Abstract
Background
Treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures includes internal fixation and arthroplasty. However, whether arthroplasty or internal fixation is the primary treatment for displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients remains a subject for debate. The literature contains conflicting evidence regarding rates of mortality, revision surgery, major postoperative complications, and function in elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fractures treated either by internal fixation or arthroplasty (either hemiarthroplasty or THA).
Questions/purpose
We determined mortality, revision surgery rates, major surgical complications (which include infection, nonunion or early redisplacement, avascular necrosis, dislocation, loosening of the prosthesis, acetabular erosion, fracture below or around the implant, and other severe general complications such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism), and function in patients treated with either internal fixation or arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly.
Methods
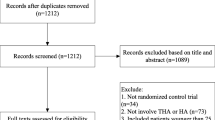
We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing internal fixation and arthroplasty. We identified 20 RCTs with 4508 patients meeting all the criteria for eligibility. We performed a meta-analysis of the major complications, reoperations, function, pain, and mortality.
Results
Compared with internal fixation, arthroplasty reduced the risk of the major complications (95% CI, 0.21–0.54 for 1 year; 95% CI, 0.16–0.31 for 5 years) and the incidence of reoperation 1 to 5 years after surgery (95% CI, 0.15–0.34 for 1 year; 95% CI, 0.08–0.24 for 5 years), and provided better pain relief (95% CI, 0.34–0.72). Function was superior (RR = 0.59; 95% CI, 0.44–0.79) for patients treated with arthroplasty than for patients treated by internal fixation. However, mortality 1 to 3 years after surgery was similar (95% CI, 0.96–1.23, p = 0.20 for 1 year; 95% CI, 0.91–1.17, p = 0.63 for 3 years).
Conclusions
Arthroplasty can reduce the risk of major complications and the incidence of reoperation compared with internal fixation, and provide better pain relief and function, but it does not reduce mortality.
Level of Evidence
Level II, prognostic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry DJ, von Knoch M, Schleck CD, Harmsen WS. Effect of femoral head diameter and operative approach on risk of dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:2456–2463.
Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Swiontkowski MF, Tornetta P 3rd, Obremskey W, Koval KJ, Nork S, Sprague S, Schemitsch EH, Guyatt GH. Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1673–1681.
Bjorgul K, Reikeras O. Hemiarthroplasty in worst cases is better than internal fixation in best cases of displaced femoral neck fractures: a prospective study of 683 patients treated with hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:368–374.
Cummings SR, Melton LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 2002;359:1761–1767.
Davison JN, Calder SJ, Anderson GH, Ward G, Jagger C, Harper WM, Gregg PJ. Treatment for displaced intracapsular fracture of the proximal femur: a prospective randomised trial in patients aged 65 to 79 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:206–212.
Frihagen F, Nordsletten L, Madsen JE. Hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation for intracapsular displaced femoral neck fractures: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2007;335:1251–1254.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ; GRADE Working Group. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336:924–926.
Hedlund R, Lindgren U, Ahlbom A. Age- and sex-specific incidence of femoral neck and trochanteric fractures: an analysis based on 20,538 fractures in Stockholm County, Sweden, 1972–1981. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;222:132–139.
Heetveld MJ, Raaymakers EL, Luitse JS, Nijhof M, Gouma DJ. Femoral neck fractures: can physiologic status determine treatment choice? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:203–212.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560.
Hudson JI, Kenzora JE, Hebel JR, Gardner JF, Scherlis L, Epstein RS, Magaziner JS. Eight-year outcome associated with clinical options in the management of femoral neck fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;348:59–66.
Johansson T, Jacobsson SA, Ivarsson I, Knutsson A, Wahlström O. Internal fixation versus total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a prospective randomized study of 100 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:597–602.
Jónsson B, Sernbo I, Carlsson A, Fredin H, Johnell O. Social function after cervical hip fracture: a comparison of hook-pins and total hip replacement in 47 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67:431–434.
Jüni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Systematic reviews in health care: assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001;323:42–46.
Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF. Randomized comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty: treatment of displaced intracapsular hip fractures in healthy older people. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:249–260.
