Abstract
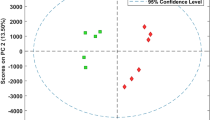
The microwave process raises considerable interest due to its advantages in the agriculture and food industries. This process has an impact on the chemical components of food. The effect of microwave treatment on the composition of maize flour is not well established. This study aims to determine the primary metabolite (amino acids, sugars, organic acids, etc.) and fatty acid profiles before and after microwave treatment (600 W, 2 min) of maize flour samples using gas chromatography (GC) techniques. Thirty-five different metabolites were identified in all maize flour samples by GC-MS through standard mass spectral libraries. Moreover, ten different fatty acids detected by GC-FID in the samples were confirmed by comparing them with the retention times of the authentic standards. Based on the statistical analyses, it was found that microwave treatment did not result in any significant effect on the general primary metabolite profile and fatty acid composition of the maize flour samples. Both the Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) and the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) indicated that the data obtained from all samples had good repeatability. The findings from the metabolite analyses provide valuable insights into establishing a background for monitoring and controlling the chemical composition of maize flour when subjected to microwave processing.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Asiedu, M., Nilsen, R., Lie, Ø., & Lied, E. (1993). Effect of processing (sprouting and/or fermentation) on sorghum and maize. I: Proximate composition, minerals and fatty acids. Food Chemistry, 46(4), 351–353.
Bhatt, K., Vaidya, D., Kaushal, M., Gupta, A., Soni, P., Arya, P., Gautam, A., & Sharma, C. (2020). Microwaves and radiowaves: In food processing and preservation. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 9(9), 118–131.
Böhme, K., Calo-Mata, P., Barros-Velázquez, J., & Ortea, I. (2019). Recent applications of omics-based technologies to main topics in food authentication. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 110, 221–232.
Calín-Sánchez, Á., Figiel, A., Hernández, F., Melgarejo, P., Lech, K., & Carbonell-Barrachina, Á. A. (2013). Chemical composition, antioxidant capacity, and sensory quality of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) arils and rind as affected by drying method. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6, 1644–1654.
Chen, M., Rao, R. S. P., Zhang, Y., Zhong, C., & Thelen, J. J. (2016). Metabolite variation in hybrid corn grain from a large-scale multisite study. The Crop Journal, 4(3), 177–187.
David, F., Sandra, P., & Wylie, P. L. (2002). Improving the analysis of fatty acid methyl esters using retention time locked methods and retention time databases. Agilent Technologies Application Note.
Deng, Y., Padilla-Zakour, O., Zhao, Y., & Tao, S. (2015). Influences of high hydrostatic pressure, microwave heating, and boiling on chemical compositions, antinutritional factors, fatty acids, in vitro protein digestibility, and microstructure of buckwheat. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 2235–2245.
Egea, M. B., De Sousa, T. L., Dos Santos, D. C., De Oliveira Filho, J. G., Guimarães, R. M., Yoshiara, L. Y., & Lemes, A. C. (2023). Application of soy, corn, and Bean By-products in the gluten-free baking process: A review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–22.
Emami, S., Perera, A., Meda, V., & Tyler, R. T. (2012). Effect of microwave treatment on starch digestibility and physico-chemical properties of three barley types. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5, 2266–2274.
Filho, I. K., Jaski, A. C., Takayanagui, M. M., De Andradre, C. K., Butik, M., & Quinaia, S. P. (2020). Determination and chemometric evaluation of the mineral profile of maize flours. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 92, 103579.
Golijan, J., Milinčić, D. D., Petronijević, R., Pešić, M. B., Barać, M. B., Sečanski, M., Lekić, S., Kostić, A., & Ž. (2019). The fatty acid and triacylglycerol profiles of conventionally and organically produced grains of maize, spelt and buckwheat. Journal of Cereal Science, 90, 102845.
Granato, D., Santos, J. S., Escher, G. B., Ferreira, B. L., & Maggio, R. M. (2018). Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 72, 83–90.
Hassan, S., Ahmad, N., Ahmad, T., Imran, M., Xu, C., & Khan, M. K. (2019). Microwave processing impact on the phytochemicals of sorghum seeds as food ingredient. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 43(5), e13924.
Jahaniaval, F., Kakuda, Y., & Marcone, M. F. (2000). Fatty acid and triacylglycerol compositions of seed oils of five Amaranthus accessions and their comparison to other oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 77, 847–852.
