Abstract
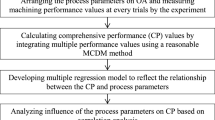
This paper deals with exploring the influences of cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut on material removal rate (MRR) and average surface roughness (Ra) during milling operation of aluminum 1100 alloy work material. The experiments are conducted based on Taguchi’s L8 design plan. It is noticed that MRR increases and Ra deteriorates with higher cutting speed and feed rate. Thus, it becomes imperative to deploy multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) tools to identify the most appropriate combination of the considered milling parameters leading to a compromise solution resulting in higher MRR and lower Ra. Six popular MCDM techniques in the form of weighted sum model, weighted product model, weighted aggregated sum product assessment, multi-objective optimization on the basis of ratio analysis, evaluation based on distance from average solution and technique for order preference by similarity to the ideal solution are employed and comprehensively assessed here to search out the optimal machining condition for the said process. It is revealed that most of the adopted MCDM techniques are successful in identifying the corresponding compromise solution. Excellent values of Spearman’s rank correlation (≥ 0.93) prove high similarities between the ranking patterns derived using the considered MCDM techniques, except weighted sum model. It can be revealed from the detailed analysis that higher MRR can be obtained at an optimal parametric combination of cutting speed = 210 rpm, feed rate = 40 mm/min and depth of cut = 0.4 mm. On the other hand, an optimal parametric intermix of cutting speed = 170 rpm, feed rate = 40 mm/min and depth of cut = 0.4 mm would lead to better surface quality of the machined components.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHP:
-
Analytic Hierarchy Process
- BBD:
-
Box–Behnken Design
- CFRP:
-
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer
- COPRAS:
-
COmplex PRoportional ASsessment
- DOC:
-
Depth of cut
- GFRP:
-
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer
- MABAC:
-
Multi-Attributive Border Approximation area Comparison
- MARICA:
-
Multi-Attributive Real–Ideal Comparative Analysis
- MOORA:
-
Multi-Objective Optimization on the basis of Ratio Analysis
- MRR:
-
Material Removal Rate
- OA:
-
Orthogonal Array
- PIV:
-
Proximity Valued Index
- SECA:
-
Simultaneous Evaluation of Criteria and Alternatives
- TOPSIS:
-
Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution
- WPM:
-
Weighted Product Model
- ARAS:
-
Additive Ratio ASsessment
- CCD:
-
Central Composite Design
- CoCoSo:
-
Combined Compromise Solution
- DFA:
-
Desirability Function Approach
- EDAS:
-
Evaluation based on Distance from Average Solution
- GRA:
-
Grey Relational Analysis
- MARCOS:
-
Measurement Alternatives and Ranking according to COmpromise Solution
- MCDM:
-
Multi-Criteria Decision Making
- MMC:
-
Metal Matrix Composite
- NSGA-II:
-
Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- Ra:
-
Average Surface Roughness
- SWARA:
-
Step-wise Weight Assessment Ratio Analysis
- WASPAS:
-
Weighted Aggregated Sum Product Assessment
- WSM:
-
Weighted Sum Model
- λ :
-
A constant (0 ≤ λ ≤ 1)
- AV j :
-
Average solution for jth criterion
- d j :
-
Degree of diversity for jth criterion
- M :
-
Number of alternatives (experimental trials)
- n ij :
-
Normalized value of xij
- NDA ij :
-
Negative distance from average solution
- NSP :
-
Normalized value of SP
- r ij :
-
Element of weighted normalized decision matrix
- S i − :
-
Distance of ith alternative from the ideal worst solution
- S i WPM :
-
Overall score for WPM method
- SN :
-
Weighted sum of NDA
- w j :
-
Weight of jth criterion
- y i :
-
Overall score for MOORA method
- AS i :
-
Appraisal score for EDAS method
- CC i :
-
Closeness coefficient of ith alternative
- e j :
-
Entropy value for jth criterion
- n :
-
Number of criteria (responses)
- \(n^{\prime}_{ij}\) :
-
Vector normalized value of xij
- NSN :
-
Normalized value of SN
- PDA ij :
-
Positive distance from average solution
- S i + :
-
Distance of ith alternative from the ideal best solution
- S i WASPAS :
-
Overall score for WASPAS method
- S i WSM :
-
Overall score for WSM method
- SP :
-
Weighted sum of PDA
- x ij :
-
Performance measure of ith alternative against jth criterion
References
