Abstract
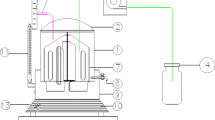
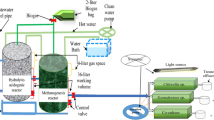
The effect of organic matter and fill time on anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (5 L, 30°C, 8-h cycles, 50 rpm) efficiency has been analyzed. Organic matter was increased by the influent concentration. Fill times investigated were in the batch mode and fed-batch followed by batch. In the batch mode organic matter removal were 93%, 81%, and 66% for influent concentration of 500, 1,000, and 2,000 mgCOD/L (0.6, 1.29, and 2.44 gCOD/L.d), respectively. At 3,000 mgCOD/L (3.82 gCOD/L.d) operational stability could not be achieved. Removal efficiency was improved by increasing the fill time, and was 85% for the 1,000 mgCOD/L condition and fill times of 2 and 4 h, and 80 and 77% for the 2,000 mgCOD/L condition and fill times of 2 and 4 h, respectively. Hence, gradual feeding seemed to improve and to smooth the profiles of organic matter and volatile acids along the cycle with 78 to 96 NmLCH4/gCOD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2006). New configurations and operation strategies of anaerobic biofilm bioreactors applied to wastewater treatment. (Chapter 1). In E. C. Hearns (Ed.), Focus on Biotechnology Research. New York: Nova Science Publishers. 233 p.
Friedl, G. F., Mockaitis, G., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2009). AnSBBR applied to organic matter and sulfate removal: interaction effect between feed strategy and COD/sulfate ratio. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 159, 95–109.
Novaes, L. F., Borges, L. O., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2010). Effect of fill time on the performance of pilot-scale ASBR and AnSBBR applied to sanitary wastewater treatment. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 885–899.
Canto, C. S. A., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2008). Anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (AnSBBR): some applications to sanitary and industrial wastewaters. (Chapter 2). In R. H. Theobald (Ed.), Environmental Management. New York: Nova Science Publishers. 429 p.
Canto, C. S. A., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2008). Feasibility of nitrification/denitrification in a sequential batch biofilm reactor with liquid circulation applied to post-treatment. Bioresource Technology, 99, 644–654.
Shizas, I., & Bagley, D. M. (2002). Improving anaerobic sequencing batch reactor performance by modifying operational parameters. Water Research, 36, 363–367.
Bergamo, C. M., Monaco, R., Ratusznei, S. M., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2009). Effects of temperature at different organic loading levels on the performance of a fluidized-bed anaerobic sequencing batch bioreactor. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 48, 789–796.
Angenent, L. T., Sung, S., & Raskin, L. (2002). Methanogenic population dynamics during startup of a full-scale anaerobic sequencing batch reactor treating swine waste. Water Research, 36, 4648–4654.
Michelan, R., Zimmer, T. R., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Moraes, D., Zaiat, M., et al. (2009). Effect of impeller type and mechanical agitation on the mass transfer and power consumption aspects of ASBR operation treating synthetic wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1357–1364.
Rodrigues, J. A. D., Pinto, A. G., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Gedraite, R. (2004). Enhancement of the performance of an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor treating low strength wastewater through implementation of a variable stirring rate program. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 21, 423–434.
Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Camargo, E. F. M., & Zaiat, M. (2003). Influence of agitation rate on the performance of an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor containing granulated biomass treating low-strength wastewater. Advances in Environmental Research, 7, 405–410.
Damasceno, L.H.S., Rodrigues, J.A.D., Ratusznei, S.M., Zaiat, M., Foresti, E. (2008). Effect of mixing mode on the behavior of an ASBBR with immobilized biomass in the treatment of cheese whey. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 25(02), 291–298.
Bagley, D. M., & Brodkorb, T. S. (1999). Modeling microbial kinetics in an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor—model development and experimental validation. Water Environment Research, 71, 1320–1332.
Bezerra, R. A., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2009). Effects of feed time, organic loading and shock loads in the anaerobic whey treatment by an AnSBBR with circulation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 157, 140–158.
Cheong, D. Y., & Hansen, C. L. (2008). Effect of feeding strategy on the stability of anaerobic sequencing batch reactor responses to organic loading conditions. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5058–5068.