Jiang, H., Liu, Z., & Wang, S. (2018). Microwave processing: Effects and impacts on food components. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58(14), 2476–2489.
Juodeikiene, G., Zadeike, D., Vidziunaite, I., Bartkiene, E., Bartkevics, V., & Pugajeva, I. (2018). Effect of heating method on the microbial levels and acrylamide in corn grits and subsequent use as functional ingredient for bread making. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 112, 22–30.
Kostić, A., Mačukanović-Jocić, M. P., Trifunović, B. D. Š., Vukašinović, I., Pavlović, V. B., & Pešić, M. B. (2017). Fatty acids of maize pollen–Quantification, nutritional and morphological evaluation. Journal of Cereal Science, 77, 180–185.
Lamine, M., & Mlikia, A. (2021). Nutritional quality perceptions through fatty acid profiling, health lipid indices and antioxidant potentialities. Open Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences, 3(1), 1016.
Lima, D. C., dos Santos, A. M., Araujo, R. G., Scarminio, I. S., Bruns, R. E., & Ferreira, S. L. (2010). Principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis for homogeneity evaluation during the preparation of a wheat flour laboratory reference material for inorganic analysis. Microchemical Journal, 95(2), 222–226.
Matthews, J. P., Gemme, S., Huebschmann, H. J., Llorente, C., Jimenez, R., & Sreenivasulu, N. (2015). Metabolomics of rice genotypes using GC-MS/MS. ThermoScientific Application Note 1–9.
Milinčić, D. D., Kostić, A., Špirović-Trifunović, B., Tešić, Ž. L., Tosti, T., Dramićanin, A. M., & Pešić, M. B. (2020). Grape seed flour of different grape pomaces: Fatty acid profile, soluble sugar profile and nutritional value. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 85(3), 305–319.
Momenzadeh, Z., Khodanazary, A., & Ghanemi, K. (2017). Effect of different cooking methods on vitamins, minerals and nutritional quality indices of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 11, 434–441.
Mssillou, I., Agour, A., Hamamouch, N., Lyoussi, B., & Derwich, E. (2021). Chemical composition and in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Marrubium vulgare L. The Scientific World Journal, 2021, 7011493.
Munir, N., Riaz, A., Mehmood, E., Mustafa, S. G., Haq, R., Ilyas, S., & Naz, S. (2021). Effect of different treatments on nutritional, microbiological and rheological properties of flours. Progress in Nutrition, 23(2), e2021113. https://doi.org/10.23751/pn.v23i2.9217
Ngoune Tandzi, L., & Mutengwa, C. S. (2019). Estimation of maize (Zea mays L.) yield per harvest area: Appropriate methods. Agronomy, 10(1), 29.
Obata, T., Witt, S., Lisec, J., Palacios-Rojas, N., Florez-Sarasa, I., Yousfi, S., Araus, J. L., Cairns, J. E., & Fernie, A. R. (2015). Metabolite profiles of maize leaves in drought, heat, and combined stress field trials reveal the relationship between metabolism and grain yield. Plant Physiology, 169(4), 2665–2683.
Pastor, K., Ačanski, M., Vujić, D., Bekavac, G., Milovac, S., & Kravić, S. (2016). Rapid method for small grain and corn flour authentication using GC/EI–MS and multivariate analysis. Food Analytical Methods, 9, 443–450.
Pérez-Quirce, S., Ronda, F., Lazaridou, A., & Biliaderis, C. G. (2017). Effect of microwave radiation pretreatment of rice flour on gluten-free breadmaking and molecular size of β-glucans in the fortified breads. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 1412–1421.
Rao, J., Cheng, F., Hu, C., Quan, S., Lin, H., Wang, J., Chen, G., Zhao, X., Alexander, D., Guo, L., Wang, G., Lai, J., Zhang, D., & Shi, J. (2014). Metabolic map of mature maize kernels. Metabolomics, 10, 775–787.
Röhlig, R. M., Eder, J., & Engel, K. H. (2009). Metabolite profiling of maize grain: Differentiation due to genetics and environment. Metabolomics, 5, 459–477.
Román, L., Martínez, M. M., Rosell, C. M., & Gómez, M. (2015). Effect of microwave treatment on physicochemical properties of maize flour. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1330–1335.
Ruge, C., Changzhong, R., & Zaigui, L. (2012). The effects of different inactivation treatments on the storage properties and sensory quality of naked oat. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5, 1853–1859.
