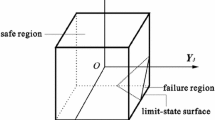
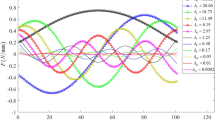
Abstract
Reliability-based design can be used to simultaneously take into account economic aspects as well as safety considerations for various failure probabilities of structures. Such problems have two categories of deterministic and probabilistic constraints. Evaluating the probabilistic constraints and calculating the reliability index, usually require a large number of evaluations of the limit state function. This increases the time and volume of computation; while there is no need to calculate the reliability index for all probable optimal solutions and this index should only be calculated for probable solutions in which deterministic constraints are met. Accordingly, in this study, a two-step approach for optimal design of reliability-based structures is proposed. In this approach, the probabilistic constraint is checked when the deterministic constraint is met; otherwise, the probabilistic constraint is not calculated and the reliability index of zero is considered as a probable solution penalty. In order to investigate the efficiency of this approach, four power transmission lines towers were studied with enhanced colliding bodies optimization (ECBO), water evaporation optimization (WEO), and enhanced vibrating particles system (EVPS). Deterministic and probabilistic constraints defined based on the members’ axial stress and nodal displacement, respectively. Monte-Carlo simulation method was used to evaluate the probabilistic constraints. The results show an appropriate safety margin than the allowable values for the probabilistic constraints.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jimoh, A.A., Rahmon, R., Ajide, S.O.: Reliability-based investigation on compressive strength characteristics of structural-Sized Iroko (Meliceae Excelsa) and Mahogany (Khaya Ivorensis) timber column found in Nigeria. Comput. Eng. Phys. Model. 1(1), 23–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22115/cepm.2018.105453.1002
Zhao, Y.G., Ono, T.: Moment methods for structural reliability. Struct. Saf. 23(1), 47–75 (2001)
Lee, S.H., Kwak, B.M.: Response surface augmented moment method for efficient reliability analysis. Struct. Saf. 28(3), 261–272 (2006)
Keshtegar, B., Chakraborty, S.: A hybrid self-adaptive conjugate first order reliability method for robust structural reliability analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 53, 319–332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.09.017
Meng, Z., Zhou, H., Hu, H., Keshtegar, B.: Enhanced sequential approximate programming using second order reliability method for accurate and efficient structural reliability-based design optimization. Appl. Math. Model. 62, 562–579 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.06.018
Deng, L., Ghosn, M., Shao, S.: Development of a shredding genetic algorithm for structural reliability. Struct. Saf. 27(2), 113–131 (2005)
Elegbede, C.: Structural reliability assessment based on particles swarm optimization. Struct. Saf. 27(2), 171–186 (2005)
Zou, D., Gao, L., Wu, J., Li, S., Li, Y.: A novel global harmony search algorithm for reliability problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 58(2), 307–316 (2010)
Zou, D., Gao, L., Li, S., Wu, J.: An effective global harmony search algorithm for reliability problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(4), 4642–4648 (2011)
Valian, E., Tavakoli, S., Mohanna, S., Haghi, A.: Improved cuckoo search for reliability optimization problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 64(1), 459–468 (2013)
Hoseini Vaez, S.R., Mehanpour, H., Fathali, M.A.: Reliability assessment of truss structures with natural frequency constraints using metaheuristic algorithms. J. Build. Eng. 28, 101065 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.101065
Hosseini, P., Hoseini Vaez, H.R., Fathali, M.A., Mehanpour, H.: Reliability assessment of transmission line towers using metaheuristic algorithms. Int. J. Optim. Civ. Eng. 10(3), 531–551 (2020)
Kaveh, A., Hoseini Vaez, S.R., Hosseini, P., Fathali, M.A.: Heuristic operator for reliability assessment of frame structures. Periodica Polytech. Civ. Eng. 65(3), 702–716 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.17580