Chandrasekaran, M., Muralidhar, M., Krishna, C.M., Dixit, U.S.: Application of soft computing techniques in machining performance prediction and optimization: a literature review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 46, 445–464 (2010)
Xu, F., Zhu, J.J., Zang, X.J., Wu, X.: Rapid parameter optimization of high-speed milling aluminum alloy thin-walled workpiece. Key Eng. Mater. 431–432, 41–44 (2010)
Pusavec, F., Kopac, J.: Achieving and implementation of sustainability principles in machining processes. J. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 3(4), 58–69 (2009)
Aruldoss, M., Lakshmi, T.M., Venkatesan, V.R.: A survey on multi criteria decision making methods and its applications. Am. J. Inf. Syst. 1(1), 31–43 (2013)
MacCrimmon, K.R.: Decision making among multiple-attribute alternatives: a survey and consolidated approach. No. RM-4823-ARPA, Rand Corp Santa Monica USA (1968)
Miller, D., Starr, M.: Executive Decisions and Operations Research. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1969)
Zavadskas, E.K., Antucheviciene, J., Saparauskas, J., Turskis, Z.: MCDM methods WASPAS and MULTIMOORA: verification of robustness of methods when assessing alternative solutions. Econom. Comput. Econom. Cybern. Stud. Res. 47(2), 5–20 (2013)
Chakraborty, S.: Applications of the MOORA method for decision making in manufacturing environment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 54, 1155–1166 (2011)
Ghorabaee, M.K., Zavadskas, E.K., Olfat, L., Turskis, Z.: Multi-criteria inventory classification using a new method of evaluation based on distance from average solution (EDAS). Informatica 26, 435–451 (2015)
Hwang, C.-L., Yoon, K.: Methods for multiple attribute decision making. In: Multiple Attribute Decision Making. Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems, pp. 58–191. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-48318-9_3
Yang, L., DeVor, R.E., Kapoor, S.G.: Analysis of force shape characteristics and detection of depth-of-cut variations in end milling. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 127(3), 454–462 (2005)
Zavadskas, E.K., Kaklauskas, A., Turskis, Z., Tamošaitien, J.: Selection of the effective dwelling house walls by applying attributes values determined at intervals. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 14, 85–93 (2008)
Zavadskas, E.K., Turskis, Z.: A new additive ratio assessment (ARAS) method in multicriteria decision-making. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 16(2), 159–172 (2010)
Najiha, M.S., Rahman, M.M., Kadirgama, K.: Experimental investigation and optimization of minimum quantity lubrication for machining of AA6061-T6. Int. J. Autom. Mech. Eng. 11, 2722–2737 (2015)
Gopal, P.M., Soorya Prakash, K.: Minimization of cutting force, temperature and surface roughness through GRA, TOPSIS and Taguchi techniques in end milling of Mg hybrid MMC. Measurement 116, 178–192 (2018)
Parvez, W., Kumar, V.: Multi response optimization using gray relation analysis for milling zirconia ceramic material. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 5(8), 523–528 (2018)
Khan, A.M., Jamil, A.M., Salonitis, K., Sarfraz, S., Zhao, W., He, N., Mia, M., Zhao, G.L.: Multi-objective optimization of energy consumption and surface quality in nanofluid SQCL assisted face milling. Energies 12, 710 (2019)
Yaser, E.K.M., Shunmugesh, K.: Multi-objective optimization of milling process parameters in glass fibre reinforce polymer via grey relational analysis and desirability function. Mater. Today Proc. 11, 1015–1023 (2019)
Singh, O.P., Kumar, G., Kumar, M.: Multi performance optimization of shoulder milling process parameters of AA6063 T6 aluminium alloy by Taguchi based GRA. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 8(10S), 420–425 (2019)
Kumar, J., Verma, R.K.: Experimental investigations and multiple criteria optimization during milling of graphene oxide (GO) doped epoxy/CFRP composites using TOPSIS-AHP hybrid module. FME Trans. 48, 628–635 (2020)
Singh, A., Shivakoti, I., Mustafa, Z., Phipon, R., Sharma, A.: TOPSIS based selection of optimal end milling process parameters. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2273, p. 050071 (2020)
Zeelanbasha, N., Senthil, V., Mahesh, G.: A hybrid approach of NSGA-II and TOPSIS for minimising vibration and surface roughness in machining process. Int. J. Oper. Res. 38(2), 221–254 (2020)
Kumar, M.B., Sathiya, P., Parameshwaran, R.: Parameters optimization for end milling of Al7075-ZrO2-C metal matrix composites using GRA and ANOVA. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 73(11), 2931–2946 (2020)