Sanjeev, P., Chaudhary, D. P., Sreevastava, P., Saha, S., Rajenderan, A., Sekhar, J. C., & Chikkappa, G. K. (2014). Comparison of fatty acid profile of specialty maize to normal maize. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 91(6), 1001–1005.
Singh, P. (2018). Physicochemical characterization, fatty acid in corn seed oil using GC-FID method. International Journal of Chemical Research and Development, 1(1), 1–4.
Skogerson, K., Harrigan, G. G., Reynolds, T. L., Halls, S. C., Ruebelt, M., Iandolino, A., Pandravada, A., Glenn, K. C., & Fiehn, O. (2010). Impact of genetics and environment on the metabolite composition of maize grain. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(6), 3600–3610.
Tang, W., Hazebroek, J., Zhong, C., Harp, T., Vlahakis, C., Baumhover, B., & Asiago, V. (2017). Effect of genetics, environment, and phenotype on the metabolome of maize hybrids using GC/MS and LC/MS. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(25), 5215–5225.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Gross chemical composition. Retrieved March 21 (2023). from https://www.fao.org/3/t0395e/T0395E01.GIF
Uthumporn, U., Nadiah, N. I., Koh, W. Y., Zaibunnisa, A. H., & Azwan, L. (2016). Effect of microwave heating on corn flour and rice flour in water suspension. International Food Research Journal, 23(6), 2493–2503.
Utpott, M., Rodrigues, E., de Oliveira Rios, A., Mercali, G. D., & Flôres, S. H. (2022). Metabolomics: An analytical technique for food processing evaluation. Food Chemistry, 366, 130685.
Uygun, E., Yildiz, E., Sumnu, G., & Sahin, S. (2020). Microwave pretreatment for the improvement of physicochemical properties of carob flour and rice starch–based electrospun nanofilms. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13, 838–850.
Velu, V., Nagender, A., Rao, P. P., & Rao, D. G. (2006). Dry milling characteristics of microwave dried maize grains (Zea mays L). Journal of Food Engineering, 74(1), 30–36.
Vidinamo, F., Fawzia, S., & Karim, M. A. (2021). Investigation of the effect of drying conditions on phytochemical content and antioxidant activity in pineapple (Ananas comosus). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–10.
Vijayakumar, K. R., Martin, A., Gowda, L. R., & Prakash, V. (2009). Detection of genetically modified soya and maize: Impact of heat processing. Food Chemistry, 117(3), 514–521.
WHO/FAO (World Health Organization/Food and Agriculture Organization) (2003). Diet, Nutrition and Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. WHO Technical Report Series 916. Retrieved May 14, 2023, from http://health.euroafrica.org/books/dietnutritionwho.pdf
Yururdurmaz, C., & Yildiz, H. (2022). Fatty acid compositions of Zea mays L. varieties in Turkey. Progress In Nutrition, 24(3).
Zhang, L., Yu, Y., & Yu, R. (2020). Analysis of metabolites and metabolic pathways in three maize (Zea mays L.) varieties from the same origin using GC–MS. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 17990.
Zhang, L., Yu, R., & Yu, Y. (2021). Analysis of metabolites and metabolic mechanism in Bt transgenic and non-transgenic maize. Microchemical Journal, 169, 106544.
Zhong, Y., Liang, W., Pu, H., Blennow, A., Liu, X., & Guo, D. (2019). Short-time microwave treatment affects the multi-scale structure and digestive properties of high-amylose maize starch. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 137, 870–877.
Acknowledgements
This study is carried out within the framework of a doctoral thesis conducted by Hacettepe University, Graduate School of Science and Engineering. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses of this study were performed at Bilkent University, Institute of Materials Science and Nanotechnology (UNAM), Ankara, Turkey. The authors thank Prof. Dr. Ümran Uygun for carefully reading the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Hacettepe University, Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project Number: FHD-2021-19443).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and data analysis were performed by Begüm Zeynep Hançerlioğulları under the supervision of Umut Toprak and Remziye Yılmaz. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Begüm Zeynep Hançerlioğulları, Umut Toprak, and Remziye Yılmaz, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hançerlioğulları, B.Z., Toprak, U. & Yılmaz, R. Analyses of Metabolites in Microwave-treated Maize Flours. Food Bioprocess Technol 17, 686–696 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03164-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03164-4