Olsson, A., Sandberg, G., Dahlblom, O.: On Latin hypercube sampling for structural reliability analysis. Struct. Saf. 25(1), 47–68 (2003)
Ibrahim, Y.: Observations on applications of importance sampling in structural reliability analysis. Struct. Saf. 9(4), 269–281 (1991)
Miao, F., Ghosn, M.: Modified subset simulation method for reliability analysis of structural systems. Struct. Saf. 33(4–5), 251–260 (2011)
Au, S., Ching, J., Beck, J.: Application of subset simulation methods to reliability benchmark problems. Struct. Saf. 29(3), 183–193 (2007)
Pradlwarter, H., Schuëller, G.: Local domain monte carlo simulation. Struct. Saf. 32(5), 275–280 (2010)
Pradlwarter, H., Schueller, G., Koutsourelakis, P.S., Charmpis, D.C.: Application of line sampling simulation method to reliability benchmark problems. Struct. Saf. 29(3), 208–221 (2007)
Kang, S.-C., Koh, H.-M., Choo, J.F.: An efficient response surface method using moving least squares approximation for structural reliability analysis. Probab. Eng. Mech. 25(4), 365–371 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2010.04.002
Bucher, C.: Asymptotic sampling for high-dimensional reliability analysis. Probab. Eng. Mech. 24(4), 504–510 (2009)
Rashki, M., Miri, M., Moghaddam, M.A.: A new efficient simulation method to approximate the probability of failure and most probable point. Struct. Saf. 39, 22–29 (2012)
Kaveh, A., Dadras, A.: An efficient method for reliability estimation using the combination of asymptotic sampling and weighted simulation. Scientia Iranica 26(4), 2108–2122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2019.21367
Meng, Z., Pang, Y., Zhou, H.: An augmented weighted simulation method for high-dimensional reliability analysis. Struct. Saf. 93, 102117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2021.102117
Nikolaidis, E., Burdisso, R.: Reliability based optimization: a safety index approach. Comput. Struct. 28(6), 781–788 (1988)
Dubourg, V., Sudret, B., Bourinet, J.-M.: Reliability-based design optimization using kriging surrogates and subset simulation. Struct. Multidiscipl. Optim. 44(5), 673–690 (2011)
Chen, Z., Qiu, H., Gao, L., Su, L., Li, P.: An adaptive decoupling approach for reliability-based design optimization. Comput. Struct. 117, 58–66 (2013)
Du, X., Chen, W.: Sequential optimization and reliability assessment method for efficient probabilistic design. J. Mech. Des. 126(2), 225–233 (2004)
Royset, J.O., Der Kiureghian, A., Polak, E.: Reliability-based optimal structural design by the decoupling approach. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 73(3), 213–221 (2001)
Shan, S., Wang, G.G.: Reliable design space and complete single-loop reliability-based design optimization. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 93(8), 1218–1230 (2008)
Chen X, Hasselman T, Neill D (1997) Reliability based structural design optimization for practical applications. In: 38th Structures, structural dynamics, and materials conference, Kissimmee, FL, U.S.A., 1997. p 1403
Schuëller, G.I., Jensen, H.A.: Computational methods in optimization considering uncertainties–an overview. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(1), 2–13 (2008)
Aoues, Y., Chateauneuf, A.: Benchmark study of numerical methods for reliability-based design optimization. Struct. Multidiscipl. Optim. 41(2), 277–294 (2010)
Yang, I.-T., Hsieh, Y.-H.: Reliability-based design optimization with cooperation between support vector machine and particle swarm optimization. Eng. Comput. 29(2), 151–163 (2013)
Hamzehkolaei, N.S., Miri, M., Rashki, M.: An enhanced simulation-based design method coupled with meta-heuristic search algorithm for accurate reliability-based design optimization. Eng. Comput. 32(3), 477–495 (2016)
Shayanfar, M., Abbasnia, R., Khodam, A.: Development of a GA-based method for reliability-based optimization of structures with discrete and continuous design variables using OpenSees and Tcl. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 90, 61–73 (2014)
Mathakari, S., Gardoni, P., Agarwal, P., Raich, A., Haukaas, T.: Reliability-based optimal design of electrical transmission towers using multi-objective genetic algorithms. Comput. Aid. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 22(4), 282–292 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8667.2007.00485.x
