Abstract
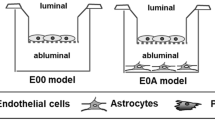
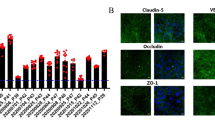
This study evaluated the feasibility of using commercially available immortalized cell lines in building an in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) co-culture model for preliminary drug development studies. Astrocytes-derived acellular extracellular matrix (aECM) was introduced in the co-culture model to provide a novel biomimetic basement membrane for the endothelial cells to form tight junctions. Trans-Endothelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) and solute mass transport studies quantitatively evaluated the tight junction formation. Immuno-fluorescence microscopy and Western blot analysis qualitatively verified the expression of occludin, one of the tight junction proteins on the samples. Experimental data from a total of 13 experiments conclusively showed that the novel BBB in vitro co-culture model with aECM (CO + aECM) is promising in terms of establishing tight junction formation represented by TEER values, transport profiles, and tight junction protein expression when compared with traditional co-culture (CO) model setup or the endothelial cells cultured alone (EC). In vitro colorimetric sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay also revealed that the “CO + aECM” samples resulted in less cell loss on the basal sides of the insert membranes than traditional co-culture models. Our novel approach using immortalized cell lines with the addition of aECM was proven to be a feasible and repeatable alternative to the traditional BBB in vitro modeling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Y., & Miller, D. W. (2005). Drug Delivery Principles and Applications. In B. Wang, T. Siahaan, & R. A. Soltero (Eds.), Hoboken. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Garcia-Garcia, E., Gil, S., Andrieux, K., Desmaele, D., Nicolas, V., Taran, F., et al. (2005). Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 62(12), 1400–1408.
Engelhardt, B. (2003). Cell and Tissue Research, 314(1), 119–129.
Hawkins, B. T., & Davis, T. P. (2005). Revelation, 57(2), 173–185.
Zlokovic, B. V. (2008). Neuron, 57(2), 178–201.
Pardridge, W. M. (1999). Journal of Neurovirology, 5(6), 556–569.
Rubin, L. L., & Staddon, J. M. (1999). Annual Review of Neuroscience, 22(1), 11–28.
Haseloff, R. F., Blasig, I. E., Bauer, H. C., & Bauer, H. (2008). BBA-Biomembranes., 1778(3), 588–600.
Kacem, K., Lacombe, P., Seylaz, J., & Bonvento, G. (1998). Glia, 23(1), 1–10.
Barrios-Rodiles, Brown, M. K. R., Ozdamar, B., Bose, R., Liu, Z., Donovan, R. S., et al. (2005). Science, 307(5715), 1621–1625.
Li, D., & Mrsny, R. J. (2000). The Journal of Cell Biology, 148(4), 791–800.
Yu, A. S. L., McCarthy, K. M., Francis, S. A., McCormack, J. M., Lai, J., Rogers, R. A., et al. (2005). American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 288(6), 1231–1241.
Murata, M., Kojima, T., Yamamoto, T., Go, M., Takano, K., Osanai, M., et al. (2005). Experimental Cell Research, 310(1), 140–151.
Osanai, M., Murata, M., Nishikiori, N., Chiba, H., Kojima, T., & Sawada, N. (2006). Cancer Research, 66(18), 9125–9133.
Wang, Z., Mandell, K. J., Parkos, C. A., Mrsny, R. J., & Nusrat, A. (2005). Oncogene, 24(27), 4412–4420.
Mizuguchi, H., Utoguchi, N., & Mayumi, T. (1997). Brain Research Protocols, 1(4), 339–343.
Abbott, N. J., Rönnbäck, L., & Hansson, E. (2006). Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 7(1), 41–53.
Haring, H. P., Akamine, B. S., Habermann, R., Koziol, J. A., & Del Zoppo, G. J. (1996). Neuropath. Exp. Neur., 55(2), 236–245.
Milner, R., & Campbell, I. L. (2002). Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 20(4), 616–626.
Abbott, N. J. (2004). Drug. Discov. Today.: Technologies, 1(4), 407–416.
Garberg, P., Ball, M., Borg, N., Cecchelli, R., Fenart, L., Hurst, R. D., et al. (2005). Toxicol In Vitro, 19(3), 299–334.
Yoo, J. W., Kim, Y. S., Lee, S. H., Lee, M. K., Roh, H. J., Jhun, B. H., et al. (2003). Pharmaceutical Research, 20(10), 1690–1696.
Li, C.-Z., Taniguchi, I., & Mulchandani, A. (2009). Bioelectrochemistry, 75, 182–188.
Gray, T. E., Guzman, K., Davis, C. W., Abdullah, L. H., & Nettesheim, P. (1996). Am. J. Resp. Cell. Mol., 14(1), 104–112.
Levashova, Z. B., Plisov, S. Y., & Perantoni, A. O. (2003). Kidney International, 63(6), 2075–2087.
Li, C.-Z., Nishiyama, K., Taniguchi, I. (2000). Electrochimica Acta, 45, 2883–2888.
Radany, E. H., Brenner, M., Besnard, F., Bigornia, V., Bishop, J. M., & Deschepper, C. F. (1992). P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89(14), 6467–6471.
Hurst, R. D., & Fritz, I. B. (1996). Journal of Cellular Physiology, 167(1), 81–88.
Vichai, V., & Kirtikara, K. (2006). Nature Protocols, 1(2), 1112–1116.
Flaten, G. E., Dhanikula, A. B., Luthman, K., & Brandl, M. (2006). European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 27(1), 80–90.
McCall, A. L., Millington, W. R., & Wurtman, R. J. (1982). Life Sciences, 31, 2709–2715.
Nakazono, T., Murakami, T., Sakai, S., Higashi, Y., & Yata, N. (1992). Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 40, 2510–2515.
Sadzuka, Y., Hatakeyama, H., Daimon, T., & Sonobe, T. (2008). International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 354(1–2), 63–69.
Diglio, C. A., Grammas, P., Giacomelli, F., & Wiener, J. (1982). Laboratory Investigation, 46(6), 554–563.
Herrmann, J., Gressner, A. M., & Weiskirchen, R. (2007). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 11(4), 704–722.
Kuchler-Bopp, S., Delaunoy, J. P., Artault, J. C., Zaepfel, M., & Dietrich, J. B. (1999). NeuroReport, 10(6), 1347–1353.
Hurst, R. D., Heales, S. J. R., Dobbie, M. S., Barker, J. E., & Clark, J. B. (1998). Brain Research, 802(1–2), 232–240.
Acknowledgements
This current work is partially supported by 2008 FIU Faculty Research Award to Dr. Chen-Zhong Li and the Dissertation Year Fellowship to Zhiqi Zhang granted by the Graduate School of Florida International University. Special thanks to Dr.Wang, Xiaotang’s Biochemistry Lab and his Ph.D. student Wang, Zheng and Hui Tian for their kind help on the Western blot assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., McGoron, A.J., Crumpler, E.T. et al. Co-culture Based Blood-brain Barrier In Vitro Model, a Tissue Engineering Approach using Immortalized Cell Lines for Drug Transport Study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163, 278–295 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9037-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9037-6