Cica, D., Caliskan, H., Panjan, P., Kramar, D.: Multi-objective optimization of hard milling using Taguchi based grey relational analysis. Tech. Gaz. 27(2), 513–519 (2020)
Wang, Z., Li, L.: Optimization of process parameters for surface roughness and tool wear in milling TC17 alloy using Taguchi with grey relational analysis. Adv. Mech. Eng. 13(2), 1–8 (2021)
Kumar, R., Katyal, P., Kumar, K., Singh, V.: Multiresponse optimization of end milling process parameters on ZE41A Mg alloy using Taguchi and TOPSIS approach. Mater. Today Proc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.271
Sharma, A., Islam, A., Sharma, K., Singh, P.K.: Optimization techniques to optimize the milling operation with different parameters for composite of AA 3105. Mater. Today Proc. 43, 224–230 (2021)
Nisar, L., Banday, B., Amatullah, M., Farooq, M., Thoker, A.N., Maqbool, A., Wahid, M.A.: An investigation on effect of process parameters on surface roughness and dimensional inaccuracy using grey based Taguchi method. Mater. Today Proc. 46, 6564–6569 (2021)
Trung, D.D.: Application of EDAS, MARCOS, TOPSIS, MOORA and PIV methods for multi-criteria decision making in milling process. J. Mech. Eng. 71(2), 69–84 (2021)
Nguyen, V.C., Nguyen, T.D., Tien, D.H.: Cutting parameter optimization in finishing milling of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy under MQL condition using TOPSIS and ANOVA analysis. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 11(1), 6775–6780 (2021)
Das, P.P., Chakraborty, S.: SWARA-CoCoSo method-based parametric optimization of green dry milling processes. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 69, 35 (2022)
Kumar, G., Goel, P., Kumar, M., Tomer, A., Wahid, M.A.: Role of end-milling process parameters on surface integrity of SS-304: integrated Taguchi-grey approach. Mater. Today Proc. 51, 1141–1146 (2022)
Kacker, R.N., Lagergren, E.S., Filliben, J.J.: Taguchi’s orthogonal arrays are classical designs of experiments. J. Res. Nat. Inst. Stand. Technol. 96(5), 577–591 (1991)
Kuo, Y., Yang, T., Huang, G.-W.: The use of grey relational analysis in solving multiple attribute decision-making problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 55, 80–93 (2008)
Saaty, T.L.: A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 15(3), 234–281 (1977)
Stanujkic, D., Karabasevic, D., Zavadskas, E.K.: A framework for the selection of a packaging design based on the SWARA method. Eng. Econ. 26(2), 181–187 (2015)
Jolliffe, I.T., Cadima, J.: Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. A 374, 20150202 (2016)
Chakraborty, S., Chakraborty, S.: A scoping review on the applications of MCDM techniques for parametric optimization of machining processes. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09731-w
Lukic, D., Cep, R., Vukman, J., Antic, A., Djurdjev, M., Milosevic, M.: Multi-criteria selection of the optimal parameters for high-speed machining of aluminum alloy Al7075 thin-walled parts. Metals 10(12), 1570 (2020)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27, 379–423 (1948)
Hafezalkotob, A., Hafezalkotob, A.: Extended MULTIMOORA method based on Shannon entropy weight for materials selection. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 12, 1–13 (2016)
Kumar, R., Singh, S., Bilga, P.S., Jatin, S.J., Singh, S., Scutaru, M.-L., Pruncu, C.I.: Revealing the benefits of entropy weights method for multi-objective optimization in machining operations: a critical review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 10, 1471–1492 (2021)
Jebaraj, M., Pradeep Kumar, M., Yuvaraj, N., Rahman, G.M.: Experimental study of the influence of the process parameters in the milling of Al6082-T6 alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 34(12), 1411–1427 (2019)
Nguyen, T.-T., Nguyen, T.-A., Trinh, Q.-H.: Optimization of milling parameters for energy savings and surface quality. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 9111–9125 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, K., Madhu, S., Ramachandran, M. et al. Experimental investigation and parametric optimization of a milling process using multi-criteria decision making methods: a comparative analysis. Int J Interact Des Manuf 17, 453–467 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-00973-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-00973-3