Nowak, A.S., Collins, K.R.: Reliability of structures, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA (2012)
Kaveh, A., Ilchi Ghazaan, M.: Enhanced colliding bodies optimization for design problems with continuous and discrete variables. Adv. Eng. Softw. 77, 66–75 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2014.08.003
Kaveh, A., Mahdavi, V.R.: Colliding bodies optimization: a novel meta-heuristic method. Comput. Struct. 139, 18–27 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.04.005
Kaveh, A., Bakhshpoori, T.: Water evaporation optimization: a novel physically inspired optimization algorithm. Comput. Struct. 167, 69–85 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2016.01.008
Wang, S., Tu, Y., Wan, R., Fang, H.: Evaporation of tiny water aggregation on solid surfaces with different wetting properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 116(47), 13863–13867 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp302142s
Kaveh, A., Hoseini Vaez, S.R., Hosseini, P.: Enhanced vibrating particles system algorithm for damage identification of truss structures. Scientia Iranica 26(1), 246–256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2017.4265
Kaveh, A., Ilchi Ghazaan, M.: A new meta-heuristic algorithm: vibrating particles system. Scientia Iranica 24(2), 551–566 (2017). https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2017.2417
Tejani, G.G., Pholdee, N., Bureerat, S., Prayogo, D.: Multiobjective adaptive symbiotic organisms search for truss optimization problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 161, 398–414 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.005
Degertekin, S.O., Lamberti, L., Ugur, I.B.: Discrete sizing/layout/topology optimization of truss structures with an advanced Jaya algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 79, 363–390 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.03.058
Kaveh, A., Dadras, A., Montazeran, A.H.: Chaotic enhanced colliding bodies algorithms for size optimization of truss structures. Acta Mech. 229(7), 2883–2907 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2149-8
Tejani, G.G., Pholdee, N., Bureerat, S., Prayogo, D., Gandomi, A.H.: Structural optimization using multi-objective modified adaptive symbiotic organisms search. Expert Syst. Appl. 125, 425–441 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.01.068
Li, L.J., Huang, Z.B., Liu, F.: A heuristic particle swarm optimization method for truss structures with discrete variables. Comput. Struct. 87(7), 435–443 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.01.004
Erbatur, F., Hasançebi, O., Tütüncü, İ, Kılıç, H.: Optimal design of planar and space structures with genetic algorithms. Comput. Struct. 75(2), 209–224 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(99)00084-X
Mortazavi, A., Toğan, V.: Simultaneous size, shape, and topology optimization of truss structures using integrated particle swarm optimizer. Struct. Multidiscipl. Optim. 54(4), 715–736 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1449-7
Degertekin, S.O., Lamberti, L., Ugur, I.B.: Sizing, layout and topology design optimization of truss structures using the Jaya algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 70, 903–928 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.10.001
Panagant, N., Bureerat, S.: Truss topology, shape and sizing optimization by fully stressed design based on hybrid grey wolf optimization and adaptive differential evolution. Eng. Optim. 50(10), 1645–1661 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2017.1417400
Ahrari, A., Atai, A.A., Deb, K.: Simultaneous topology, shape and size optimization of truss structures by fully stressed design based on evolution strategy. Eng. Optim. 47(8), 1063–1084 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2014.947972
Husseinzadeh Kashan, A., Jalili, S., Karimiyan, S.: Premier league championship algorithm: a multi-population-based algorithm and its application on structural design optimization. In: Kulkarni, A.J., Singh, P.K., Satapathy, S.C., Husseinzadeh Kashan, A., Tai, K. (eds.) Socio-cultural inspired metaheuristics, pp. 215–240. Springer, Singapore (2019)
