Abstract
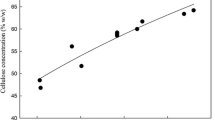
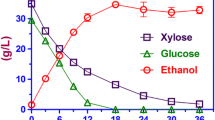
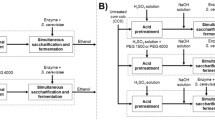
In scale-up, the potential of ethanol production by dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment using corncob was investigated. Pretreatments were performed at 170 °C with various acid concentrations ranging from 0% to 1.656% based on oven dry weight. Following pretreatment, pretreated biomass yield ranged from 59% to 67%. More than 90% of xylan was removed at 0.828% of sulfuric acid. At same pretreatment condition, the highest glucose yield obtained from pretreated biomass by enzymatic hydrolysis was about 76%, based on a glucan content of 37/100 g. In hydrolysate obtained by pretreatment, glucose concentration was low, while xylose concentration was significantly increased above 0.368% of sulfuric acid. At 1.656% of sulfuric acid, xylose and glucose concentration was highest. In subsequent, fermentation with hydrolysate, maximal ethanol yield was attained after 24 h with 0.368% of sulfuric acid. The fermentation efficiency of hydrolysate obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis reached a maximum of 75% at an acid charge of 0.368%.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barl, B., Biliaderis, C. G., Murray, E. D., & Macgregor, A. W. (1991). Combined chemical and enzymatic treatment of corn husks lignocellulosics. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 56, 195–214.
Becall, D. S., & Ingram, L. O. (1992). Conversion of hydrolysate of corncobs and hulls into ethanol by recombinant Escherichia coli B containing integrated genes for ethanol production. Biotechnology Letters, 14, 857–862.
Cao, N. J., Krishnan, M. S., Du, J. X., Gong, C. S., Ho, N. W. Y., & Chen, Z. D. (1996). Ethanol production from corncob pretreated by the ammonia steeping process using genetically engineered yeast. Biotechnology Letters, 18, 1013–1018.
Chen, Y., Dong, B., Qin, W., & Xiao, D. (2010). Xylose and cellulose fractionation from corncob with three different strategies and separate fermentation of them to bioethanol. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6994–6999.
Himmel, M. E., Ding, S. Y., Johnson, D. K., Adney, W. S., Nimlos, M. R., & Brady, J. W. (2007). Biomass recalcitrance: Engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science, 315, 804–807.
Larsson, S., Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hagerdal, B., Tengborg, C., Stenberg, K., & Zacchi, G. (1999). The generation of fermentation inhibitors during dilute acid hydrolysis of softwood. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 24, 151–159.
Lee, J. W., Rodrigues, R. C. L. B., & Jeffries, T. W. (2009). Simultaneous saccharification and ethanol fermentation of corncob pretreated with oxalic acid using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 100, 6307–6311.
Liu, K., Lin, L., Yue, J., Li, X., Fang, X., & Zhu, M. (2010). High concentration ethanol production from corncob residues by fed-batch strategy. Bioresource Technology, 101, 4952–4958.
Shen, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, T., Bao, X., Du, F., Zhuang, G., et al. (2008). Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of acid-pretreated corncobs with recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing beta-glucosidase. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5099–5103.
Wang, G. S., Lee, J.-W., Zhu, J. Y., & Jeffries, T. W. (2011). Dilute acid pretreatment of corncob for efficient sugar production. Applied Biochemisty and Biotechnology, 163, 658–668.
Zhang, M., Wang, F., Su, R., Qi, W., & He, Z. (2010). Ethanol production from high dry matter corncob using fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation after combined pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 101, 4959–4964.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Priority Research Centers Programs through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (Project No. 2011-0018393) to J.-W. Lee and by EdenIQ under CRADA 08-RD-11111126-007 with the Forest Products Laboratory. The authors thank Frederick J. Matt of the Analytical Chemistry and Microscopy Laboratory of the USDA Forest Products Laboratory (FPL) for carrying out the carbohydrate determination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JW., Zhu, J.Y., Scordia, D. et al. Evaluation of Ethanol Production from Corncob Using Scheffersomyces (Pichia) stipitis CBS 6054 by Volumetric Scale-up. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 814–822 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9299-7