Leonardsson O, Sernbo I, Carlsson A, Akesson K, Rogmark C. Long-term follow-up of replacement compared with internal fixation for displaced femoral neck fractures: results at ten years in a randomised study of 450 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92:406–412.
Lu-Yao GL, Keller RB, Littenberg B, Wennberg JE. Outcomes after displaced fractures of the femoral neck: a meta analysis of one hundred and six published reports. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:15–25.
Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: the Barthel index. Md State Med J. 1965;14:61–65.
Neander G, Adolphson P, Von Sivers K, Dahlborn M, Dalén N. Bone and muscle mass after femoral neck fracture: a controlled quantitative computed tomography study of osteosynthesis versus primary total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997;116:470–474.
Parker M, Johansen A. Hip fracture. BMJ. 2006;333:27–30.
Parker MJ, Khan RJ, Crawford J, Pryor GA. Hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly: a randomized trial of 455 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:1150–1155.
Puolakka TJ, Laine HJ, Tarvainen T, Aho H. Thompson hemiarthroplasty is superior to Ullevaal screws in treating displaced femoral neck fractures in patient over 75 years: a prospective randomized study with two-year follow-up. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 2001;90:225–228.
Ravikumar KJ, Marsh G. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced subcapital fractures of femur: 13 year results of a prospective randomised study. Injury. 2000;31:793–797.
Rödén M, Schön M, Fredin H. Treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized minimum 5-year follow-up study of screws and bipolar hemiprostheses in l00 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:42–44.
Rogmark C, Carlsson A, Johnell O, Sernbo I. A prospective randomised trial of internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the neck of the femur: functional outcome for 450 patients at two years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:183–188.
Rogmark C, Johnell O. Primary arthroplasty is better than internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures: a meta-analysis of 14 randomized studies with 2,289 patients. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:359–367.
Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA. 1995;273:408–412.
Shepherd SM, Prescott RJ. Use of standardised assessment scales in elderly hip fracture patients. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1996;30:335–343.
Sierra RJ, Raposo JM, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME. Dislocation of primary THA done through a posterolateral approach in the elderly. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:262–267.
Sikorski JM, Barrington R. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for the displaced subcapital fracture of the femur: a prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63:357–361.
Skinner P, Riley D, Ellery J, Beaumont A, Coumine R, Shafighian B. Displaced subcapital fractures of the femur: a prospective randomized comparison of internal fixation, hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement. Injury. 1989;20:291–293.
Söderman P, Malchau H. Is the Harris hip score system useful to study the outcome of total hip replacement? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;384:189–197.
Söreide O, Mölster A, Raugstad TS. Internal fixation versus primary prosthetic replacement in acute femoral neck fractures: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Br J Surg. 1979;66:56–60.
Svenningsen S, Benum P, Nesse O, Furset OI. [Femoral neck fractures in the elderly: a comparison of 3 methods of treatment] [in Norwegian]. Nord Med. 1985;100:256–259.
The EuroQol Group. EuroQol: a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. The EuroQol Group. Health Policy. 1990;16:199–208.
Thomsen NO, Jensen CM, Skovgaard N, Pedersen MS, Pallesen P, Soe-Nielsen NH, Rosenklint A. Observer variation in the radiographic classification of fractures of the neck of the femur using Garden’s system. Int Orthop. 1996;20:326–329.
Tidermark J, Ponzer S, Svensson O, Söderqvist A, Törnkvist H. Internal fixation compared with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly: a randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85:380–388.
van Vugt AB, Oosterwijk WM, Goris RJ. Osteosynthesis versus endoprosthesis in the treatment of unstable intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly: a randomised clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993;113:39–45.
Wang J, Jiang B, Marshall RJ, Zhang P. Arthroplasty or internal fixation for displaced femoral neck fractures: which is the optimal alternative for elderly patients? A meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2009;33:1179–1187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of their immediate family, has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research neither advocates nor endorses the use of any treatment, drug or device. Readers are encouraged to always seek additional information, including FDA-approval status, of any drug or device prior to clinical use.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Liu, Z., Xing, D. et al. Which is the Best Alternative for Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly?: A Meta-Analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470, 1782–1791 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2250-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2250-6