Abstract
Background
Although morphometric hip parameters measured on radiographs are valuable tools guiding diagnosis and therapy in patients with hip disorders, some clinicians use MRI for such measurements, although it is unclear whether the parameters assessed on MRI differ from those assessed on radiographs.
Questions/purposes
We asked whether the lateral center-edge angle (LCE), Tönnis angle, extrusion index, and anterior center-edge angle (ACE) are similar on MRI and radiography.
Methods
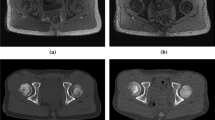
We retrospectively reviewed the imaging data of 103 hips from 103 patients: 46 with femoroacetabular impingement and 57 with hip dysplasia. We manually measured the LCE, Tönnis angle, extrusion index, and ACE from radiographs and MRI in all 103 hips. Four straight coronal (Ant-10 mm, Ant-5 mm, Center, and Post-5 mm), three straight sagittal (S-Med-5 mm, S-Center, S-Lat-5 mm), and three 25º oblique sagittal (OS-Med-5 mm, OS-Center, OS-Lat-5 mm) reformats were reconstructed from a three-dimensional isotropic morphologic MRI sequence. MRI measurements were compared against the gold standard radiographic measurements.
Results
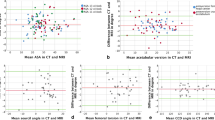
We found good agreement for the LCE angle, Tönnis angle, and extrusion index between radiographic and coronal slice MRI measurements. The mean differences between radiographic and MRI measurements were 5º or less or 5% or less (for the extrusion index) in all coronal MRI slices. However, the differences between ACE angles on sagittal MRI slices and radiographs ranged from 5° to 28º.
Conclusions
LCE, Tönnis angle, and extrusion index can be measured on MRI with comparable results to radiography. The ACE angle on radiographs cannot be estimated reliably from MRI.
Clinical Relevance
MRI provides similar morphometric measurements as radiography for most hip parameters, except for the ACE angle.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LA, Gililland J, Pelt C, Linford S, Stoddard GJ, Peters CL. Center edge angle measurement for hip preservation surgery: technique and caveats. Orthopedics. 2011;34:86.
Beaule PE, Allen DJ, Clohisy JC, Schoenecker PL, Leunig M. The young adult with hip impingement: deciding on the optimal intervention. Instr Course Lect. 2009;58:213–222.
Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:1012–1018.
Chosa E, Tajima N. Anterior acetabular head index of the hip on false-profile views: new index of anterior acetabular cover. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85:826–829.
Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Beaule PE, Kim YJ, Trousdale RT, Sierra RJ, Leunig M, Schoenecker PL, Millis MB. A systematic approach to the plain radiographic evaluation of the young adult hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(suppl 4):47–66.
Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Trousdale R, Kim YJ, Beaule PE, Morgan P, Steger-May K, Schoenecker PL, Millis M. Radiographic evaluation of the hip has limited reliability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:666–675.
Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;175:79–85.
Crockarell JR Jr, Trousdale RT, Guyton JL. The anterior centre-edge angle: a cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82:532–534.
Delaunay S, Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Alford BA. Radiographic measurements of dysplastic adult hips. Skeletal Radiol. 1997;26:75–81.
Domayer SE, Ziebarth K, Chan J, Bixby S, Mamisch TC, Kim YJ. Femoroacetabular cam-type impingement: diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of radiographic views compared to radial MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:805–810.
Fowkes LA, Petridou E, Zagorski C, Karuppiah A, Toms AP. Defining a reference range of acetabular inclination and center-edge angle of the hip in asymptomatic individuals. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:1427–1434.
Fujii M, Nakashima Y, Yamamoto T, Mawatari T, Motomura G, Matsushita A, Matsuda S, Jingushi S, Iwamoto Y. Acetabular retroversion in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:895–903.
Ganz R, Leunig M, Leunig-Ganz K, Harris WH. The etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip: an integrated mechanical concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:264–272.
Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Notzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417:112–120.
Ito K, Minka MA 2nd, Leunig M, Werlen S, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect: a MRI-based quantitative anatomical study of the femoral head-neck offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:171–176.
Jamali AA, Mladenov K, Meyer DC, Martinez A, Beck M, Ganz R, Leunig M. Anteroposterior pelvic radiographs to assess acetabular retroversion: high validity of the “cross-over-sign”. J Orthop Res. 2007;25:758–765.
Jessel RH, Zurakowski D, Zilkens C, Burstein D, Gray ML, Kim YJ. Radiographic and patient factors associated with pre-radiographic osteoarthritis in hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1120–1129.
Kappe T, Kocak T, Reichel H, Fraitzl CR. Can femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia be distinguished by clinical presentation and patient history? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20:387–392.
Kim YJ, Bixby S, Mamisch TC, Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC. Imaging structural abnormalities in the hip joint: instability and impingement as a cause of osteoarthritis. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2008;12:334–345.
Lequesne M. [Coxometry: measurement of the basic angles of the adult radiographic hip by a combined protractor][in French]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1963;30:479–485.
Lequesne M, de Seze S. [False profile of the pelvis: a new radiographic incidence for the study of the hip. Its use in dysplasias and different coxopathies][in French]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1961;28:643–652.
Leunig M, Ganz R. [The Bernese method of periacetabular osteotomy][in German]. Orthopade. 1998;27:743–750.
Leunig M, Huff TW, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement: treatment of the acetabular side. Instr Course Lect. 2009;58:223–229.
Li PL, Ganz R. Morphologic features of congenital acetabular dysplasia: one in six is retroverted. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;416:245–253.
Locher S, Werlen S, Leunig M, Ganz R. [Inadequate detectability of early stages of coxarthrosis with conventional roentgen images][in German]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2001;139:70–74.
Mast JW, Brunner RL, Zebrack J. Recognizing acetabular version in the radiographic presentation of hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;418:48–53.
Mast NH, Impellizzeri F, Keller S, Leunig M. Reliability and agreement of measures used in radiographic evaluation of the adult hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:188–199.
Mose K. Methods of measuring in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease with special regard to the prognosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;150:103–109.
Nelitz M, Guenther KP, Gunkel S, Puhl W. Reliability of radiological measurements in the assessment of hip dysplasia in adults. Br J Radiol. 1999;72:331–334.
Reynolds D, Lucas J, Klaue K. Retroversion of the acetabulum: a cause of hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:281–288.
Sakai T, Nishii T, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H, Sugano N. Is vertical-center-anterior angle equivalent to anterior coverage of the hip? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:2865–2871.
Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE. [Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis–what the radiologist should know][in Spanish]. Radiologia. 2008;50:271–284.
Toennis D. [On changes in the acetabular vault angle of the hip joint in rotated and tilted positions of the pelvis in children][in German]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1962;96:462–478.
Treguier C, Chapuis M, Branger B, Grellier A, Chouklati K, Bruneau B, Fraisse B, Violas P, Pladys P, Darnault P, Gandon Y. [Developmental dysplasia of the hip][in French]. J Radiol. 2011;92:481–493.
Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint. Acta Chir Scand 1939. 1939;58:5–135.
Acknowledgments
We thank Catherine Stamoulis PhD, for help with the statistics and Kerri Murray and Jeffrey Tsang for help with database research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The institution of one of the authors (Y-JK) received research funding from Siemens Healthcare and the Orthopaedic Research and Education Foundation.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved or waived approval for the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Stelzeneder, D., Hingsammer, A., Bixby, S.D. et al. Can Radiographic Morphometric Parameters for the Hip Be Assessed on MRI?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471, 989–999 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2654-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2654-3