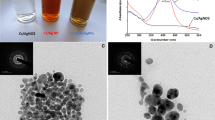
Abstract
Developing a scalable and cost-effective coating process is critical to manufacturing cotton-based hydrophobic antimicrobial fabric for various commercial applications. This paper describes a scalable, cost-effective coating process that is compatible with the existing industrial finishing processes of fabrics. In this process, the fabric is continuously dipped in water-based silver salt and the reducing agent solution to impart silver particles on the fiber surface to produce different coated samples. The process is tuned to minimize process cost and material cost and maximize the antimicrobial effectiveness and durability of the fabric. This paper also introduces an easy protective coating technique with silicone binder of the antimicrobial fabric that improves the durability and hydrophobicity of the antimicrobial fabric without sacrificing the comfort properties of textile fabrics. In the presence of silicone binder, the samples show significant antibacterial effectiveness against two microorganisms, gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and gram-negative Escherichia coli bacteria. Qualitative assessment is carried out to evaluate the antimicrobial properties of the silicone encapsulated silver particles-coated fabrics. Moreover, among the silver-coated fabrics of different cycles, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are deposited in the 1 cycle of silver-coated fabric and the average particle size deposited onto the fiber surface is 65.52 ± 2.71 nm. After silicone encapsulation, among all encapsulated samples, 1 cycle of silver-coated silicone encapsulated sample shows the best result in terms of antimicrobial efficacy where silicone encapsulated 1 cycle silver-coated sample shows around the zone of inhibition 0.53 and 0.25 mm and encapsulated 2 cycles silver-coated sample shows the zone of inhibition 0.14 and 0.06 mm for S. aureus and E. coli, respectively. Coated fabrics with and without silicone encapsulation are characterized by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neely, AN, Maley, MP, “Survival of Enterococci and Staphylococci on Hospital Fabrics and Plastic.” J. Clin. Microbiol., 38 (2) 724–726 (2000)
Slaughter, S, et al., “A Comparison of the Effect of Universal Use of Gloves and Gowns with That of Glove Use Alone on Acquisition of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in a Medical Intensive Care Unit.” Annu. Int. Med., 125 448–456 (1996)
Montazer, M, Rangchi, F, Siavoshi, F, “Preparation of Protective Disposable Hygiene Fabrics for Medical Applications,” Medical and Healthcare Textiles, 164–170 (2010).
Fernandez, L, Deaton, JE, Gordon, CR, “Ostomy bag.”. United States Patent US10238529B2, 2014.
Watanabe, T, Yum, SI, Lee, ES, Chin, IW, “Antimicrobial Device for Urine Drainage Container.” United States Patent US5176665A, 1992.
Chirila, C, Deselnicu, V, Crudu, M, “Comparative Study Regarding Resistance of Wet-White and Wet-Blue Leather to the Growth of Fungi.” Leather and Footwear Journal, 14 (2) 107–120 (2014)
Chirila, C, Crudu, M, Deselnicu, V, “Study Regarding the Resistance of Wet-White Leather Tanned with Titanium – Aluminum to the Growth of Fungi.” Proc. 5th ICAMS 2014, 31–35 October 2014, Bucharest, 2014.
Sun, J, Li, J, Qiu, X, Qing, F, “Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) of Novel Perfluoroalkyl-Containing Quaternary Ammonium Salts.” J. Fluor. Chem., 126 (9–10) 1425–1431 (2005)
Ali, S, Joshi, S, Rajendran, M, “Novel Self-Assembled Antimicrobial Textile Coating Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles.” AATCC Rev., 11 (5) 49–55 (2011)
Kalyon, BD, Olgun, U, “Antibacterial Efficacy of Triclosan-Incorporated Polymers.” Am. J. Infect. Control, 29 (2) 124–125 (2001)
Jiang, T, Liu, L, Yao, J, “Synthesis of Ag Nanoparticles on the Cotton Characterization of Ag Deposited Fabrics.” Fibers Polym., 12 (5) 620–625 (2011)
Joshi, M, Ali, SW, Rajendran, S, “Antibacterial Finishing of Polyester/Cotton Blend Fabrics Using Neem (Azadirachta indica): A Natural Bioactive Agent.” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 106 (2) 793–800 (2007)