Zaiat, M., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Camargo, E. F. M., & Borzani, W. (2001). Anaerobic sequencing batch reactors for wastewater treatment: a developing technology. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 55, 29–35.
Moreira, M. B., Ratusznei, S. M., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2008). Influence of organic shock loads in an ASBBR treating synthetic wastewater with different concentration levels. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3256–3266.
Ndegwa, P. M., Hanilton, D. W., Lalman, J. A., & Cumba, H. J. (2005). Optimization of anaerobic sequencing batch reactors treating dilute swine slurries. Transactions of the ASAE, 48, 1575–1583.
Damasceno, L. H. S., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2007). Effects of feeding time and organic loading in an anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (ASBBR) treating diluted whey. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 927–935.
Massé, D. I., & Masse, L. (2000). Treatment of slaghterhouse wastewater in anaerobic sequencing batch reactors. Canadian Agricultural Engineering, 42, 131–137.
Oliveira, R. P., Ghilardi, J. A., Ratusznei, S. M., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2008). Anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor applied to automobile industry wastewater treatment: volumetric loading rate and feed strategy effects. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 47, 1380–1389.
Bouallagui, H., Lahdheb, H., Ben Romdan, E., Rachdi, B., & Hamdi, M. (2009). Improvement of fruit and vegetable waste anaerobic digestion performance and stability with co-substrates addition. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1844–1849.
Xiangwen, S., Dangcong, P., Zhaohua, T., & Xinghua, J. (2008). Treatment of brewery wastewater using anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (ASBR). Bioresource Technology, 99, 3182–3186.
Oliveira, D. S., Prinholato, A. C., Ratusznei, S. M., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2009). AnSBBR applied to the treatment of wastewater from a personal care industry: effect of organic load and fill time. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 3070–3081.
Sahinkaya, E., & Dilek, F. B. (2007). Effect of feeding time on the performance of a sequencing batch reactor treating a mixture of 4-CP and 2, 4-DCP. Journal of Environmental Management, 83, 427–436.
Sirianuntapiboon, S., Chairattanawan, K., & Surasinanant, P. (2007). Some properties of a sequencing batch reactor for treatment of wastewater containing thiocyanate compounds. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 330–337.
Sirianuntapiboon, S., Sadahiro, O., & Salee, P. (2007). Some properties of a granular activated carbon-sequencing batch reactor (GAC-SBR) system for treatment of textile wastewater containing direct dyes. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 162–170.
Yazdani, S. S., & Gonzalez, R. (2007). Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol: a path to economic viability for the biofuels industry. Biotechnology, 18, 213–219.
Ito, T., Nakashimada, Y., Senba, K., Matsui, T., & Nishio, N. (2005). Hydrogen and ethanol production from glycerol containing wastes discharges after biodiesel manufacturing process. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100, 260–265.
Suehara, K., Kawamoto, Y., Fujii, E., Kohda, J., Nakano, Y., & Yano, T. (2005). Biological treatment of wastewater discharged from biodiesel fuel production plant with alkali-catalyzed transesterification. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100, 437–442.
Nishio, N., & Nakashimada, Y. (2007). Recent development of digestion process for energy recovery from wastes. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 103, 105–112.
Yang, Y., Tsukahara, K., & Sawayama, S. (2008). Biodegradation and methane production from glycerol-containing synthetic wastes with fixed-bed bioreactor under mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic conditions. Process Biochemistry, 43, 362–367.
Sabourin-Provost, G., & Hallenbeck, P. C. (2009). High yield conversion of a crude glycerol fraction from biodiesel production to hydrogen by photofermentation. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3513–3517.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. (1995). APHA, AWWA, WPCF (19th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo—FAPESP (São Paulo, Brazil), process numbers 01/05.489-0 and 08/55.527-5 (V.C. Selma). The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Baltus C. Bonse for the revision of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selma, V.C., Cotrim, L.H.B., Rodrigues, J.A.D. et al. ASBR Applied to the Treatment of Biodiesel Production Effluent: Effect of Organic Load and Fill Time on Performance and Methane Production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162, 2365–2380 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9009-x