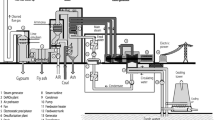
Abstract
Slurry erosion is the surface degradation process occurring due to the mechanical interactions between the solid surface and the particles in the presence of a fluid medium. Due to the slurry erosion, machinery components in the industrial fields (like the hydraulic turbines, slurry pipelines, etc.) conditions undergo severe damage such that the machine parts couldn’t be repaired and should be replaced with the new ones sooner. The present research work described a slurry jet erosion test rig based on the modified venturi devices. Slurry erosion tests were conducted by varying the parameters such as the impingement angle, velocity, concentration, silica sand as the erosive particles with size, and with cast iron as the test coupon. Artificial neural network methodology based on machine learning and artificial intelligence was adopted to identify the dominating parameter among the chosen test parameters. The experimental and the artificial neural networks method results confirmed that the impingement angle was the most significant parameter for causing the material removal amongst the other parameters. Specifically, from the artificial neural network prediction, it was found that the contribution of parameters for erosion prediction was impingement angle (highest) > velocity > concentration > erosive particle size (lowest). It was also reported that with an increase in the velocity the erosion of the test coupon also increased. This investigation may help the materials scientists to accelerate their studies on cast iron material domain.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Kleis, I., Kulu, P.: Solid Particle Erosion: Occurrence, Prediction and Control. Springer Science & Business Media, USA (2007)
Finnie, I.: Erosion of surfaces by solid particles. Wear (1960). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(60)90055-7
Karthik, S., Amarendra, H.J.: Slurry jet erosion test rig: a review of erosive particles induction methods and its test parameters. J. Bio Tribo Corros. 100, 200 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00395-2
Belchamber, R.M.: Process analysis | Acoustic emission. In: Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd edn., pp. 324–331. Elsevier (2005)
Finnie, I.: 1962 Erosion by solid particles in a fluid stream. In: Symposium on Erosion and Cavitation. ASTM International. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP45081S
Gnanavelu, A.B.: A geometry independent integrated method to predict erosion wear rates in a slurry environment. Doctoral dissertation, University of Leeds (2010). https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/4398/
Compton, W.A., Steward, K.P.: Dust erosion of compressor materials: experience and prospects. ASME (1968). https://doi.org/10.1115/68-GT-55
Wood, R.J.K., Wheeler, D.W.: Design and performance of a high velocity air–sand jet impingement erosion facility. Wear (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00196-3
Mann, B.S.: Laser surface treatment of hydro and thermal power plant components and their coatings: a review and recent findings. J. Mater. Eng Perfrom. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1685-9
Wood, R.J.K., Wharton, J.A., Speyer, A.J., Tan, K.S.: Investigation of erosion–corrosion processes using electrochemical noise measurements. Tribol. Int. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(02)00054-3
Clark, H.M.: The influence of the flow field in slurry erosion. Wear (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(92)90122-O
Rajahram, S.S.: Erosion-corrosion mechanisms of stainless steel UNS S31603. Doctoral dissertation, University of Southampton (2010). http://eprints.soton.ac.uk/id/eprint/195255
Winkler, K.: Hydro-abrasive erosion: problems and solutions. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/22/5/052022
Benchaita, M.T.: Erosion of metal pipe by solid particles entrained in a liquid. Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1980). http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/16096
Turenne, S., Fiset, M., Masounave, J.: The effect of sand concentration on the erosion of materials by a slurry jet. Wear (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(89)90116-6
ASTM G76-04 2004 Standard test method for conducting erosion tests by solid particle impingement using gas jets (2004)
Adin, M.Ş: Performances of cryo-treated and untreated cutting tools in machining of AA7075 aerospace aluminium alloy. Eur. Mech. Sci. 7(2), 70–81 (2023). https://doi.org/10.26701/ems.1270937
Grewal, H.S., Agrawal, A., Singh, H.: Design and development of high-velocity slurry erosion test rig using CFD. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0219-y
