Abstract
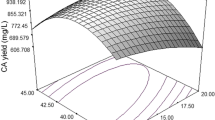
Response surface methodology was used to optimize the fermentation medium for enhancing naringinase production by Staphylococcus xylosus. The first step of this process involved the individual adjustment and optimization of various medium components at shake flask level. Sources of carbon (sucrose) and nitrogen (sodium nitrate), as well as an inducer (naringin) and pH levels were all found to be the important factors significantly affecting naringinase production. In the second step, a 22 full factorial central composite design was applied to determine the optimal levels of each of the significant variables. A second-order polynomial was derived by multiple regression analysis on the experimental data. Using this methodology, the optimum values for the critical components were obtained as follows: sucrose, 10.0%; sodium nitrate, 10.0%; pH 5.6; biomass concentration, 1.58%; and naringin, 0.50% (w/v), respectively. Under optimal conditions, the experimental naringinase production was 8.45 U/mL. The determination coefficients (R 2) were 0.9908 and 0.9950 for naringinase activity and biomass production, respectively, indicating an adequate degree of reliability in the model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puri, M., Marwaha, S. S., & Kothari, R. M. (1996). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 18, 281–285.
Zverlov, V., Hertel, C., Bronnernmeier, K., Hroch, A., Kellermann, J., & Schwarz, W. H. (2000). Molecular Microbiology, 35, 173–179.
Hashimoto, W., Miyake, O., Nankai, H., & Murata, K. (2003). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 415, 235–244.
Birgisson, H., Hreggvidson, G. O., Fridjonsson, O. H., Mort, A. Kristjansson, J. K., & Mattiasson, B. (2004). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 34, 561–571.
Miyata, T., Kashige, N., Satho, T., Yamaguci, T., Aso, Y., & Miake, F. (2005). Current Microbiology, 51, 105–109.
Puri, M., Banerjee, A., & Banerjee, U. C. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 195–201.
Puri, M., Kaur, A., Kanwar, J. R., & Singh, R. S. (2009). Immobilized enzymes for debittering citrus fruit juices. In M. D. Busto & N. Ortega (Eds.), Food enzymes: Application of new technologies (pp. 91–103). India: Transworld Research Network.
Caldini, C. (1994). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 16, 286–291.
Thirkettle, J. (2000). Journal of Antibiotic, 53, 733–735.
Kamiya, S., Esaki, S., & Tanaka, R. (1985). Agriculture and Biological Chemistry, 49, 55–62.
Gonzalez-Barrio, R., Trinidale, L. M., Manzanares, P., deGraaff, L. H., Tomas-Barberan, F. A., & Espin, J. C. (2004). Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 52, 6136–6142.
Gokhale, D. V., Patil, S. G., & Bastawde, K. B. (1991). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 30, 99–109.
Cochran, W. G., & Cox, G. M. (1992). In experimental designs (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley Classics Library.
Balusu, R., Paduru, R. R., Kuravi, S. K., Seenayya, G., & Reddy, G. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 3025–3030.
Rao, Y. K., Lub, S. C., Liub, B., & Tzeng, Y. M. (2006). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 28, 57–66.
Adinarayana, K., & Ellaiah, P. (2002). Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 5, 272–278.
Dutt, K., Gupta, P., Saran, S., Misra, S., & Saxena, R. K. (2009). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. doi:10.1007/s12010-008-8504-9.
Chandel, M., & Azmi, W. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 1840–1846.
Hujanen, M., Linko, S., Linko, Y. Y., & Leisola, M. (2001). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 126–130.
Yu, X., Hallet, S. G., Sheppard, J., & Watson, A. K. (1997). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 47, 301–305.
Lhomme, B., & Roux, J. C. (1991). Bioresource Technology, 35, 301–312.
Montgomery, D. C. (2001). In design and analysis of experiments. New York: Wiley.
Kalil, S. J., Maugeri, F., & Rodrigues, M. I. (2000). Process Biochemistry, 35, 539–550.
Singh, R. S., Singh, H., & Saini, G. K. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. doi:10/1007s12010-008-8180-9.
Mutalik, S. R., Vaidya, B. K., Joshi, R. M., Desai, K. M., & Nene, S. N. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 7875–7880.
Huang, Y., Zheng, H., & Yan, Y. (2009). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. doi:10.1007/s12010-008-8377-y.
Kamble, A., & Banerjee, U. C. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 143–150.
Purama, R. K., & Goel, R. K. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 182–192.
Puri, M., Kaur, A., & Singh, R. S. (2009). A process for the production of bacterial naringinase for debittering of citrus fruit juice. TIFA/2007.
Myers, R. H., & Montgomery, D. C. (2002). Response surface methodology: Process and product optimization using designed experiments (p. 824). New York: Wiley.
Kim, H. M., Kim, J. G., Cho, J. D., & Hong, J. W. (2003). Polymer Testing, 22, 899–906.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for providing financial assistance to carry out this study from a project grant CSIR 38(1133)/07/ EMR-II. Aneet Kaur gratefully acknowledges the award of SRF (Senior Research Fellowship).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puri, M., Kaur, A., Singh, R.S. et al. Response Surface Optimization of Medium Components for Naringinase Production from Staphylococcus xylosus MAK2 . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162, 181–191 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8765-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8765-y