Abstract
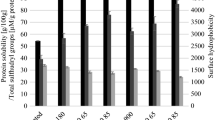
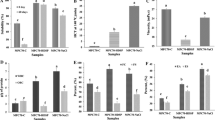
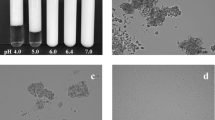
This study investigated the technological properties of barley hydrocolloids to produce a kinetically stable plant-based non-dairy alternative milk. The impact of mechanical extraction assisted by electrolysis treatments (0, 5, and 15 V) on the barley protein content was examined. The protein-rich barley aqueous extract was used to emulsify canola oil enriched with vitamin D at different pH conditions (5, 5.6, 6, and 7) and temperatures (30 and 60 °C). The homogenization treatment performed at 60 °C allowed higher protein solubilization and better kinetic stabilization than the one obtained at 30 °C. This temperature probably promoted water retention in barley’s hydrocolloids and protein agglomeration, producing samples with larger Sauter mean diameters of ~ 14 µm and higher apparent viscosities from 13 to 16 mPa s. The rise in pH from 5 to 7 increased the electrostatic charges of the samples. In contrast, the pH decrease allowed a higher reduction in the interfacial tension between barley aqueous extract and canola oil up to 3.2 mN/m at pH 5. Despite these electrostatic and steric forces provided by the barley hydrocolloids, the beverage only showed better kinetic stability after the homogenization treatment at 60 °C. Therefore, the barley hydrocolloids acted as structuring agents in the production of barley-based non-dairy alternative milk, contributing to its kinetic stability by high internal phase Pickering emulsions.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon suitable request.
References
Abdullah, Weiss, J., Ahmad, T., Zhang, C., & Zhang, H. (2020). A review of recent progress on high internal-phase Pickering emulsions in food science. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 106, 91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.10.016
Aydar, E. F., Tutuncu, S., & Ozcelik, B. (2020). Plant-based milk substitutes: Bioactive compounds, conventional and novel processes, bioavailability studies, and health effects. Journal of Functional Foods, 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.103975
Berggren, S. (2018). Water holding capacity and viscosity of ingredients from oats: The effect of beta-glucan and starch content, particle size, pH and temperature. Bachelor thesis (Chemistry), Linnaeus University Sweden, Sweden.
Bishop, L. (1928). First report on barley proteins: The composition and quantitative estimation of barley proteins. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 34(2), 101–118.
Bocker, R., & Silva, E. K. (2022). Innovative technologies for manufacturing plant-based non-dairy alternative milk and their impact on nutritional, sensory and safety aspects. Future Foods, 5, 100098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2021.100098
Boostani, S., Hosseini, S. M. H., Golmakani, M. -T., Marefati, A., Hadi, N. B. A., & Rayner, M. (2020). The influence of emulsion parameters on physical stability and rheological properties of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hordein nanoparticles. Food Hydrocolloids, 101, 105520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105520
Boukid, F., Rosell, C. M., & Castellari, M. (2021). Pea protein ingredients: A mainstream ingredient to (re)formulate innovative foods and beverages. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 110, 729–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.040
Bradley, R. L. (2010). Moisture and total solids analysis. In Food analysis (pp. 85–104): Springer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2004.03.010
Chen, G., & Tao, D. (2005). An experimental study of stability of oil–water emulsion. Fuel Processing Technology, 86(5), 499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2004.03.010
Da Silva, L. R., Velasco, J. I., & Fakhouri, F. M. (2023). Use of rice on the development of plant-based milk with antioxidant properties: From raw material to residue. LWT, 173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.114271
Dai, T., Li, T., Li, R., Zhou, H., Liu, C., Chen, J., & McClements, D. J. (2020). Utilization of plant-based protein-polyphenol complexes to form and stabilize emulsions: Pea proteins and grape seed proanthocyanidins. Food Chemistry, 329, 127219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127219
Dairy Alternatives Market. (2023). Dairy alternatives market outlook. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/dairy-alternatives-market. Accessed 13 January 2023.
Domke, F. (2018). Vegetarian and vegan products-labelling and definitions. European Food and Feed Law Review, 13(2), 102–107. https://www.jstor.org/stable/90021310
Ekaette, I. U. (2020). Rutin and barley starch modification using subcritical water, ultrasonication and electrolysis technologies. PhD thesis (Bioresource and Food Engineering), 263 pp, Department of Agricultural, Food, and Nutritional Science, University of Alberta, Canada.
Ekaette, I. U., & Saldaña, M. D. A. (2021). The effect of rutin on starch hydrogels/aerogels made from electrolyzed barley flour. Starch, 73, 2000099. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202000099
Flom, J. D., & Sicherer, S. H. (2019). Epidemiology of cow’s milk allergy. Nutrients, 11(5), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051051
Gajzago, I., & Czukor, B. (1993). Rapid protein determination with LECO FP-428 protein detector. Elelmezesi Ipar (hungary), 47(8), 229–232.