Zu, J.B., Hutchings, I.M., Burstein, G.T.: Design of a slurry erosion test rig. Wear (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(90)90093-P
Thapa, B.: Sand erosion in hydraulic machinery. Doctoral dissertation, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (2004). http://hdl.handle.net/11250/231204
Karthik, S., Amarendra, H.J., Rokhade, K.K., Prathap, M.S.: Experimental and numerical approach to predict slurry erosion in jet erosion test rig. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2022.105807
Verma, A., Singh, V.K.: Mechanical, microstructural and thermal characterization of epoxy-based human hair–reinforced composites. J. Test. Eval. 47(2), 1193–1215 (2019)
Verma, A., Gaur, A., Singh, V.K.: Mechanical properties and microstructure of starch and sisal fiber biocomposite modified with epoxy resin. Mater. Perform. Charact. 6(1), 500–520 (2017)
Verma, A., Negi, P., Singh, V.K.: Experimental investigation of chicken feather fiber and crumb rubber reformed epoxy resin hybrid composite: mechanical and microstructural characterization. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 27(3–4), 20180014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/jmbm-2018-0014
Verma, A., Joshi, K., Gaur, A., Singh, V.K.: Starch-jute fiber hybrid biocomposite modified with an epoxy resin coating: fabrication and experimental characterization. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 27(5–6), 20182006 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/jmbm-2018-2006
Rastogi, S., Singh, V.K., Verma, A.: Experimental response of nonwoven waste cellulose fabric–reinforced epoxy composites for high toughness and coating applications. Mater. Perform. Charact. 9(1), 151–172 (2020)
Verma, A., Singh, C., Singh, V.K., Jain, N.: Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-coated sisal fiber–Phytagel modified soy protein-based green composite. J. Compos. Mater. 53(18), 2481–2504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319831748
Singh, K., Singh, V.K., Chauhan, S., Jain, N., Verma, A.: Functionalized graphite–reinforced cross-linked poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites for vibration isolator application: morphology, mechanical, and thermal assessment. Mater. Perform. Charact. 9(1), 215–230 (2020)
Bisht, N., Verma, A., Chauhan, S., Singh, V.K.: Effect of functionalized silicon carbide nano-particles as additive in cross-linked PVA based composites for vibration damping application. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 27(4), 920–932 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/vnl.21865
Verma, A., Budiyal, L., Sanjay, M.R., Siengchin, S.: Processing and characterization analysis of pyrolyzed oil rubber (from waste tires)-epoxy polymer blend composite for lightweight structures and coatings applications. Polym. Eng. Sci. 59(10), 2041–2051 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25204
Verma, A., Baurai, K., Sanjay, M.R., Siengchin, S.: Mechanical, microstructural, and thermal characterization insights of pyrolyzed carbon black from waste tires reinforced epoxy nanocomposites for coating application. Polym. Compos. 41(1), 338–349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25373
Chaurasia, A., Verma, A., Parashar, A., Mulik, R.S.: Experimental and computational studies to analyze the effect of h-BN nanosheets on mechanical behavior of h-BN/polyethylene nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(32), 20059–20070 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b05965
Nagaraju, S.B., Sathyanarayana, K., Somashekara, M.K., Pradeep, D.G., Puttegowda, M., Verma, A.: Artificial neural networks for predicting mechanical properties of Al2219-B4C-Gr composites with multireinforcements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062231196038
Agrawal, P.K., Sharma, P., Verma, A., Singh, V.K., Chaudhary, A.K., Chauhan, S.: Impact of graphite particle surface modification on the strengthening of cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol composites: A comprehensive investigation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/14644207231188601
Dogra, V., Kishore, C., Mishra, A., Gaur, A., Verma, A.: Sol-Gel preparation and wetting behaviour analysis of hydrophobic Zirconium based nano-coating: implications for solar panel coating. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 15, 100507 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2023.100507
Arpitha, G.R., Jain, N., Verma, A.: Banana biofiber and glass fiber reinforced hybrid composite for lightweight structural applications: mechanical, thermal, and microstructural characterization. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04300-y
