Abstract
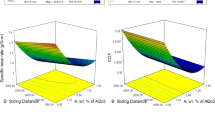
Functionally graded A333/6wt.%B4C/4wt.%ZrO2 hybrid composite manufactured through horizontal-centrifuge casting is subjected to statistical investigation focused on the parametric influences and interactions on wear responses–specific wear rate and coefficient of friction. Taguchi’s L27 orthogonal array design facilitates accurate trend analysis of factors against responses. Mathematical model development using Response Surface Methodology optimizes the wear responses, identifying the most efficient parametric combinations using Analysis of Variance and Signal to Noise ratios. Applied load (10, 30, 50 N), sliding distance (500, 1000, 1500 m) and counter plate hardness (210, 260, 300 HV) are compared to identify the influential hierarchy of factors during pin on plate reciprocating wear tests. The lowest specific wear rate is identified at a combination of 10 N, 500 m, 210 VHN. Whereas, the optimum COF is identified at a combination of 10 N, 500 m, 260 VHN. Quadratic model predicts the wear responses and confirm the closeness (5.2% variance) of predicted values against actual values. The model terms (Load, Distance, Counter plate hardness) of ANOVA with ‘P-value’ less than 0.05 are identified as significant terms. Superior micro-hardness (178.9 ± 1.6 HV) and tensile strength (248.3 ± 2.7 MPa) are observed at the outermost layer (18 mm), which are 35 and 14% higher than the innermost layer (2 mm). Worn surface analysis on the composite specimens identify their corresponding wear mechanisms and counter plate analysis confirm the formation of unstable tribolayer that regulate wear trend.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirane, H., Belarbi, M.O., Houari, M.S.A., Tounsi, A.: On the layerwise finite element formulation for static and free vibration analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates. Eng. Comput. 1, 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01250-1
Shanmugasundaram, A., Arul, S., Sellamuthu, R.: Study on the effect of GTA surface melting and SiC reinforcement on the hardness, wear and corrosion properties of AA 5086. Mater. Today: Proc. 5, 6597–6606 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.315
Oza, M.J., Schell, K.G., Bucharsky, E.C., Laha, T., Roy, S.: Developing a hybrid Al–SiC-graphite functionally graded composite material for optimum composition and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 805, 140625 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140625
Lv, M., Chen, W., Liu, C.: Fabrication and mechanical properties of TiB2/ZrO2 functionally graded ceramics. Int J Refract. Hard Met. 46, 1–5 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.04.019
Bhoi, N.K., Singh, H., Pratap, S.: Developments in the aluminum metal matrix composites reinforced by micro/nano particles–a review. J Compos. Mater. 54, 813–833 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319865307
Islak, S., Abushraida, A.M.: Characterization of functionally graded Bronze matrix ceramic reinforced composite materials. Sakarya J Univ. Sci. 23, 1137–1143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.16984/saufenbilder.574251
Phi, L.T., Nguyen, T.T., Lee, J.: Free vibration of thin-walled open-section beams with functionally graded materials along the contour direction. Thin-Walled Struct. 159, 107146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.107146
Salem, T., Xie, X., Jiao, P., Lajnef, N.: Maneuverable postbuckling of extensible mechanical metamaterials using functionally graded materials and carbon nanotubes. Thin-Walled Struct. 159, 107264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.107264
Vijaya Kumar, P., Jebakani, D., Velmurugan, C., Senthilkumar, V.: Effect of SiC on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of al based functionally graded material. SILICON 14, 1247–1252 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00933-0
Sudhakar, I., Madhu, V., Reddy, G.M., Rao, K.S.: Enhancement of wear and ballistic resistance of armour grade AA7075 aluminium alloy using friction stir processing. Def. Technol. 11, 10–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2014.08.003
Wang, M., Song, B., Wei, Q., Shi, Y.: Improved mechanical properties of AlSi7Mg/nano-SiCp composites fabricated by selective laser melting. J Alloy Compd. 810, 151926 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151926
Saleh, B., Jiang, J., Fathi, R., Xu, Q., Li, Y., Ma, A.: Influence of gradient structure on wear characteristics of centrifugally cast functionally graded magnesium matrix composites for automotive applications. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 21, 1–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00168-1
Manjunath, R., Kumar, D., Kumar, A.: A review on the significance of hybrid particulate reinforcements on the mechanical and tribological properties of stir-casted aluminum metal matrix composites. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 7, 1–1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-021-00558-9
Srivyas, P.D., Charoo, M.S.: Tribological behavior of hybrid aluminum self-lubricating composites under dry sliding conditions at elevated temperature. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces. 16, 153–167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/17515831.2021.1931771
Kumar, T.S., Raghu, R., Shalini, S.: Hardness and wear behavior of al 6061/zrc composite processed by friction stir processing. Tribol. Ind. 42, 582 (2020). https://doi.org/10.24874/ti.855.02.20.10
Manohar, G., Pandey, K.M., Maity, S.R.: Effect of sintering mechanisms on mechanical properties of AA7075/B4C composite fabricated by powder metallurgy techniques. Ceram Int 47, 15147–15154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.073
Bachchhav, B.D., Salunkhe, S., Naranje, V.: Drilling of high volume fraction Al2O3 metal matrix composites. Mater. Perform. Charact. 10, 317–327 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1520/MPC20200053
Nisar, M., Charoo, M.S.: Optimization of fretting wear parameters and effect of high temperature on fretting wear behavior of Al6061 alloy and Al6061-SiC composite. SILICON 14, 3949–3961 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01172-7
Toptan, F., Kerti, I., Rocha, L.A.: Reciprocal dry sliding wear behaviour of B4Cp reinforced aluminium alloy matrix composites. Wear 290, 74–85 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.05.007
