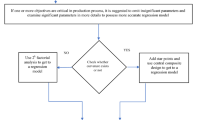
Abstract
3D printing is a process used in many industrial sectors like automobile, aircraft, buildings and several medical fields to fabricate products.Fused deposition modeling is a type of 3D printing processes also known as fused filament manufacturing. Two main response parameters must be considered when using FDM to manufacture parts: Part strength and dimensional accuracy. Though FDM is a popular method for producing complicated geometric products in a less time, it has limitations, including poor mechanical characteristics and dimensional accuracy. An extensive review is carried to know the influence of following process variables on mechanical characteristics such as Thickness of layers, Printing speed, Extrusion Temperature, Infill Density, Infill Patterns, nozzle Diameter, raster Angle, build orientation. It is crucial to choose the best possible combination of process parameters. The FDM process parameters can be optimized using a variety of strategies. As a result, a comprehensive review has been presented on pre-processing to examine the characteristics for printed parts. The two components of study are critical for increasing overall characteristics, i.e., improving functional utility and enriching the uses of FDM printed parts. The current report meant to provide basic assistance and guidance to researchers working on the subject of FDM Process Parameters.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardan, J.: Smart materials in additive manufacturing: state of the art and trends. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 14, 1–18 (2019)
Qader, I., Kök, M., Dagdelen, F., Aydogdu, Y.: A review of smart materials researches and applications. El-Cezeri Fen ve Mühendislik Dergisi 6, 755–788 (2019)
Mustapha, K.B., Metwalli, K.M.: A review of fused deposition modelling for 3D printing of smart polymeric materials and composites. Eur. Polym. J 156, 110591 (2021)
Kumaresan, R., Samykano, M., Kadirgama, K., Harun, W.S.W., Rahman, P.D.M.M.: Fused deposition modeling: process, materials, parameters, properties, and applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08860-7
Wang, Y., Xu, Z., Wu, D., Bai, J.: Current status and prospects of polymer powder 3D printing technologies. Materials 13, 2406 (2020)
Mwema, F.M., Akinlabi, E.T.: Basics of fused deposition modelling (FDM). In: Mwema, F.M., Akinlabi, E.T. (eds.) Fused Deposition Modeling: Strategies for Quality Enhancement, pp. 1–15. Springer, Cham (2020)
Dizon, J.R.C., Gache, C.C.L., Cascolan, H.M.S., Cancino, L.T., Advincula, R.C.: Post-processing of 3D-printed polymers, technologies, p. 9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030061
Cano-Vicent, A., Tambuwala, M.M., Hassan, S.S., Barh, D., Aljabali, A.A.A., Birkett, M., Arjunan, A., Serrano-Aroca, Á.: Fused deposition modelling: Current status, methodology, applications and future prospects. Addit. Manuf. 47, 102378 (2021)
Bardot, M., Schulz, M.D.: Biodegradable poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites for fused deposition modeling 3D printing. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10, 2567 (2020)
Chiulan, I., Frone, A.N., Brandabur, C., Panaitescu, D.M.: Recent advances in 3D printing of aliphatic polyesters. Bioengineering (Basel) 5, 2 (2017)
Wasti, S., Adhikari, S.: Use of biomaterials for 3D printing by fused deposition modeling technique: a review. Front. Chem. 8, 315 (2020)
Peng, A.H., Wang, Z.M.: Researches into influence of process parameters on FDM parts precision. Appl. Mech. Mater. 34–35, 338–343 (2010)
Sood, A.K., Ohdar, R.K., Mahapatra, S.S.: Parametric appraisal of mechanical property of fused deposition modelling processed parts. Mater. Des. 31, 287–295 (2010)
Vishwas, M., Basavaraj, C.K., Vinyas, M.: Experimental investigation using Taguchi method to optimize process parameters of fused deposition modeling for ABS and nylon materials. Mater. Today Proc. 5, 7106–7114 (2018)
Medibew, T.M.: A comprehensive review on the optimization of the fused deposition modeling process parameter for better tensile strength of PLA-printed parts. Hindawi Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 5490831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5490831
Yang, T.-C., Yeh, C.-H.: Morphology and mechanical properties of 3D printed wood fiber/polylactic acid composite parts using fused deposition modeling (FDM): the effects of printing speed. Polymers 12, 1334 (2020)
Sbriglia, L.R., Baker, A.M., Thompson, J.M., Morgan, R.V., Wachtor, A.J., Bernardin, J.D.: Embedding sensors in FDM plastic parts during additive manufacturing. In: Mains, M. (ed.) Topics in Modal Analysis & Testing, vol. 10, pp. 205–214. Springer, Cham (2016)
Kuznetsov, V.E., Solonin, A.N., Tavitov, A., Urzhumtsev, O., Vakulik, A.: Increasing strength of FFF three-dimensional printed parts by influencing on temperature-related parameters of the process. Rapid Prototyp. J. 26, 107–121 (2020)
