Abstract
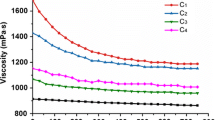
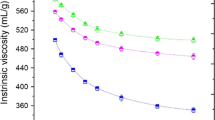
The aim of this study is to compare the effect of different homogenization treatments on the physicochemical properties and the hydrolysis rate of a pure bleached cellulose. Results obtained show that homogenization treatments improve the enzymatic hydrolysis rate of the cellulose fibers by 25 to 100 %, depending of the homogenization treatment applied. Characterization of the samples showed also that homogenization had an impact on some physicochemical properties of the cellulose. For moderate treatment intensities (pressure below 500 b and degree of homogenization below 25), an increase of water retention values (WRV) that correlated to the increase of the hydrolysis rate was highlighted. Result also showed that the overall crystallinity of the cellulose properties appeared not to be impacted by the homogenization treatment. For higher treatment intensities, homogenized cellulose samples developed a stable tridimentional network that contributes to decrease cellulase mobility and slowdown the hydrolysis process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heungjo, A., Wilbert, E. W., & Stephen, W. S. (2011). Biomass and Bioenergy, 35, 3763–3774.
Sarkar, N., Ghosh, S. K., Bannerjee, S., & Aikat, K. (2012). Renewable Energy, 37, 19–27.
Franklin, K.R., Hopkinson, A., Webb, N., White, M.S. (2002). Patent WO/2002/032914. 280.
Han, S., Baigude, H., Hattori, K., Yoshida, T., & Uryu, T. (2007). Carbohydrate Polymers, 68(1), 26–34.
Wang, K., Jiang, J. X., Xu, F., & Sun, R. C. (2009). Polymer Degradation and Stability, 94, 1379–1388.
Sassner, P., Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (2008). Biomass and Bioenergy, 32, 422–430.
Alvira, P., Tomás-Pejó, E., Ballesteros, M., & Negro, M. J. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 4851–4861.
Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (2007). Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 108, 41–65.
Avellar, B. K., & Glasser, W. G. (1998). Biomass and Bioenergy, 14, 205–218.
Jacquet, N., Vanderghem, C., Blecker, C., & Paquot, M. (2010). BASE, 14(S2), 561–566.
Pérez, J. A., Ballesteros, I., Ballesteros, M., Sáez, F., Negro, M. J., & Manzanares, P. (2008). Fuel, 87, 3640–3647.
Wyman, C. E., Dale, B. E., Elander, R. T., Holtzapple, M., Ladisch, M. R., & Lee, Y. Y. (2005). Bioresource Technology, 96, 1959–1966.
Palonen, H., Thomsen, A. B., Tenkanen, M., Schmidt, A. S., & Viikari, L. (2004). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 117, 1–17.
Schacht, C., Zetzl, C., & Brunner, G. (2008). Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 46, 299–321.
Zhu, S., Wu, Y., Yu, Z., Wang, C., Yu, F., Jin, S., et al. (2006). Biosystems Engineering, 93, 279–283.
Sun, R. C., & Tomkinson, R. C. (2002). Carbohydrate Polymers, 50(3), 263–271.
Floury, J., Desrumaux, A., Axelos, M., & Legrand, J. (2002). Food Hydrocolloids, 16(1), 47–53.
Pandolfe, W. D. (1999). Wiley encyclopedia of food science and technology (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Walstra, P. (1983). In P. Becher (Ed.), Encyclopedia of emulsion technology, vol. 1: Formation of emulsion (pp. 57–127). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Siro, I., & Plackett, D. (2012). Cellulose, 17(3), 459–494.
Dinand, E., Chanzy, H., & Vignon, R. M. (1999). Food Hydrocolloids, 13(3), 275–283.
Agoda-Tandjawa, G., Durand, S., Berot, S., Blassel, C., Gaillard, C., Garnier, C., et al. (2010). Carbohydrate Polymers, 80, 677–686.
Bhatnagar, A., & Sain, M.M. (2003). Canadian Intellectual Property Office No. 2437616.
Nakagaito, A. N., & Yano, H. (2004). Applied Physics A-Materials Science Processing, 78, 547–552.
Habibi, Y., Mahrouz, M., & Vignon, M. R. (2008). Food Chemistry, 115(2), 423–429.
Vanderghem, C., Boquel, P., Blecker, C., & Paquot, M. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160(8), 2300–2307.
Ioannis, N., Konstantina, T., & Stavros, M. (2006). European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 63, 278–287.
Leviton, A., & Pallansch, M. J. (1959). Journal of Dairy Science, 42(1), 20–27.
Vanderghem, C., Jacquet, N., Danthine, S., Blecker, C., & Paquot, M. (2012). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166(6), 1423–1432.
Yeh, A. I., Huang, Y. C., & Chen, S. H. (2010). Carbohydrate Polymers, 79, 192–199.
Nelson, M. L., & O’Connor, R. T. (1964). Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 8, 1325–1341.
Segal, L., Creely, J. J., Martin, A. E., & Conrad, C. M. (1962). Texas Research Journal, 29, 786–794.
Thygesen, A., Oddershede, J., Lilholt, H., Thomsen, A. B., & Ståhl, K. (2005). Cellulose, 12, 563–576.
Bibin, M. C., Alcides Lopes, L., Ferreira de Souza, S., Sabu, T., Pothan, L. A., & Kottaisamy, M. (2010). Carbohydrate Polymers, 81, 720–725.
Mantanis, G. I., Young, R. A., & Rowell, R. M. (1995). Cellulose, 2, 1–22.
Paquot, M., Thonart, P., Jacquemin, P., & Rassel, A. (1981). Holzforschung, 35, 87–93.
Azizi Samir, M. A. S., Alloin, F., & Dufresne, A. (2005). Biomacromolecules, 6, 612–626.
Tabilo-Munizaga, G., & Barbosa-Canovas, G. V. (2005). Journal of Food Engineering, 67, 147–156.
Guo, Q., Cui, S. W., Wang, Q., Douglas Goff, H., & Smith, A. (2008). Food Hydrocolloids, 23, 1542–1547.
Eichhorna, S. J., Young, R. J., Davies, R. J., & Riekel, C. (2003). Polymer, 44, 5901–5908.
Eriksson, R., Pajari, H., & Rosenholm, J. B. (2009). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 332, 104–112.
Rudraraju, V. S., & Wyandt, C. M. (2004). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 292, 53–61.
Jacquet, N., Vanderghem, C., Danthine, S., Quiévy, N., Blecker, C., Devaux, J., Paquot, M. (2012). Bioresour Technol., In press.10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.073
Lee, S. B., Shin, H. S., Ryu, D. D. Y., & Mandels, M. (1982). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 24, 2137–2153.
Stone, J. E., Scallan, A. M., Donefer, E., & Ahlgren, E. (1969). Advances in Chemistry Series, 95, 219–307.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the Walloon Region in the frame of the NACELL program (convention 031/5575), LIGNOFUEL program (convention no. 716721) and TECHNOSE program (convention no. 716757). Mr. Maniet Guillaume, Mr. Frederic Meyer, and Me Doran Lynn are acknowledged for excellent assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacquet, N., Vanderghem, C., Danthine, S. et al. Influence of Homogenization Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Rate of Pure Cellulose Fibers. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 1315–1328 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0057-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0057-2