Gonzalez Ortiz, D., Pochat-Bohatier, C., Cambedouzou, J., Bechelany, M., & Miele, P. (2020). Current trends in Pickering emulsions: Particle morphology and applications. Engineering, 6(4), 468–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2019.08.017
Good Food Institute (GFI). (2021). State of the Industry report: plant-based meat, eggs and dairy. [Internet]. Accessed on January 13 2023. Available from: https://gfi.org/resource/plant-based-meat-eggs-and-dairy-state-of-the-industry-report/
Gumus, C. E., Decker, E. A., & McClements, D. J. (2017). Formation and stability of ω-3 oil emulsion-based delivery systems using plant proteins as emulsifiers: Lentil, pea, and faba bean proteins. Food Biophysics, 12(2), 186-197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-017-9475-6
Henry, R. J. (1988). The carbohydrates of barley grains - A review. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 94(2), 71–78.
Karp, S., Wyrwisz, J., & Kurek, M. A. (2019). Comparative analysis of the physical properties of o/w emulsions stabilised by cereal β-glucan and other stabilisers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 132, 236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.212
Kaushik, I., Singh, R., & Bhisnoi, J. P. (2017). Effect of barley malt, chickpea and peanut on quality of barley based beverage. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 9(2), 1182–1186. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v9i2.1563
Krentz, A., García-Cano, I., Ortega-Anaya, J., & Jiménez-Flores, R. (2022). Use of casein micelles to improve the solubility of hydrophobic pea proteins in aqueous solutions via low-temperature homogenization. Journal of Dairy Science, 105(1), 22–31. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2021-20902
Kumari, S., Yadav, B. S., & Yadav, R. B. (2022). Effect of nano-conversion on morphological, rheological and thermal properties of barley starch. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 59(2), 467–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05029-0
Lazaridou, A., Chornick, T., Biliaderis, C. G., & Izydorczyk, M. S. (2008). Composition and molecular structure of polysaccharides released from barley endosperm cell walls by sequential extraction with water, malt enzymes, and alkali. Journal of Cereal Science, 48(2), 304–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2007.09.011
Li, Y., You, M., Liu, H., & Liu, X. (2021). Comparison of distribution and physicochemical properties of β-glucan extracted from different fractions of highland barley grains. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 189, 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.094
McClements, D. J. (2020). Development of next-generation nutritionally fortified plant-based milk substitutes: Structural design principles. Foods, 9(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040421
Manassero, C. A., Beaumal, V., Vaudagna, S. R., Speroni, F., & Anton, M. (2018). Calcium addition, pH and high hydrostatic pressure effects on soybean protein isolates—Part 2: Emulsifying properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(11), 2079–2093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2164-8
Mekala, S., Silva, E. K., & Saldaña, M. D. A. (2021). Mechanism, kinetics, and physicochemical properties of ultrasound-produced emulsions stabilized by lentil protein: A non-dairy alternative in food systems. European Food Research and Technology, 248, 185–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-021-03871-2
Mekala, S., Silva, E. K., & Saldaña, M. D. A. (2022). Ultrasound-assisted production of emulsion-filled pectin hydrogels to encapsulate vitamin complex: Impact of the addition of xylooligosaccharides, ascorbic acid and supercritical CO2 drying. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 76, 102907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102907
Mishra, N., Gupta, E., Prasad, R., & Singh, P. (2020). Formulation and optimization of malted barley based symbiotic beverage by response surface methodology. Journal of Advances in Food Science & Technology, 7(1), 12–20.