Bousser, E., Martinu, L., Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E.: Solid particle erosion mechanisms of protective coatings for aerospace applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.08.037
ISO 5167-4 2003. Measurement of fluid flow by means of pressure differential devices inserted in circular cross-section conduits running full—Part 4: venturi tubes (2003)
Karthik, S., Amarendra, H.J.: Development of slurry jet erosion test rig–An aid to investigate erosion resistance of materials. Mater. Tod Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.674
Ortega-Rivas, E.: Unit Operations of Particulate Solids: Theory and Practice. CRC Pres, Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton (2011)
Arpitha, G.R., Mohit, H., Madhu, P., Verma, A.: Effect of sugarcane bagasse and alumina reinforcements on physical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics of epoxy composites using artificial neural networks and response surface methodology. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03886-7
Thimmaiah, S.H., Narayanappa, K., Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y., Gulihonenahali Rajakumara, A., Hemath, M., Thiagamani, S.M.K., Verma, A.: An artificial neural network and Taguchi prediction on wear characteristics of Kenaf-Kevlar fabric reinforced hybrid polyester composites. Polym. Compos. 44(1), 261–273 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.27043
Sharma, A., Kumar, S.A., Kushvaha, V.: Effect of aspect ratio on dynamic fracture toughness of particulate polymer composite using artificial neural network. Eng. Fract. Mech. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.106907
Riazi, A., Türker, U.: The drag coefficient and settling velocity of natural sediment particles. Comput. Parct. Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00223-6
Lee-Sullivan, P., Lu, G.: Erosion of impact-notched holes in GFRP composites. Wear (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(94)90200-3
Clark, H.M.: Slurry erosion: macro-and micro-aspects. In: Fundamentals of Tribology and Bridging the Gap Between the Macro-and Micro/Nanoscales. NATO Science Series. Springer (2001)
Handbook, A.S.M.: Friction, Lubrication, and Wear Technology. ASM International, Ohio (2017). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v18.9781627081924
Lin, H.C., Lin, K.M., Chen, Y.S., Yang, C.H.: Ion nitriding of Fe–30Mn–6Si–5Cr shape memory alloy: II. Erosion characteristics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 100, 200 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.05.010
Wood, R.J.K., Puget, Y., Trethewey, K.R., Stokes, K.: The performance of marine coatings and pipe materials under fluid-borne sand erosion. Wear (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00231-2
Manisekaran, T., Kamaraj, M., Sharrif, S.M., Joshi, S.V.: Slurry erosion studies on surface modified 13Cr-4Ni steels: effect of angle of impingement and particle size. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9068-5
Singh, H., Grewal, H.S., Bhandari, S.: Parametric study of slurry-erosion of hydroturbine steels with and without detonation gun spray coatings using taguchi technique. Metall. Mater. Trans. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1148-y
Alqallaf, J., Ali, N., Teixeira, J.A., Addali, A.: Solid particle erosion behaviour and protective coatings for gas turbine compressor blades—A review. Processes (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080984
Sandstrom, M.J.: The solid particle erosion of tungsten carbide in silicon carbide slurry. Master’s thesis, University of Utah, USA (2003). https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/276267034.pdf
Mishra, S., Singal, S.K., Khatod, D.K.: Sizing and quantity estimation for desilting tank of small hydropower projects—An analytical approach. Int. J. Green Energy (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2012.668864
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received from any organization for the submitted work and during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors equally contributed to conceptualization, methodology, writing, reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare by the authors.
Ethical approval
The authors hereby state that the present work is in compliance with the ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karthik, S., Sharath, B.N., Madhu, P. et al. Experimental and artificial neural network-based slurry erosion behavior evaluation of cast iron. Int J Interact Des Manuf (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01618-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-023-01618-9