanov, F. I. (2000). Anion permeability and erythrocyte swelling. Bioelectrochemistry, 52, 169–177.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Olayemi, F. O., & Oyewale, J. O. (2002). Comparative assessment of the erythrocyte osmotic fragility and of haematological and plasma biochemical values in the Nigerian white Fulani and N’dama breeds of cattle. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 34, 181–187.
Adenkola, A. Y., Ayo, J. O., Sackey, A. K. B., & Adelaiye, A. B. (2010). Erythrocyte osmotic fragility of pigs administered ascorbic acid and transported by road for short-term duration during the harmattan season. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9, 226–233.
Paleari, R. and Mosca, A. (2008). Controversies on the osmotic fragility test. Enerca (The European network aimed at improving the diagnosis, epidemiological knowledge and medical education on rare and congenital anaemia), News, pp. 1–3.
Burger, S. P., Fujii, T., & Hanahan, D. J. (1968). Stability of the bovine erythrocyte membrane. Release of enzymes and lipid components. Biochemistry, 7, 3682–3700.
Florin-Christensen, J., Suarez, C. E., Florin-Christensen, M., Wainszelbaum, M., Brown, W. C., McElwain, T. F., & Palmer, G. H. (2001). A unique phospholipid organization in bovine erythrocyte membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 7736–7741.
Gimenez, G., Florin-Christensen, M., Belaunzarán, M. L., Isola, E. L., Suárez, C. E., & Florin-Christensen, J. (2007). Evidence for a relationship between bovine erythrocyte lipid membrane peculiarities and immune pressure from ruminal ciliates. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 119, 171–179.
Nakashima, H., & Makino, S. (1980). State of association of band 3 protein from bovine erythrocyte membrane in nonionic detergent. Journal of Biochemistry, 88, 933–947.
Sato, Y., Yamakose, H., & Suzuki, Y. (1993). Participation of band 3 protein in hypotonic hemolysis of human erythrocyte. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 16, 188–194.
Bogner, P., Sipos, K., Ludány, A., Somogyi, B., & Miseta, A. (2002). Steady-state volumes and metabolism-independent osmotic adaptation in mammalian erythrocytes. European Biophysics Journal, 31, 145–152.
Palek, J., Curby, W. A., & Lionetti, F. J. (1972). Size dependence of ghosts from stored erythrocytes on calcium and adenosine triphosphate. Blood, 40, 261–275.
Kummerow, D., Hamann, J., Browning, J. A., Wilkins, R., Ellory, J. C., & Bernhardt, I. (2000). Variations of intracellular pH in human erythrocytes via K(+)(Na(+))/H(+) exchange under low ionic strength conditions. Journal of Membrane Biology, 176, 207–216.
Jacobs, M. H., & Parpart, A. K. (1931). Osmotic properties of the erythrocyte. II. The influence of pH, temperature, and oxygen tension on hemolysis by hypotonic solutions. Biology Bulletin, 60, 95–119.
Lowenstein, L. M. (1960). The effect of albumin on osmotic hemolysis. Experimental Cell Research, 20, 56–65.
Parpart, A. K., Lorenz, P. B., Parpart, E. R., Gregg, J. R., & Chase, A. M. (1947). The osmotic resistance (fragility) of human red cells. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 26, 636–640.
Sheffield, C. L., Spates, G. E., Droleskey, R. E., Green, R., & DeLoach, J. R. (1987). Preparation of lipid-free human hemoglobin by dialysis and ultrafiltration. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 9, 230–238.
Elmer, J., Harris, D. R., Sun, G., & Palmer, A. F. (2009). Purification of hemoglobin by tangential flow filtration with diafiltration. Biotechnology Progress, 25, 1402–1410.
Bugarski, B., Dovezenski, N., Stojanovic, N., Bugarski, D. & Hemofarm Koncern (2003). Emulsion containing hydrophobic nanodrops with bound hemoglobin molecules in a hydrophilic phase as a blood substitute, Deutsches Patentamt DE 2002-10209860 WO 2003074022.
Zijlstra, W. G., Buursma, A. A., & Meeuwsen-van der Roest, W. P. (1991). Absorption spectra of human fetal and adult oxyhemoglobin, de-oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin. Clinical Chemistry, 37, 1633–1638.
Okamura, M., Yokoyama, N., Takabatake, N., Okubo, K., Ikehara, Y., & Igarashi, I. (2007). Modification of host erythrocyte membranes by trypsin and chymotrypsin treatments and effects on the in vitro growth of bovine and equine Babesia parasites. Journal of Parasitology, 93, 208–211.
Elmer, J., Buehler, P. W., Jia, Y., Wood, F., Harris, D. R., Alayash, A. I., & Palmer, A. F. (2010). Functional comparison of hemoglobin purified by different methods and their biophysical implications. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 106, 76–85.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by grants III46010 and E!4486 from the Ministry of Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia. The authors thank to Dr Ivana Klun for the assistance in microscopy and image analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stojanović, R., Ilić, V., Manojlović, V. et al. Isolation of Hemoglobin from Bovine Erythrocytes by Controlled Hemolysis in the Membrane Bioreactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 1491–1506 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9543-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9543-9