Riahi, A.R., Alpas, A.T.: The role of tribo-layers on the sliding wear behavior of graphitic aluminum matrix composites. Wear 251, 1396–1407 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00796-7
Vieira, A.C., Sequeira, P.D., Gomes, J.R., Rocha, L.A.: Dry sliding wear of Al alloy/SiCp functionally graded composites: influence of processing conditions. Wear 267, 585–592 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.01.041
Srinivas, P.N.S., Balakrishna, B.: Microstructural, mechanical and tribological characterization on the Al based functionally graded material fabricated powder metallurgy. Mater. Res. Express 7, 026513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6f41
Sam, M., Radhika, N.: Mechanical and tribological analysis of functionally graded aluminium hybrid composite using RSM approach. Mater. Res. Express 6, 096595 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab3168
Nwobi-Okoye, C.C., Ochieze, B.Q.: Age hardening process modeling and optimization of aluminum alloy A356/Cow horn particulate composite for brake drum application using RSM. ANN Simul. Annealing. Def. Technol. 14, 336–345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2018.04.001
Daniel, S.A.A., Pugazhenthi, R., Kumar, R., Vijayananth, S.: Multi objective prediction and optimization of control parameters in the milling of aluminium hybrid metal matrix composites using ANN and Taguchi-grey relational analysis. Def. Technol. 15, 545–556 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2019.01.001
Dev, S., Aherwar, A., Patnaik, A.: Preliminary evaluations on development of recycled porcelain reinforced LM-26/Al-Si10Cu3Mg1 alloy for piston materials. SILICON 11, 1557–1573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9979-9
Arsha, A.G., Jayakumar, E., Rajan, T.P.D., Antony, V., Pai, B.C.: Design and fabrication of functionally graded in-situ aluminium composites for automotive pistons. Mater. Des. 88, 1201–1209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.09.099
Pawar, S.Y., Kharde, Y.R.: Effect of dual reinforced ceramic particles on elevated temperature tribological properties of hybrid aluminium matrix composites. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 1, 1–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2020.1853495
Elkotb, H.H., Rania Mostafa, A.A., Samad, A., Enab, T.A.: Manufacturing and characterization of functionally graded material automotive piston using centrifugal casting technique. Solid. State Phenomena. 318, 13–24 (2021). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.318.13
Kennedy, A.R., Karantzalis, A.E., Wyatt, S.M.: The microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC and TiB2-reinforced cast metal matrix composites. J Mater. Sci. 34, 933–940 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004519306186
Ambigai, R., Prabhu, S.: Analyzing the mechanical properties and characterization of aluminium (ADC-14) based functionally graded materials (FGM). SILICON 14, 2839–2850 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01050-2
Kumar, S.N., Devarajaiah, R.M., Prabhu, T.R.: Review on aluminium based functionally graded composites. Mater. Today: Proc. 39, 1743–1749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.307
Mohan, N.S., Kulkarni, S.M., Ramachandra, A.: Delamination analysis in drilling process of glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP) composite materials. J Mater. Process Technol. 186, 265–271 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.12.043
Montgomery, D.C.: Design and analysis of experiments, 8th edn. John wiley & sons, New York (2017)
Vettivel, S.C., Selvakumar, N., Narayanasamy, R., Leema, N.: Numerical modelling, prediction of Cu–W nano powder composite in dry sliding wear condition using response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 50, 977–996 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.072
Saravanan, I., Perumal, A.E., Vettivel, S.C., Selvakumar, N., Baradeswaran, A.: Optimizing wear behavior of TiN coated SS 316L against Ti alloy using response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 67, 469–482 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.051
Radhika, N., Raghu, R.: Prediction of mechanical properties and modeling on sliding wear behavior of LM25/TiC composite using response surface methodology. Particul. Sci. Technol. 36, 104–111 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2016.1223773
Sam, M., Jojith, R., Radhika, N.: Progression in manufacturing of functionally graded materials and impact of thermal treatment—A critical review. J Manuf. Process 68, 1339–1377 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.062
Radhika, N., Raghu, R.: Experimental investigation on abrasive wear behavior of functionally graded aluminum composite. J Tribol. 137, 031606 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029941
Karthikeyan, G., Jinu, G.R.: Dry sliding wear behavior optimization of stir cast LM6/ZrO2 composites by response surface methodology analysis. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 40, 351–369 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1139/tcsme-2016-0026
Rajesh, S., Rajakarunakaran, S., Pandian, R.S.: Modeling and optimization of sliding specific wear and coefficient of friction of aluminum based red mud metal matrix composite using taguchi method and response surface methodology. Mater. Phys. Mech. 15, 150–166 (2012)
Jojith, R., Sam, M., Radhika, N.: Recent advances in tribological behavior of functionally graded composites: a review. Int. J Eng. Sci. Technol. 25, 100999 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.05.003
Sam, M., Radhika, N.: Comparative study on reciprocal tribology performance of mono-hybrid ceramic reinforced Al-9Si-3Cu graded composites. Silicon 13, 2671–2687 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00623-x
Funding
This research is funded by Aeronautics Research and Development Board: [Grant Number ARDB/01/2031877/M/1].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors hereby state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare which are relevant to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sam, M., Radhika, N., Ramu, M. et al. Optimizing reciprocal wear responses of centrifugally cast A333 hybrid functionally graded composite using Taguchi and response surface methodology. Int J Interact Des Manuf 17, 1323–1338 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01125-3