Abstract
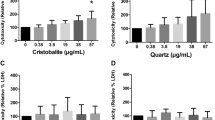
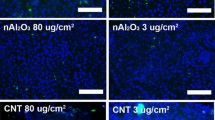
Health risks associated with inhalation and deposition of biological materials have been a topic of great concern due to highly publicized cases of inhalation anthrax, of new regulations on the release of particulate matter, and to increased concerns on the hazards of indoor air pollution. Here, we present an evaluation of the sensitivity of two immortal cell lines (A549, human lung carcinoma epithelia) and NR8383 (rat alveolar macrophages) to a variety of bacterial-derived inhalation hazards and simulants including etoposide, gliotoxin, streptolysin O, and warfarin. The cell response is evaluated through quantification of changes in mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase activity, release of lactate dehydrogenase, initiation of apoptosis, and through changes in morphology as determined by visible light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. These cells display dose–response relations to each toxin, except for triton which has a step change response. The first observable responses of the epithelial cells to these compounds are changes in metabolism for one toxin (warfarin) and alterations in membrane permeability for another (gliotoxin). The other four toxins display a similar time course in response as gauged by changes in metabolism and loss of membrane integrity. Macrophages are more sensitive to most toxins; however, they display a lower level of stability. This information can be used in the design of cell-based sensors responding to these and similar hazards.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stenger, D. A., Gross, G. W., Keefer, E. W., Shaffer, K. M., Andreadis, J. D., Ma, W., & Pancrazio, J. J. (2001). Trends in Biotechnology, 19, 304–310. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(01)01690-0.
DeBusschere, B. D., & Kovacs, G. T. A. (2001). Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 16, 543–556. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(01)00168-3.
Gilchrist, K. H., Barker, V. N., Fletcher, L. E., DeBusschere, B. D., Ghanouni, P., Giovangrandi, L., & Kovacs, G. T. A. (2001). Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 16, 557–564. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(01)00169-5.
Thach, D. C., Shaffer, K. M., Ma, W., & Stenger, D. A. (2003). Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 18, 1065–1072. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00246-4.
Sutton, G. P., Soper, J. T., Park, R. C., & Hatch, K. D. (1991). Gynecologic Oncology, 40, 179. doi:10.1016/0090-8258(91)90161-W.
Grovel, O., Pouchus, Y. F., & Verbist, J.-F. (2003). Toxicon, 42, 297–300. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(03)00146-6.
Boesewetter, D. E., Collier, J. M., Kim, A. M., & Riley, M. R. (2006). Cell Biology and Toxicology, 22, 101–118. doi:10.1007/s10565-006-0150-9.
Palmer, M. (2001). Toxicon, 39, 1681–1689. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00155-6.
Vock, E. H., Lutz, W. K., Hormes, P., Hoffmann, H. D., & Vamvakas, S. (1998). Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 413, 83–94. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(98)00019-9.
Riley, M. R., Boesewetter, D. E., Kim, A. M., & Sirvent, F. P. (2003). Toxicology, 190, 171–185. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00162-8.
Riley, M. R., Boesewetter, D. E., Turner, R. A., Kim, A. M., Collier, J. M., & Hamilton, A. (2005). Toxicology In Vitro, 19, 411–419. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2005.01.001.
Okeson, C. D., Riley, M. R., & Riley-Saxton, E. (2004). Toxicology In Vitro, 18, 673–680. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2004.03.006.
Katterman, M. E., Birchard, S., Seraphin, S., & Riley, M. R. (2007). Chemosphere, 66, 567–573. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.037.
Johnson, D. R., Kaplan, E. L., Sramek, J., Bicova, R., Havlicek, J., Havlickova, H., Motlova, J., & Kriz, P. (1996). Laboratory Diagnosis of Group A Streptococcal Infections. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
Riley, M. R., Jordan, K. A., & Cox, M. L. (2004). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 19, 95–99. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2003.12.003.
Hicks, C. R. (1982). Fundamental concepts in the design of experiments (pp. 38–52, 3rd ed.). New York, NY: Saunders College.
