Abstract
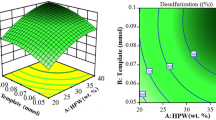
For desulfurization of gasoline, novel chitosan-based molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was prepared by cross-linking chitosan with epichlorohydrin in the presence of dibenzothiophene (DBT) as the template. The influence of cross-linking ratio on the specific adsorption was evaluated. The effects of the types and the amounts of porogen on selectivity of the chitosan MIP were also examined. Results showed that MIP has a higher recognition property to DBT. The maximum rebinding capacities of the MIP reached 22.69 mg g−1 in the model solution. The adsorption behaviors of the MIP including adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic parameters were investigated and the experimental data agreed well with the Langmuir model. The dynamical adsorption behaved in first-order kinetics. Negative values for the Gibbs free energy showed that the adsorptions were spontaneous processes. The MIP was further used to selectively adsorb organosulfur from gasoline.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, T. H., Whang, W. T., Shen, J. Y., et al. (2006). Advanced Functional Materials, 16, 1449–1456. doi:10.1002/adfm.200500823.
Wang, B. H., Yin, J., Xue, M. Z., et al. (2003). Synthetic Metals, 132, 191–195. doi:10.1016/S0379-6779(02)00445-9.
Yang, W., Niu, Y., Liu, C., et al. (2003). Synthetic Metals, 135–136, 183–184. doi:10.1016/S0379-6779(02)00527-1.
EPA, Reducing Non-road Diesel Emissions, US Environmental Protection Agency, April 2003.
Hou, Y. F., Kong, Y., & Yang, J. R. (2005). Fuel, 84, 1975–1979. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2005.04.004.
Babich, I. V., & Moulijn, J. A. (2003). Fuel, 82, 607–631. doi:10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00324-1.
Hernandez-Maldonado, A. J., & Yang, R. T. (2004). Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 43, 1081–1087. doi:10.1021/ie034206v.
Salem, S. H., & Hamid, H. S. (1997). Chemical Engineering & Technology, 20, 342–347. doi:10.1002/ceat.270200511.
Ma, X. L., Velu, S., Kim, J. H., et al. (2005). Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 56, 137–147. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.08.013.
Caro, E., Marcé, R. M., & Peter, A. G. (2004). Journal of Chromatography A, 1047, 175–180.
Hunnius, M., Rufińska, A., & Maier, W. F. (1999). Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 29, 389–403. doi:10.1016/S1387-1811(99)00008-6.
Weetall, H. H., & Rogers, K. R. (2004). Talanta, 62, 329–335. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2003.07.014.
Castro, B., Whitcombe, M. J., & Vulfson, E. N. (2001). Analytica Chimica Acta, 435, 83–90. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(01)00799-1.
Chang, Y. H., Liu, B., & Ying, H. J. (2003). Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 19, 450–456.
Aburto, J., Mendez-Orozco, A., & Borgne, S. L. (2004). Chemical Engineering and Processing, 43, 1587–1595. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2004.02.006.
Wan Ngah, W. S., Ab Ghani, S., & Kamari, A. (2005). Bioresource Technology, 96, 443–450. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.022.
Baroni, P., Vieira, R. S., & Meneghetti, E. (2008). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 1155–1163. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.099.
Varmaa, A. J., Deshpandea, S. V., & Kennedy, J. F. (2004). Carbohydrate Polymers, 55, 77–93. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2003.08.005.
Xia, Y. Q., Guo, T. Y., & Song, M. D. (2008). Reactive & Functional Polymers, 68, 63–69. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.10.018.
Umpleby, R. J., Baxter, S. C., & Bode, M. (2001). Polymers. Analytica Chimica Acta, 435, 35–42. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01211-3.
Wong, Y. C., Szeto, Y. S., & Cheung, W. H. (2003). Langmuir, 19, 7888–7894. doi:10.1021/la030064y.
Velu, S., Watanabe, S., & Ma, X. (2003). American Chemical Society Division of Petroleum Chemistry Preprints, 48, 56–57.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Graduate Student Innovation Project of Jiansu Province (Proj. NO. xm04-45) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program NO.2007CB714305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., Zhang, L., Ying, H. et al. Desulfurization of Gasoline using Molecularly Imprinted Chitosan as Selective Adsorbents. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 593–603 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8441-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8441-7