Yang, Z, Peng, H, Wang, W, Liu, T, “Crystallization Behavior of Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposites.” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 116 (5) 2658–2667 (2010)
Montazer, M, Seifollahzadeh, S, “Enhanced Self-Cleaning, Antibacterial and UV Protection Properties of Nano TiO2 Treated Textile Through Enzymatic Pretreatment.” Photochem. Photobiol., 87 (4) 877–883 (2011)
Vasilev, K, Sah, VR, Goreham, RV, Ndi, C, Short, RD, Griesser, HJ, “Antibacterial Surfaces by Adsorptive Binding of Polyvinyl-Sulphonate- Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles.” Nanotechnology, 21 (21) 215102 (2010)
Xia, N, Cai, Y, Jiang, T, Yao, J, “Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Chemical Reduction with Hyaluronan.” Carbohydr. Polym., 86 (2) 956–961 (2011)
Alemdar, S, Agaoglu, S, “Investigation of In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Aloe Vera Juice.” J. Anim. Vet. Adv., 8 (1) 99–102 (2009)
Hebeish, A, El-Naggar, ME, Fouda, MMG, Ramadan, MA, Al-Deyab, SS, El-Rafie, MH, “Highly Effective Antibacterial Textiles Containing Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles.” Carbohydr. Polym., 86 (2) 936–940 (2011)
Rai, M, Yadav, A, Gade, A, “Silver Nanoparticles as a New Generation of Antimicrobials.” Biotechnol. Adv., 27 (1) 76–83 (2009)
Sharma, VK, Yngard, RA, Lin, Y, “Silver Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Their Antimicrobial Activities.” Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 145 (1–2) 83–96 (2009)
Ilić, V, Šaponjić, Z, Vodnik, V, Potkonjak, B, Jovančić, P, Nedeljković, J, Radetić, M, “The Influence of Silver Content on Antimicrobial Activity and Color of Cotton Fabrics Functionalized with Ag Nanoparticles.” Carbohydr. Polym., 78 (3) 564–569 (2009)
El-Rafie, MH, Ahmed, HB, Zahran, MK, “Characterization of Nanosilver Coated Cotton Fabrics and Evaluation of Its Antibacterial Efficacy.” Carbohydr. Polym., 107 174–181 (2014)
Perelshtein, I, Applerot, G, Perkas, N, Guibert, G, Mikhailov, S, Gedanken, A, “Sonochemical Coating of Silver Nanoparticles on Textile Fabrics (Nylon, Polyester and Cotton) and Their Antibacterial Activity.” Nanotechnology, 19 (24) 12 (2008)
Shahid-ul-Islam, Butola, BS, Kumar, A, “Green Chemistry Based In-Situ Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Finishing of Chitosan Polysaccharide Modified Cellulosic Textile Substrate.” Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 152 1135–1145 (2020)
Mamun, MAA, Islam, MT, Islam, MM, Sowrov, K, Hossain, MA, Ahmed, DM, Shahariar, H, “Scalable Process to Develop Durable Conductive Cotton Fabric,” Adv. Fiber Mater. (2020).
Umer, A, Naveed, S, Ramzan, N, Rafique, MS, “Selection of a Suitable Method for the Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles.” Nano, 7 (5) 1230005 (2012)
Shahariar, H, Jur, JS, “Correlation of Printing Faults with the RF Characteristics of Coplanar Waveguides (CPWs) Printed on Nonwoven Textiles.” Sensors Actuators, A Phys., 273 240–248 (2018)
Hamedi, M, Forchheimer, R, Inganäs, O, “Towards Woven Logic from Organic Electronic Fibres.” Nat. Mater., 6 (5) 357–362 (2007)
Polte, J, et al., “Mechanism of Gold Nanoparticle Formation in the Classical Citrate Synthesis Method Derived from Coupled In Situ XANES and SAXS Evaluation.” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132 (4) 1296–1301 (2010)
Yeo, SY, Jeong, SH, “Preparation and Characterization of Polypropylene/Silver Nanocomposite Fibers.” Polym. Int., 52 (7) 1053–1057 (2003)
Bradford, A, Handy, RD, Readman, JW, Atfield, A, Mühling, M, “Impact of Silver Nanoparticle Contamination on the Genetic Diversity of Natural Bacterial Assemblages in Estuarine Sediments.” Environ. Sci. Technol., 43 (12) 4530–4536 (2009)
Miao, AJ, Luo, Z, Chen, CS, Chin, WC, Santschi, PH, Quigg, A, “Intracellular Uptake: A Possible Mechanism for Silver Engineered Nanoparticle Toxicity to a Freshwater Alga Ochromonas Danica.” PLoS One, 5 (12) 6–13 (2010)
El-Rafie, MH, Mohamed, AA, Shaheen, TI, Hebeish, A, “Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Fungal Process on Cotton Fabrics.” Carbohydr. Polym., 80 (3) 779–782 (2010)
Wimalasiri, VK, Weerathunga, HU, Kottegoda, N, Karunaratne, V, “Silica Based Superhydrophobic Nanocoatings for Natural Rubber Surfaces,” J. Nanomater., 2017 (2017).