Oliete, B., Potin, F., Cases, E., & Saurel, R. (2019). Microfluidization as homogenization technique in pea globulin-based emulsions. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(5), 877–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02265-3
Ozturk, B., & McClements, D. J. (2016). Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions. Current Opinion in Food Science, 7, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2015.07.008
Robins, M. M. (2000). Emulsions — creaming phenomena. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 5(5), 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-0294(00)00065-0
Roselló-Soto, E., Barba, F. J., Parniakov, O., Galanakis, C. M., Lebovka, N., Grimi, N., & Vorobiev, E. (2015). High voltage electrical discharges, pulsed electric field, and ultrasound assisted extraction of protein and phenolic compounds from olive kernel. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(4), 885–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1456-x
Sankaran, R., Show, P. L., Cheng, Y. -S., Tao, Y., Ao, X., Nguyen, T. D. P., & Van Quyen, D. (2018). Integration process for protein extraction from microalgae using liquid biphasic electric flotation (LBEF) system. Molecular Biotechnology, 60(10), 749–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0111-6
Sarantis, S. D., Eren, N. M., Kowalcyk, B., Jimenez–Flores, R., & Alvarez, V. B. (2021). Thermodynamic interactions of micellar casein and oat β-glucan in a model food system. Food Hydrocolloids, 115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106559
Sarkar, A., & Dickinson, E. (2020). Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 49, 69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2020.04.004
Sethi, S., Tyagi, S. K., & Anurag, R. K. (2016). Plant-based milk alternatives an emerging segment of functional beverages: A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(9), 3408–3423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2328-3
Silva, A. R. A., Silva, M. M. N., & Ribeiro, B. D. (2020). Health issues and technological aspects of plant-based alternative milk. Food Research International, 131, 108972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108972
Silva, E. K., Azevedo, V. M., Cunha, R. L., Hubinger, M. D., & Meireles, M. A. A. (2016). Ultrasound-assisted encapsulation of annatto seed oil: Whey protein isolate versus modified starch. Food Hydrocolloids, 56, 71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.12.006
Silva, E. K., Gomes, M. T. M., Hubinger, M. D., Cunha, R. L., & Meireles, M. A. A. (2015). Ultrasound-assisted formation of annatto seed oil emulsions stabilized by biopolymers. Food Hydrocolloids, 47, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.001
Silva, K., Machado, A., Cardoso, C., Silva, F., & Freitas, F. (2019). Rheological behavior of plant-based beverages. Food Science and Technology, 40, 258–263. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.09219
Şirin, E., & Yalçın, E. (2019). Effects of concentration and partial hydrolysis on functional properties of hull-less barley protein concentrates. Quality Assurance and Safety of Crops & Foods, 11(2), 201–210. https://doi.org/10.3920/QAS2018.1390
Strieder, M. M., Neves, M. I. L., Silva, E. K., & Meireles, M. A. A. (2021). Impact of thermosonication pretreatment on the production of plant protein-based natural blue colorants. Journal of Food Engineering, 299, 110512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2021.110512
Strieder, M. M., Silva, E. K., Mekala, S., Meireles, M. A. A., & Saldaña, M. D. A. (2022). Pulsed high-pressure processing of barley-based non-dairy alternative milk: β-carotene retention, protein solubility and antioxidant activity. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 82, 103212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2022.103212
Sivabalan, S., & Sablani, S. (2022). Design of β-carotene encapsulated emulsions for thermal processing and storage. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(2), 338–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02754-4
Tan, Y., & McClements, D. J. (2021). Plant-based colloidal delivery systems for bioactives. Molecules, 26(22), 6895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226895
Vo, H. H. P., & Saldaña, M. D. A. (2023). Hydrolysis of pea protein concentrate in subcritical water media with addition of citrus pectin and citric acid, The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 195, 105866.
Wang, C., Tian, Z., Chen, L., Temelli, F., Liu, H., & Wang, Y. (2010). Functionality of barley proteins extracted and fractionated by alkaline and alcohol methods. Cereal Chemistry, 87(6), 597–606. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-06-10-0097
Waterborg, J. H. (2009). The Lowry method for protein quantitation. In The protein protocols handbook (pp. 7–10). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-198-7_2
Wu, Y. V., & Inglett, G. E. (1974). Denaturation of plant proteins related to functionality and food applications. A Review. Journal of Food Science, 39(2), 218–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1974.tb02861.x
Xia, T., Xue, C., & Wei, Z. (2021). Physicochemical characteristics, applications and research trends of edible Pickering emulsions. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 107, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.11.019
Xiao, K., & Zhou, Y. (2020). Protein recovery from sludge: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 249, 119373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119373
Yu, J. J., Li, N., Li, S., & Chen, Y. (2022). Solubilization mechanism and structural properties of high‐denatured peanut protein treated by shearing. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 45(2), e13951. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13951
Funding
We acknowledge the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC, #04371–2019, Discovery Grant of Dr. Saldaña) for providing funds to conduct this research; Monique Martins Strieder thanks the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, grant number 141110/2018–0) for her doctorate assistantship; and Maria Angela A. Meireles thanks CNPq (grant number 309825/2020–2) for her productivity grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Monique Martins Strieder: Conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing — original draft. Eric Keven Silva: Conceptualization, visualization, supervision, writing — review and editing. Srujana Mekala: Investigation, methodology. Maria Angela A. Meireles: Supervision, resources. Marleny D.A. Saldaña: Conceptualization, supervision, resources, funding acquisition, project administration, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Strieder, M.M., Silva, E.K., Mekala, S. et al. Barley-Based Non-dairy Alternative Milk: Stabilization Mechanism, Protein Solubility, Physicochemical Properties, and Kinetic Stability. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 2231–2246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03037-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03037-w