Coogan, T.J., Kazmer, D.O.: Bond and part strength in fused deposition modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 23, 414–422 (2017)
Wang, L., Gramlich, W.M., Gardner, D.J.: Improving the impact strength of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) in fused layer modeling (FLM). Polymer. 114, 242–248 (2017)
Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Wu, B., Cui, C., Yu, G., Yan, C.: A critical review of 3D printing technology in manufacturing polylactic acid parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 2877–2889 (2019)
Shanmugam, V., Pavan, M.V., Babu, K., Karnan, B.: Fused deposition modeling based polymeric materials and their performance: a review. Polym. Compos. 42, 5656–5677 (2021)
Zhou, X., Hsieh, S.-J., Sun, Y.: Experimental and numerical investigation of the thermal behaviour of polylactic acid during the fused deposition process. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 12, 221–233 (2017)
Vinaykumar, S.V.J., Jatti, S., Patel, A.P., Vijaykumar, S., Jatti,: A study on effect of fused deposition modeling process parameters on mechanical properties. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 8, 689–693 (2019)
Vicente, C.M.S., Martins, T.S., Leite, M., Ribeiro, A., Reis, L.: Influence of fused deposition modeling parameters on the mechanical properties of ABS parts. Polym. Adv. Technol. 31, 501–507 (2020)
Ouballouch, A., alaiji, R.E., Ettaqi, S., Bouayad, A., Sallaou, M., Lasri, L.: Evaluation of dimensional accuracy and mechanical behavior of 3D printed reinforced polyamide parts. Procedia Struct. Integr. 19, 433–441 (2019)
Ramkumar, P.L.: Investigation on the effect of process parameters on impact strength of fused deposition modelling specimens. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 491, 012026 (2019)
Alafaghani, A., Qattawi, A., Alrawi, B., Guzman, A.: Experimental optimization of fused deposition modelling processing parameters: a design-for-manufacturing approach. Procedia Manuf. 10, 791–803 (2017)
Akhoundi, B., Behravesh, A.H.: Effect of filling pattern on the tensile and flexural mechanical properties of FDM 3D printed products. Exp. Mech. 59, 883–897 (2019)
Aloyaydi, B., Sivasankaran, S., Mustafa, A.: Investigation of infill-patterns on mechanical response of 3D printed poly-lactic-acid. Polym. Test. 87, 106557 (2020)
Chadha, A., Ul Haq, M.I., Raina, A., Singh, R.R., Penumarti, N.B., Bishnoi, M.S.: Effect of fused deposition modelling process parameters on mechanical properties of 3D printed parts. World J. Eng. 16, 550–559 (2019)
Ćwikła, G., Grabowik, C., Kalinowski, K., Paprocka, I., Ociepka, P.: The influence of printing parameters on selected mechanical properties of FDM/FFF 3D-printed parts. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 227, 012033 (2017)
Triyono, J., Sukanto, H., Saputra, R.M., Smaradhana, D.F.: The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material. Open Eng. 10, 762–768 (2020)
Al Rashid, A., Abdul Qadir, S., Koç, M.: Microscopic analysis on dimensional capability of fused filament fabrication three-dimensional printing process. J. Elastomers Plast. 54, 385–403 (2021)
Kuznetsov, V.E., Solonin, A.N., Urzhumtsev, O.D., Schilling, R., Tavitov, A.G.: Strength of PLA components fabricated with fused deposition technology using a desktop 3D printer as a function of geometrical parameters of the process. Polymers 10, 313 (2018)
Chung Wang, C., Lin, T.W., Hu, S.S.: Optimizing the rapid prototyping process by integrating the Taguchi method with the Gray relational analysis. Rapid Prototyp. J. 13, 304–315 (2007)
Nidagundi, V.B., Keshavamurthy, R., Prakash, C.P.S.: Studies on parametric optimization for fused deposition modelling process. Mater. Today Proc. 2, 1691–1699 (2015)
Panda, S., Padhee, S., Sood, A.K., Mahapatra, S.: Optimization of fused deposition modelling (FDM) process parameters using bacterial foraging technique. Intell. Inform. Manag. 1, 89–97 (2009)
Ziemian, S., Okwara, M., Ziemian, C.W.: Tensile and fatigue behavior of layered acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. Rapid Prototyp. J. 21, 270–278 (2015)
Zhou, Y.-G., Su, B., Turng, L.: Deposition-induced effects of isotactic polypropylene and polycarbonate composites during fused deposition modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 23, 869–880 (2017)
Raut, S., Jatti, V.S., Khedkar, N.K., Singh, T.P.: Investigation of the effect of built orientation on mechanical properties and total cost of FDM parts. Procedia Mater. Sci. 6, 1625–1630 (2014)
Abdelrhman, A.M., Wei Gan, W., Kurniawan, D.: Effect of part orientation on dimensional accuracy, part strength, and surface quality of three dimensional printed part. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 694, 012048 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, R., Jani, S. & Joshi, A. Review on multi-objective optimization of FDM process parameters for composite materials. Int J Interact Des Manuf 17, 2115–2125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01111-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-01111-9