Morones, JR, et al., “The Bactericidal Effect of Silver Nanoparticles.” Nanotechnology, 16 (10) 2346–2353 (2005)
Matsumura, Y, Yoshikata, K, Ichi Kunisaki, S, Tsuchido, T, “Mode of Bactericidal Action of Silver Zeolite and its Comparison with that of Silver Nitrate.” Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69 (7) 4278–4281 (2003)
El-Rafie, MH, Shaheen, TI, Mohamed, AA, Hebeish, A, “Bio-Synthesis and Applications of Silver Nanoparticles Onto Cotton Fabrics.” Carbohydr. Polym., 90 (2) 915–920 (2012)
Gupta, P, Bajpai, M, Bajpai, SK, “Textile Technology: Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Poly (Acrylamide-Co-Itaconic Acid)-Grafted Cotton Fabric.” J. Cotton Sci., 12 (3) 280–286 (2008)
Ki, HY, Kim, JH, Kwon, SC, Jeong, SH, “A Study on Multifunctional Wool Textiles Treated with Nano-Sized Silver.” J. Mater. Sci., 42 (19) 8020–8024 (2007)
Hermans, MH, “Silver-Containing Dressings and the Need for Evidence.” Am. J. Nurs., 106 (12) 60–68 (2006)
Lee, HY, Park, HK, Lee, YM, Kim, K, Park, SB, “A Practical Procedure for Producing Silver Nanocoated Fabric and Its Antibacterial Evaluation for Biomedical Applications.” Chem. Commun., 28 2959–2961 (2007)
Kim, HW, Kim, BR, Rhee, YH, “Imparting Durable Antimicrobial Properties to Cotton Fabrics Using Alginate-Quaternary Ammonium Complex Nanoparticles.” Carbohydr. Polym., 79 (4) 1057–1062 (2010)
Lee, HJ, Yeo, SY, Jeong, SH, “Antibacterial Effect of Nanosized Silver Colloidal Solution on Textile Fabrics.” J. Mater. Sci., 38 (10) 2199–2204 (2003)
Gorenšek, M, Recelj, P, “Reactive Dyes and Nano-Silver on PA6 Micro Knitted Goods.” Text. Res. J., 79 (2) 138–146 (2009)
Shateri Khalil-Abad, M, Yazdanshenas, ME, Nateghi, MR, “Effect of Cationization on Adsorption of Silver Nanoparticles on Cotton Surfaces and Its Antibacterial Activity.” Cellulose, 16 (6) 1147–1157 (2009)
Pollini, M, Russo, M, Licciulli, A, Sannino, A, Maffezzoli, A, “Characterization of Antibacterial Silver Coated Yarns.” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 20 (11) 2361–2366 (2009)
Purwar, R, Joshi, M, “Recent Developments in Antimicrobial Finishing of Textiles. A Review.” AATCC Rev., 4 (3) 22–26 (2004)
Williams, U, Halo Source, J, Cho, V, “Antimicrobial Functions for Synthetic Fibers: Recent Developments.” AATCC Rev., 5 17–21 (2005)
Hebbar, RS, Isloor, AM, Ismail, AF, Contact Angle Measurements. Elsevier B.V. (2017).
Gourley, L, Britten, M, Gauthier, SF, Pouliot, Y, “Characterization of Adsorptive Fouling on Ultrafiltration Membranes by Peptides Mixtures Using Contact Angle Measurements.” J. Memb. Sci., 97 (C) 283–289 (1994)
Agnihotri, S, Mukherji, S, Mukherji, S, “Size-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Over the Range 5–100 nm Using the Same Protocol and Their Antibacterial Efficacy.” RSC Advances, 4 (8) 3974–3983 (2014)
Raza, M, Kanwal, Z, Rauf, A, Sabri, A, Riaz, S, Naseem, S, “Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes.” Nanomaterials, 6 (4) 74 (2016)
Pal, S, Tak, YK, Song, JM, “Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli.” Appl. Environm. Microbiol., 73 (6) 1712–1720 (2007)
Xiu, Z, Zhang, Q, Puppala, HL, Colvin, VL, Alvarez, PJJ, “Negligible Particle-Specific Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles.” Nano Letters, 12 (8) 4271–4275 (2012)
Funding
This work is supported by the research grant from Bangladesh University of Textiles, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Code: 3631108, FY-2020-21, SN- 13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.T., Mamun, M.A.A., Hasan, M.T. et al. Scalable coating process of AgNPs-silicone on cotton fabric for developing hydrophobic and antimicrobial properties. J Coat Technol Res 18, 887–898 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-020-00451-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-020-00451-z