Abstract
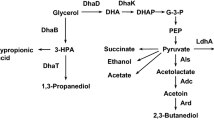
1,3-Propanediol (1,3-PD) biosynthesis plays a key role in NADH consumption to regulate the intracellular reducing equivalent balance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. This study aimed to increase reducing equivalent for enhancing 1,3-PD production through cofermentation of glycerol and xylose. Adding xylose as cosubstrate resulted in more reducing equivalent generation and higher cell growth. In batch fermentation under microaerobic condition, the 1,3-PD concentration, conversion from glycerol, and biomass (OD600) relative to cofermentation were increased significantly by 9.1%, 20%, and 15.8%, respectively. The reducing equivalent (NADH) was increased by 1–3 mg/g (cell dry weight) compared with that from glycerol alone. Furthermore, 2,3-butannediol was also doubly produced as major byproduct. In fed-batch fermentation with xylose as cosubstrate, the final 1,3-PD concentration, conversion from glycerol, and productivity were improved evidently from 60.78 to 67.21 g/l, 0.52 to 0.63 mol/mol, and 1.64 to1.82 g/l/h, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji, X. J., Huang, H., Du, J., Zhu, J. G., Ren, L. J., Hu, N., et al. (2009). Enhanced 2,3-butanediol production by Klebsiella oxytoca using a two-stage agitation speed control strategy. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3410–3414.
Selembo, P. A., Perez, J. M., Lloyd, W. A., & Logan, B. E. (2009). Enhanced hydrogen and 1,3-propanediol production from glycerol by fermentation using mixed cultures. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 104, 1098–1106.
Cheng, K. K., Liu, D. H., Sun, Y., & Liu, W. B. (2004). 1,3-Propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae under different aeration strategies. Biotechnology Letters, 26, 911–915.
Huang, H., Gong, C. S., & Tsao, G. T. (2002). Production of 1, 3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 98–100, 687–698.
Boenigk, R., Bowien, S., & Gottschalk, G. (1993). Fermentation of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol in continuous cultures of Citrobacter freundii. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 3, 453–457.
Abbad-Andaloussi, S., Du, C., Raval, G., & Petitdemange, H. (1996). Carbon and electron flow in Clostridium butyricum grown in chemostat culture on glycerol and on glucose. Microbiology, 142, 1149–1158.
Schutz, H., & Radler, F. (1984). Anaerobic reduction of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol by Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus buchneri. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 5, 169–178.
Zeng, A. P., Biebl, H., Schlieker, H., & Deckwer, W. D. (1993). Pathway analysis of glycerol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae: regulation of reducing equivalent balance and product formation. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 15, 770–779.
Zhang, Y. P., Li, Y., Du, C. Y., Liu, M., & Cao, Z. A. (2006). Inactivation of aldehyde dehydrogenase: a key factor for engineering 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Metabolic Engineering, 8, 578–586.
Xu, Y. Z., Guo, N. N., Zheng, Z. M., Ou, X. J., Liu, H. J., & Liu, D. H. (2009). Metabolism in 1,3-propanediol fed-batch fermentation by a D-lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 104, 965–972.
Zhang, Y. P., Huang, Z. H., Du, C. Y., Li, Y., & Cao, Z. A. (2009). Introduction of an NADH regeneration system into Klebsiella oxytoca leads to an enhanced oxidative and reductive metabolism of glycerol. Metabolic Engineering, 11, 101–106.
San, K. Y., Bennett, G. N., Berríos-Rivera, S. J., Vadali, R. V., Yang, Y. T., Horton, E., et al. (2002). Metabolic engineering through cofactor manipulation and its effects on metabolic flux redistribution in Escherichia coli. Metabolic Engineering, 4, 182–192.
Jeffries, T. W. (1983). Utilization of xylose by bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 27, 1–32.
Miseta, A., Tokes-Fuzesi, M., Aiello, D., & Bedwell, D. (2003). A Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant unable to convert glucose to glucose-6-phosphate accumulates excessive glucose in the endoplasmic reticulum due to core oligosaccharide trimming. Eukaryotic Cell, 2, 534–541.
Sato, K., Yoshida, Y., & Hirahata, T. (2000). On-line measurement of intracellular ATP of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and pyruvate during sake mashing. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 90, 294–301.
Stanley, P. E. (1986). Extraction of adenosine triphosphate from microbial and somatic acid. Methods in Enzymology, 133, 14–22.
Abbad-Andaloussi, S., Amne, J., Ferard, P., & Petitdemange, H. (1998). Effect of glucose on glycerol metabolism by Clostridium butyricum. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 84, 515–522.
Yang, G., Tian, J., & Li, J. (2007). Fermentation of 1,3-propanediol by a lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella oxytoca under microaerobic conditions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 73, 1017–1024.
Ragout, A., Sineriz, F., Diekmann, H., & Valdez, G. F. (1996). Shift in the fermentation balance of Lactobacillus reuteri in the presence of glycerol fermentation. Biotechnology Letters, 18, 1105–1108.
Tong, I., & Cameron, D. C. (1992). Enhancement of 1,3-propanediol production by cofermentation in Escherichia coli expressing Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon gene. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 34-35, 149–159.
Petrov, P., & Petrova, P. (2009). High production of 2,3-butanediol from glycerol by Klebsiella pneumoniae G31. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 84, 659–665.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the key program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 200936002), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB710800), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2006AA020103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, P., Lu, Sg., Huang, H. et al. Enhanced Reducing Equivalent Generation for 1,3-Propanediol Production Through Cofermentation of Glycerol and Xylose by Klebsiella pneumoniae . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 1532–1542 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9373-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9373-1