Abstract
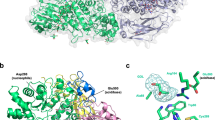
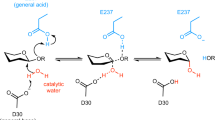
β-d-Xylosidase from Selenomonas ruminantium is revealed as the best catalyst known (k cat, k cat/K m) for promoting hydrolysis of 1,4-β-d-xylooligosaccharides. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance experiments indicate the family 43 glycoside hydrolase acts through an inversion mechanism on substrates 4-nitrophenyl-β-d-xylopyranoside (4NPX) and 1,4-β-d-xylobiose (X2). Progress curves of 4-nitrophenyl-β-d-xylobioside, xylotetraose and xylohexaose reactions indicate that one residue from the nonreducing end of substrate is cleaved per catalytic cycle without processivity. Values of k cat and k cat/K m decrease for xylooligosaccharides longer than X2, illustrating the importance to catalysis of subsites −1 and +1 and the lack there of subsite +2. Homology models of the enzyme active site with docked substrates show that subsites bey ond−1 are blocked by protein and subsites bey ond +1 are not formed; they suggest that D14 and E186 serve catalysis as general base and general acid, respectively. Individual mutations, D14A and E186A, erode k cat and k cat/K m by <103 and to asimilar extent for substrates 4NPX and 4-nitrophenyl-α-l-arabinofuranoside (4NPA), indicating that the two substrates share the same active site. With 4NPX and 4NPA, pH governs k cat/K m with pK a values of 5.0 and 7.0 assigned to D14 and E186, respectively. k cat (4NPX) has a pK a value of 7.0 and k cat (4NPA) is pH independent above pH 4.0, suggesting that the catalytically inactive, “dianionic” enzyme form (D14-E187-) binds 4NPX but not 4NPA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha, B. C. (2003), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 279–291.
Zechel, D. L., and Withers, S. G. (2001), Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 643–649.
Sinnott, M. L. (1990), Chem. Rev. 90, 1171–1202.
Herrmann, M. C., Vrsanska, M., Jurickova, M., Hirsch, J., Biely, P., and Kubicek, C. P. (1997), Biochem. J. 321, 375–381.
Marshall, P. J., and Sinnott, M. L. (1983), Biochem. J. 215, 67–74.
Shallom, D., Leon, M., Bravman, T., Ben-David, A., Zaide, G., Belakhov, V., Shoham, G., Schomburg, D., Baasov, T., and Shoham, Y. (2005), Biochemistry 44, 387–397.
Vocadlo, D. J., Wicki, J., Rupitz, K., and Withers, S. G. (2002), Biochemistry 41, 9727–9735.
Bravman, T., Zolotnitsky, G., Belakhov, V., Shoham, G., Henrissat, B., Baasov, T., and Shoham, Y. (2003), Biochemistry 42, 10,528–10,536.
Lee, R. C., Hrmova, M., Burton, R. A., Lahnstein, J., and Fincher, G. B. (2003), J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5377–5387.
Cotta, M. A. (1993), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 3557–3563.
Williams, A. G., Withers, S. E., and Joblin, K. N. (1991), Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 12, 232–235.
Cotta, M. A., and Whitehead, T. R. (1998), Curr. Microbiol. 36, 183–189.
Whitehead, T. R., and Cotta, M. A. (2001), Curr. Microbiol. 43, 293–298.
Barshop, B. A., Wrenn, R. F., and Frieden, C. (1983), Anal. Biochem. 130, 134–145.
Guex, N., and Peitsch, M. C. (1997), Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723.
Pettersen, E. F., Goddard, T. D., Huang, C. C., Couch, G. S., Greenblatt, D. M., Meng, E. C., and Ferrin, T. E. (2004), J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612.
Sanner, M. F., Olson, A. J., and Spehner, J. C. (1996), Biopolymers 38, 305–320.
Gill, S. C., and von Hippel, P. H. (1989), Anal. Biochem. 182, 319–326.
Kezdy, F. J., and Bender, M. L. (1962), Biochemistry 1, 1097–1106.
Nurizzo, D., Turkenburg, J. P., Charnock, S. J., Roberts, S. M., Dodson, E. J., McKie, V. A., Taylor, E. J., Gilbert, H. J., and Davies, G. J. (2002), Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 665–668.
Davies, G. J., Wilson, K. S., and Henrissat, B. (1997), Biochem. J. 321, 557–559.
Kersters-Hilderson, H., Claeyssens, M., Van Doorslaer, E., and De Bruyne, C. K. (1976), Carbohydr. Res. 47, 269–273.
Braun, C., Meinke, A., Ziser, L., and Withers, S. G. (1993), Anal. Biochem. 212, 259–262.
Van Doorslaer, E., Kersters-Hilderson, H., and De Bruyne, C. K. (1985), Carbohydr. Res. 140, 342–346.
Wagschal, K., Franqui-Espiet, D., Lee, C. C., Robertson, G. H., and Wong, D. W. (2005), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 5318–5323.
Kimura, I., and Tajima, S. (1999), J. Biosci. Bioeng. 87, 572–575.
Wolfenden, R., Lu, X., and Young, G. (1998), J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 6814–6815.
Cleland, W. W. (1982), Methods Enzymol. 87, 390–405.
Ferrer, M., Golyshina, O. V., Chernikova, T. N., Khachane, A. N., Reyes-Duarte, D., Martins Dos Santos, V. A. P., Strompl, C., Elborough, K., Jarvis, G., Neef, A., Yakimov, M. M., Timmis, K. N., and Golyshin, P. N. (2005), Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1996–2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The mention of firm names or trade products does not imply that they are end orsed or recommended by the US Department of Agriculture over other firms or similar products not mentioned.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordan, D.B., Li, XL., Dunlap, C.A. et al. Structure-function relationships of a catalytically efficient β-D-xylosidase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 141, 51–76 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9210-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9210-8