Abstract
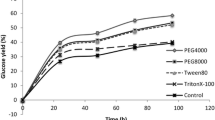
The potential economic benefits of surfactants addition on enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-exploded lodgepole pine (SELP) and ethanol-pretreated lodgepole pine (EPLP) were investigated in this study. Free cellulase readsorption on fresh substrate was used to recover and recycle cellulase enzymes during the hydrolysis of SELP and EPLP substrate. Supplementing Tween 80 during the hydrolysis could facilitate enzyme recycling for EPLP substrate. A logarithmic correlation was established between surfactant concentration and free cellulase content after lignocellulosic hydrolysis, which was used to compute enzyme cost savings over various Tween 80 concentrations. A simple economic analysis of enzyme cost savings versus the cost of surfactant was undertaken. The results indicated that the addition of Tween 80 (priced at US $0.25/kg) during the hydrolysis of the EPLP substrate could save 60% of the total enzyme cost at concentrations in the 0.025% to 0.2% range. The addition of Tween for the hydrolysis of the SELP substrate significantly reduced the material cost by 24% per 1 gal of ethanol produced, and the ethanol production cost could be reduced by 8.6% with the addition of Tween and enzymes recycle for the hydrolysis of SELP substrate. A schematic concept of recycling enzyme and surfactant was also presented with a recirculation of process streams during hydrolysis. Further analysis indicated a 66% reduction in total enzyme cost could potentially be achieved under the concept.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurabi, A., Berlin, A., Gilkes, N., Kilburn, D., Bura, R., Robinson, J., et al. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121, 219–230.
Robinson, J., Keating, J. D., Boussaid, A., Mansfield, S. D., & Saddler, J. N. (2002). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 443–448.
Robinson, J., Keating, J. D., Mansfield, S. D., & Saddler, J. N. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 757–765.
Duff, S. J. B., & Murray, W. D. (1996). Bioresource Technology, 55, 1–33.
Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (2002). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 59, 618–628.
Wyman, C. E. (1999). Annual Review of Energy and the Environment, 24, 189–226.
Chum, H. L., Johnson, D. K., Black, S., Baker, J., Grohmann, K., Sarkanen, K. V., et al. (1988). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 31, 643–649.
Saha, B. C., Iten, L. B., Cotta, M. A., & Wu, Y. V. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 3693–3700.
Alizadeh, H., Teymouri, F., Gilbert, T. I., & Dale, B. E. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121, 1133–1141.
Ballesteros, M., Oliva, J. M., Negro, M. J., Manzanares, P., & Ballesteros, I. (2004). Process Biochemistry, 39, 1843–1848.
Pan, X. J., Gilkes, N., Kadla, J., Pye, K., Saka, S., Gregg, D., et al. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94, 851–861.
Pan, X. J., Arato, C., Gilkes, N., Gregg, D., Mabee, W., Pye, K., et al. (2005). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 90, 473–481.
Tu, M. B., Chandra, R. P., & Saddler, J. N. (2007). Biotechnology Progress, 23, 1130–1137.
Steele, E., Raj, S., Nghiem, J., & Stowers, M. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121, 901–910.
Gregg, D. J., Boussaid, A., & Saddler, J. N. (1998). Bioresource Technology, 63, 7–12.
Lynd, L. R., Weimer, P. J., van Zyl, W. H., & Pretorius, I. S. (2002). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 66, 506–577.
Hayward, T. K., Hamilton, J., Tholudar, A., & McMillan, J. D. (2000). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 84–6, 859–874.
Zhang, Y. H. P., Himmel, M. E., & Mielenz, J. R. (2006). Biotechnology Advances, 24, 452–481.
Merino, S. T., & Cherry, J. (2007). Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 108, 95–120.
Tu, M. B., Chandra, R. P., & Saddler, J. N. (2007). Biotechnology Progress, 23, 398–406.
Jensen, J. K. (2003). Palo Alto: Genencor International, Inc.
Cherry, J. R., & Fidantsef, A. L. (2003). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 14, 438–443.
Castanon, M., & Wilke, C. R. (1980). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 22, 1037–1053.
Reese, E. T., & Mandels, M. (1980). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 22, 323–335.
Knutsen, J. S., & Davis, R. H. (2002). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 98, 1161–1172.
Lu, Y. P., Yang, B., Gregg, D., Saddler, J. N., & Mansfield, S. D. (2002). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 98, 641–654.
Xu, J., & Chen, H. Z. (2007). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 143, 93–100.
Eriksson, T., Borjesson, J., & Tjerneld, F. (2002). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 31, 353–364.
Castanon, M., & Wilke, C. R. (1981). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 23, 1365–1372.
Alkasrawi, M., Eriksson, T., Borjesson, J., Wingren, A., Galbe, M., Tjerneld, F., et al. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 71–78.
Duff, S. J. B., Moritz, J. W., & Casavant, T. E. (1995). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 45, 239–244.
Helle, S. S., Duff, S. J. B., & Cooper, D. G. (1993). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 42, 611–617.
Kaar, W. E., & Holtzapple, M. T. (1998). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 59, 419–427.
Kim, S. B., & Chun, J. W. (2004). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 113–116, 1023–1031.
Ooshima, H., Sakata, M., & Harano, Y. (1986). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 28, 1727–1734.
Park, J. W., Takahata, Y., Kajiuchi, T., & Akehata, T. (1992). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 39, 117–120.
Yang, B., & Wyman, C. E. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94, 611–617.
Keating, J. D., Panganiban, C., & Mansfield, S. D. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 93, 1196–1206.
Starcher, B. (2001). Analytical Biochemistry, 292, 125–129.
Tu, M. (2007). In The Faculty of Graduate Studies (p. 195). Vancouver: University of British Columbia.
Tu, M. B., Zhang, X., Kurabi, A., Gilkes, N., Mabee, W., & Saddler, J. (2006). Biotechnological Letters, 28, 151–156.
Demirbas, A. (2005). Energy Sources, 27, 327–337.
Ewanick, S. M., Bura, R., & Saddler, J. N. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 98, 737–746.
Alkasrawi, M., Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (2002). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 98, 849–861.
Wingren, A., Galbe, M., Roslander, C., Rudolf, A., & Zacchi, G. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121, 485–499.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Novozymes North America Inc. for providing the enzymes. The funding was provided by Natural Resources Canada and the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, M., Saddler, J.N. Potential Enzyme Cost Reduction with the Addition of Surfactant during the Hydrolysis of Pretreated Softwood. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 161, 274–287 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8869-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8869-4