Abstract
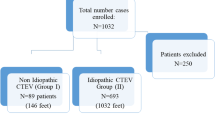
Although the Ponseti method has been effective in patients up to 2 years old, limited information is available on the use of this method in older patients. We retrospectively reviewed the records of 171 patients (260 feet) to determine whether initial correction of the deformity (a plantigrade foot) could be achieved using the Ponseti method in untreated idiopathic clubfeet in patients presenting between the ages of 1 and 6 years. A mean of seven casts was required, and there were no differences in the number of casts between the different age groups. Two hundred fifty (95%) of the 260 feet were treated surgically for residual equinus after a plateau in casting, and procedures included percutaneous tendo-Achilles release (n = 205 [79%]), open tendo-Achilles lengthening (n = 8 [3%]), posterior release (n = 21 [8%]), and extensive soft tissue release (posteromedial release, n = 16 [6%]). The mean dorsiflexion after removal of the last cast was 12.5° for the entire group and was greater in 1 year olds compared with 3 year olds. Although all patients achieved a plantigrade foot, the importance of the mild loss of passive dorsiflexion remains to be determined. An extensive soft tissue release was avoided in 94% of patients using the Ponseti method. We intend a followup study to ascertain whether the correction is maintained.
Level of Evidence: Level III, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bor N, Herzenberg JE, Frick SL. Ponseti management of clubfoot in older infants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;444:224–228.
Chotel F, Parot R, Durand JM, Garnier E, Hodgkinson I, Bérard J. Initial management of congenital varus equinus clubfoot by Ponseti’s method [in French]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2002;88:710–717.
Colburn M, Williams M. Evaluation of the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot using the Ponseti method. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003;42:259–267.
Cooper DM, Dietz FR. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. A thirty-year follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1477–1489.
Dobbs MB, Nunley R, Schoenecker PL. Long-term follow-up of patients with clubfeet treated with extensive soft-tissue release. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:986–996.
Dobbs MB, Rudzki JR, Purcell DB, Walton T, Porter KR, Gurnett CA. Factors predictive of outcome after use of the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfeet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:22–27.
Dyer PJ, Davis N. The role of the Pirani scoring system in the management of club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1082–1084.
Eberhardt O, Schelling K, Parsch K, Wirth T. Treatment of congenital clubfoot with the Ponseti method. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2006;144:497–501.
Garg S, Dobbs MB. Use of the Ponseti method for recurrent clubfoot following posteromedial release. Indian J Orthop. 2008;42:68–72.
Goksan SB. Treatment of congenital clubfoot with the Ponseti method. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2002;36:281–287.
Goksan SB, Bursali A, Bilgili F, Sivacioglu S, Ayanoglu S. Ponseti technique for the correction of idiopathic clubfeet presenting up to 1 year of age. A preliminary study in children with untreated or complex deformities. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126:15–21.
Gupta A, Singh S, Patel P, Patel J, Varshney MK. Evaluation of the utility of the Ponseti method of correction of clubfoot deformity in a developing nation. Int Orthop. 2008;32:75–79.
Herzenberg JE, Radler C, Bor N. Ponseti versus traditional methods of casting for idiopathic clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22:517–521.
Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C. Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1286–1294.
Kite JH. Some suggestions on the treatment of clubfoot by casts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1963;45:406–412.
Laaveg SJ, Ponseti IV. Long-term results of treatment of congenital club foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62:23–31.
Lourenco AF, Morcuende JA. Correction of neglected idiopathic club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:378–381.
Morcuende JA, Abbasi D, Dolan LA, Ponseti IV. Results of an accelerated Ponseti protocol for clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25:623–626.
Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV. Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics. 2004;113:376–380.
Pirani S, Outerbridge HK, Sawatzky B, Stothers K. A reliable method of clinically evaluating a virgin clubfoot evaluation. 21st SICOT conference, 1999.
Ponseti IV. Treatment of congenital clubfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:448–454.
Ponseti IV. Congenital Clubfoot: Fundamentals of Treatment. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1996.
Ponseti IV, Smoley EN. Congenital club foot: the results of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1963;45:261–266.
Radler C, Suda R, Manner HM, Grill F. Early results of the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2006;144:80–86.
Segev E, Keret D, Lokiec F, Yavor A, Wientraub S, Ezra E, Hayek S. Early experience with the Ponseti method for the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005;7:307–310.
Shack N, Eastwood DM. Early results of a physiotherapist-delivered Ponseti service for the management of idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus foot deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:1085–1089.
Thacker MM, Scher DM, Sala DA, van Bosse HJ, Feldman DS, Lehman WB. Use of the foot abduction orthosis following Ponseti casts: is it essential? J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25:225–228.
Tindall AJ, Steinlechner CWB, Lavy CBD, Mannion S, Mkandawire N. Results of manipulation of idiopathic clubfoot deformity in Malawi by orthopaedic clinical officers using the Ponseti method: a realistic alternative for the developing world? J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25:627–629.
Acknowledgments
We thank Seema Sonnad and Meredith Bergey for their help in performing the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Study conducted at the Hospital and Rehabilitation Centre for Disabled Children, Banepa, Nepal.
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved or waived approval for the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Spiegel, D.A., Shrestha, O.P., Sitoula, P. et al. Ponseti Method for Untreated Idiopathic Clubfeet in Nepalese Patients From 1 to 6 Years of Age. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467, 1164–1170 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0600-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0600-1