Abstract
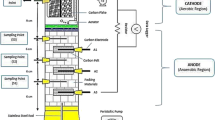
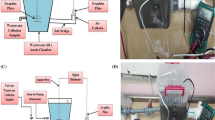
Performance of two microbial fuel cells (MFCs) was investigated under batch and continuous mode of operation using different cathodic electrolyte. The wastewater was supplied from the bottom port provided to the anode chamber in both the MFCs and the effluent left the anode chamber from the top port in MFC-1, whereas in MFC-2, the effluent exit was provided close to membrane. Stainless steel (SS) mesh anode was used in both the MFCs with surface area of 167 and 100 cm2 in MFC-1 and MFC-2, respectively. Under batch mode and continuous mode of operation, these MFCs gave chemical oxygen demand removal efficiency more than 85% and about 68%, respectively. Under batch mode of operation, maximum power density of 39.95 and 56.87 mW/m2 and maximum current density of 180.83 and 295 mA/m2 were obtained in MFC-1 and MFC-2, respectively. Under continuous mode of operation, a reduction in power and current density was observed. Even with less surface area of the anode, MFC-2 produced more current (1.77 mA) than MFC-1 (1.40 mA). Among the cathodic electrolyte tested, these can be listed in decreasing order of power density as aerated KMnO4 solution > KMnO4 solution without aeration > aerated tap water > aerated tap water with NaCl.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabaey, K., & Verstraete, W. (2005). Trends in Biotechnology, 23(6), 291–298.
Zhang, X. C., & Aarme, H. (1995). Biotechnology Letters, 17(8), 809–814.
Angenent, L. T., Karim, K., Al-Dahhan, M. H., Wrenn, B. A., & Domiguez, E. R. (2004). Trends in Biotechnology, 22(9), 477–485.
Jang, J. K., Pham, T. H., Chang, I. S., Kang, K. H., Moon, H., Cho, K. S., & Kim, B. H. (2004). Process Biochemistry, 39, 1007–1012.
Pham, C. A., Jung, S. J., Phung, N. T., Lee, J., Chang, I. S., Kim, B. H., Yi, H., & Chun, J. (2003). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 223, 129–134.
Oh, S., Min, B., & Logan, B. E. (2004). Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 4900–4904.
You, S., Zhao, Q., Zhang, J., Jiang, J., & Zhao, S. (2006). Journal of power sources, 162, 1409–1415.
Cheng, S., Liu, H., & Logan, B. E. (2006). Electrochemistry Communications, 8, 489–494.
Gil, G. C., Chang, I. S., Kim, B. H., Kim, M., Jang, J. K., Park, H. S., & Kim, H. J. (2003). Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 18, 327–334.
Liu, H., & Logan, B. E. (2004). Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 4040–4046.
Kim, B. H., Chang, I. S., & Gadd, G. M. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76, 485–494.
Ghangrekar, M. M., & Shinde, V. B. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 2879–2885.
Ginkel, S. V., Sung, S., & Lay, J. J. (2001). Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 4726–4730.
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1998). Standard Methods for examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Picoreanu, C., Head, I. M., Katuri, K. P., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & Scott, K. (2007). Water Research, 41, 2921–2940.
Tartakovsky, B., & Guiot, S. R. (2006). Biotechnology Progress, 22, 241–246.
Venkata Mohan, S., Saravanan, R., Veer Raghavulu, S., Mohanakrishna, G., & Sarma, P. N. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 596–603.
Zhang, T., Cui, C., Chen, S., Yang, H., & Shen, P. (2008). Electrochemistry Communications, 10, 293–297.
Biffinger, J. C., Byrd, J. N., Dudley, B. L., & Ringeisen, B. R. (2008). Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 23, 820–826.
Liu, H., Cheng, S., & Logan, B. E. (2005). Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 5488–5493.
Pham, T. H., Jang, J. K., Moon, H. S., Chang, I. S., & Kim, D. H. (2005). Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 17, 438–441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jadhav, G.S., Ghangrekar, M.M. Improving Performance of MFC by Design Alteration and Adding Cathodic Electrolytes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151, 319–332 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8195-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8195-2