Kaveh, A., Mahdavi, V.R.: Colliding bodies optimization method for optimum discrete design of truss structures. Comput. Struct. 139, 43–53 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.04.006
Lee, K.S., Geem, Z.W., Lee, S.-h, Bae, K.-w: The harmony search heuristic algorithm for discrete structural optimization. Eng. Optim. 37(7), 663–684 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150500211895
Jalili, S., Husseinzadeh Kashan, A.: Optimum discrete design of steel tower structures using optics inspired optimization method. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 27(9), e1466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.1466
Do, D.T.T., Lee, J.: A modified symbiotic organisms search (mSOS) algorithm for optimization of pin-jointed structures. Appl. Soft Comput. 61, 683–699 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.08.002
Ho-Huu, V., Hartjes, S., Visser, H.G., Curran, R.: An improved MOEA/D algorithm for bi-objective optimization problems with complex Pareto fronts and its application to structural optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 92, 430–446 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.051
Ho-Huu, V., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Vo-Duy, T., Nguyen-Trang, T.: An adaptive elitist differential evolution for optimization of truss structures with discrete design variables. Comput. Struct. 165, 59–75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.11.014
Barbosa, H.J.C., Lemonge, A.C.C., Borges, C.C.H.: A genetic algorithm encoding for cardinality constraints and automatic variable linking in structural optimization. Eng. Struct. 30(12), 3708–3723 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.06.014
Groenwold, A.A., Stander, N.: Optimal discrete sizing of truss structures subject to buckling constraints. Struct. Optim. 14(2), 71–80 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01812508
Kaveh, A., Shojaee, S.: Optimal design of skeletal structures using ant colony optimization. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 70(5), 563–581 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1898
Saka, M.P.: Optimum design of pin-jointed steel structures with practical application. J. Struct. Eng. 116(10), 2599–2620 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1990)116:10(2599)
Toğan, V., Daloğlu, A.T.: Optimization of 3d trusses with adaptive approach in genetic algorithms. Eng. Struct. 28(7), 1019–1027 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2005.11.007
Toğan, V., Daloğlu, A.T.: An improved genetic algorithm with initial population strategy and self-adaptive member grouping. Comput. Struct. 86(11), 1204–1218 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2007.11.006
AISC-ASD (1989) Manual of steel construction-Allowable stress design. 9th edn. American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), Chicago, IL, USA
Kaveh, A., Ghazaan, M.I.: Optimal design of steel lattice transmission line towers. In: Ghazaan, M.I., Kaveh, A. (eds.) Meta-heuristic algorithms for optimal design of real-size structures, pp. 123–137. Springer, Cham (2018)
Kaveh, A., Ilchi Ghazaan, M.: A comparative study of CBO and ECBO for optimal design of skeletal structures. Comput. Struct. 153, 137–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.02.028
Fathali, M.A., Hoseini Vaez, S.R.: Optimum performance-based design of eccentrically braced frames. Eng. Struct. 202, 109857 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109857
Kaveh, A., Eslamlou, A.D.: Optimal design of steel curved roof frames by enhanced vibrating particles system algorithm. In: Kaveh, A., Eslamlou, A.D. (eds.) Metaheuristic optimization algorithms in civil engineering: new applications, pp. 73–97. Springer, Cham (2020)
Kaveh, A., Izadifard, R.A., Mottaghi, L.: Optimal design of planar RC frames considering CO2 emissions using ECBO, EVPS and PSO metaheuristic algorithms. J. Build. Eng. 28, 101014 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.101014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoseini Vaez, S.R., Fathali, M.A. & Mehanpour, H. A two-step approach for reliability-based design optimization in power transmission line towers. Int J Interact Des Manuf 16, 1015–1039 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-00838-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-022-00838-9