Abstract
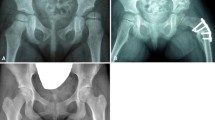
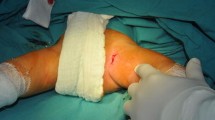
When Pavlik introduced his method of treating congenital dislocation of the hip, he emphasized reducing the rate of osteonecrosis. Graf’s method of sonographic evaluation afforded earlier accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. To ascertain whether treatment duration, gender, age at diagnosis, clinical stability, and/or treatment onset correlate with the risk of osteonecrosis in Graf Type III or IV hips, we clinically and sonographically screened 18,067 neonates (36,134 hips) for developmental dysplasia of the hip over a 4-year period; 151 had Graf Type III or IV hips, and 78 of these were treated by us and had known outcomes. Of these 78 hips, 65 (0.18%) had Graf Type III and 13 (0.036%) had Graf Type IV hips. Sixteen of the 65 Type III hips (25%) reduced spontaneously. Using Pavlik’s method, reduction was achieved in 46 of 65 (88.5%) Type III hips and eight of 13 Type IV hips. None of the hips treated exclusively by Pavlik’s method developed osteonecrosis. Thus, the method achieves one of Pavlik’s original goals of decreasing osteonecrosis incidence to close to zero.
Level of Evidence: Level II, prognostic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atalar H, Sayli U, Yavuz OY, Uras I, Dogruel H. Indicators of successful use of the Pavlik harness in infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop. 2007;31:145–150.
Barlow TG. Early diagnosis and treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. Proc R Soc Med. 1963;56:804–806.
Bialik V, Bialik GM, Blazer S, Sujov P, Wiener F, Berant M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: a new approach to incidence. Pediatrics. 1999;103:93–99.
Committee on Quality Improvement, American Academy of Pediatrics. Clinical practice guidelines: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatrics. 2000;105:896–905.
Eidelman M, Katzman A, Freiman S, Peled E, Bialik V. Treatment of true developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik’s method. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12:253–258.
Felus J, Kowalczyk B. Clinicaly silent developmental hip dysplasia—significance of the hip ultrasonographic examination [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2005;70:397–400.
Graf R. Guide to Sonography of the Infant Hip. Stuttgart, Germany: Thieme Medical; 1987:1–114.
Graf R, Tschauner C, Klapsch W. Progress in prevention of late developmental dislocation of the hip by sonographic newborn hip screening: results of a comparative follow-up study. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988;8:12–16.
MacEwen GD, Millet C. Congenital dislocation of the hip. Pediatr Rev. 1990;11:249–252.
Malkawi H. Sonographic monitoring of the treatment of developmental distribution of the hip by the Pavlik harness. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1998;7:144–149.
Moony JF, Emans JB. Developmental dislocation of the hip: a clinical overview. Pediatr Rev. 1995;16:299–303.
Mostert AK, Tulp NJ, Castelein RM. Results of Pavlik harness treatment for neonatal hip dislocation as related to Graf’s sonographic classification. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20:306–310.
Ortolani M. Congenital hip dysplasia in the light of early and very early diagnosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;119:6–10.
Pavlik A. Stirrups as an aid in the treatment of congenital dysplasias of the hip in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989;9:157–159.
Pavlik A. The functional method of treatment using a harness with stirrups as a primary method of conservative therapy for infants with congenital dislocation of the hip: 1957. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;281:4–10.
Smergel E, Losik SB, Rosenberg HK. Sonography of hip dysplasia. Ultrasound Q. 2004;20:201–216.
Toma P, Valle M, Rossi U, Brunenghi GM. Paediatric hip—ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a review. Eur J Ultrasound. 2001;14:45–55.
Tönnis D. An evaluation of conservative and operative methods in the treatment of congenital hip dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;119:76–88.
Ucar DH, Isiklar ZU, Kandemir U, Tumer Y. Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip with Pavlik harness: prospective study in Graf type IIc or more severe hips. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2004;13:70–74.
Vitale MG, Skaggs DL. Developmental dysplasia of the hip from six months to four years of age. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9:401–411.
Von Rosen S. Diagnosis and treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip joint in the new-born. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1962;44:284–291.
Weinstein SL. Developmental hip dysplasia, dislocation. In: Morrissy RT, Weinstein SL, eds. Lovell and Winter’s Pediatric Orthopaedics. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1996:903–943.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Myrna Perlmutter for her help in the preparation of this manuscript. We also are very grateful to the medical staff of the Neonatal Unit who performed all the routine clinical examinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his institution has waived or does not require approval for the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Peled, E., Bialik, V., Katzman, A. et al. Treatment of Graf’s Ultrasound Class III and IV Hips Using Pavlik’s Method. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 825–829 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0119-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0119-5