Souid-Mensi, G., Moukha, S., Mobio, T. A., Maaroufi, K., & Creppy, E. E. (2008). Toxicon, 51, 1338–1334. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.03.002.
Davoren, M., Herzog, E., Casey, A., Cottineau, B., Chambers, G., Byrne, H. J., & Lyng, F. M. (2007). Toxicology in Vitro, 21, 438–448. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2006.10.007.
Wallaert, B., Fahy, O., Tsicopoulos, A., Gosset, P., & Tonnel, A. B. (2000). Toxicology Letters, 157, 112–113.
Huang, E.-S., Benson, J. D., Huong, S.-M., Wilson, B., & van der Horst, C. (1992). Antiviral Research, 17, 17–32. doi:10.1016/0166-3542(92)90087-L.
Solovyan, V., Bezvenyuk, Z., Huotari, V., Tapiola, T., Suuronen, T., & Salminen, A. (1998). Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research, 62, 43–55. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(98)00234-4.
Kreja, L., & Seidel, H.-J. (2002). Chemosphere, 49, 105–110. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00159-5.
Eichner, R. D., Waring, P., Geue, A. M., Braithwaite, A. W., & Mullbacher, A. (1988). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 263, 3772–3777.
Waring, P., Newcombe, N., Edel, M., Lin, Q. H., Jiang, H., Sjaarda, A., Piva, T., & Mullbacher, A. (1994). Toxicon, 32, 491–504. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(94)90301-8.
Zhou, X., Zhao, A., Goping, G., & Hirszel, P. (2000). Toxicological Sciences, 54, 194–202. doi:10.1093/toxsci/54.1.194.
Fitzpatrick, F. A., & Wheeler, R. (1999). International Immunopharmacology, 3, 1699–1714. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2003.08.007.
Kreja, L., & Seidel, H.-J. (2002). Chemosphere, 105, 49.
Cullen, P., Tegelkamp, K., Kobker, M., Kannenberg, F., & Assmann, G. (1997). Analytical Biochemistry, 251, 39–44. doi:10.1006/abio.1997.2227.
Bellini, M. J., Polo, M. P., de Alaniz, M. J. T., & de Bravo, M. G. (2003). Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids, 69, 351–357. doi:10.1016/S0952-3278(03)00149-2.
Riley, M. R., DeRosa, D., Blaine, J., Potter Jr, B. G., Lucas, P., Le Coq, D., Juncker, C., Boesewetter, D. E., Collier, J. M., Boussard-Plédel, C., & Bureau, B. (2006). Biotechnology Progress, 22, 24–31. doi:10.1021/bp050125d.
Riley, M. R., Lucas, P., Le Coq, D., Collier, J. M., Boesewetter, D. E., DeRosa, D. M., Katterman, M. E., Boussard-Plédel, C., & Bureau, B. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 95, 599–612. doi:10.1002/bit.21152.
Lucas, P., Le Coq, D., Collier, J. M., Boesewetter, D. E., Boussard-Plédel, C., Bureau, B., & Riley, M. R. (2005). Applied Spectroscopy, 59, 1–9. doi:10.1366/0003702052940387.
Lucas, P., Le Coq, D., Juncker, C., Collier, J. M., Boesewetter, D. E., Boussard-Plédel, C., Bureau, B., & Riley, M. R. (2005). Applied Spectroscopy, 59, 1–9. doi:10.1366/0003702052940387.
Notingher, I., Selvakumaran, J., & Hench, L. L. (2004). Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 20, 780–789. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2004.04.008.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by DARPA contract # N66001-C-8041, by the NIEHS sponsored Southwest Environmental Health Sciences Center # P30 ES06694, and by the Arizona Board of Regents Technology and Research Initiative Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peterson, D.E., Collier, J.M., Katterman, M.E. et al. Cytotoxicity of Bacterial-Derived Toxins to Immortal Lung Epithelial and Macrophage Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 751–763 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8526-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8526-y