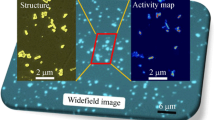
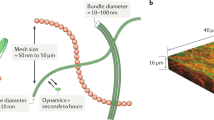
Abstract
Super-resolution microscopy (SRM) techniques have revolutionized the process of obtaining images beyond Abbe’s diffraction limit (∼200 nm) of the light microscopes. It is possible to obtain images in 2D and 3D by reaching a lateral resolution of up to 10 nm of the cellular ultrastructure and biomolecules labelled with fluorophores. However, SRM is relatively unknown and rarely applied in food science, yet it has huge potential for the development of food nanotechnology. There is a focus on structured illumination microscopy (SIM), stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy, photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM), stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM), and minimal photon fluxes (MINFLUX) microscopy as well as a compilation and discussion of the main fluorophores used in these techniques, the recent advances, microscope systems, challenges, and future perspectives of SRM in the food science. This review provides significant insights into SRM techniques, operation principles, recent advances, and applications in food materials. This contribution can be considered a brief guide for introducing non-experts in the food area to the knowledge of SRM techniques and contains useful information for experts in fluorescence and confocal microscopy interested in the use of SRM.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and material are results from research and properly referenced along with the manuscript.
References
Achimovich, A. M., Ai, H., & Gahlmann, A. (2019). Enabling technologies in super-resolution fluorescence microscopy: Reporters, labeling, and methods of measurement. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 58, 224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.05.001
Bach, J. N., Giacomelli, G., & Bramkamp, M. (2017). Sample preparation and choice of fluorophores for single and dual color photo-activated localization microscopy (PALM) with bacterial cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1563, 129–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6810-7_9
Bachmann, M., Fiederling, F., & Bastmeyer, M. (2016). Practical limitations of superresolution imaging due to conventional sample preparation revealed by a direct comparison of CLSM, SIM and dSTORM. Journal of Microscopy, 262(3), 306–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12365
Balzarotti, F., Eilers, Y., Gwosch, K. C., Gynnå, A. H., Westphal, V., Stefani, F. D., Elf, J., & Hell, S. W. (2017). With minimal photon fluxes. Science, 355, 606–612. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aak9913
Barentine, A. E. S., Schroeder, L. K., Graff, M., Baddeley, D., & Bewersdorf, J. (2018). Simultaneously measuring image features and resolution in live-cell STED images. Biophysical Journal, 115(6), 951–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2018.07.028
Bates, M., Huang, B., & Zhuang, X. (2008). Super-resolution microscopy by nanoscale localization of photo-switchable fluorescent probes. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 12(5), 505–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.08.008
Beun, L. H., Albertazzi, L., van der Zwaag, D., de Vries, R., & Cohen Stuart, M. A. (2016). Unidirectional living growth of self-assembled protein nanofibrils revealed by super-resolution microscopy. ACS Nano, 10(5), 4973–4980. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b01017
Blythe, K. L., & Willets, K. A. (2016). Super-resolution imaging of fluorophore-labeled DNA bound to gold nanoparticles: A single-molecule, single-particle approach. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(2), 803–815. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b08534
Bonilla, J. C., & Clausen, M. P. (2022). Super-resolution microscopy to visualize and quantify protein microstructural organization in food materials and its relation to rheology: Egg white proteins. Food Hydrocolloids, 124, 107281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107281
Breedijk, R. M. P., Wen, J., Krishnaswami, V., Bernas, T., Manders, E. M. M., Setlow, P., Vischer, N. O. E., & Brul, S. (2020). A live-cell super-resolution technique demonstrated by imaging germinosomes in wild-type bacterial spores. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62377-1
Carsten, A., Rudolph, M., Weihs, T., Schmidt, R., Wurm, C. A., Diepold, A., Failla, A. V., Wolters, M., & Aepfelbacher, M. (2021). Visualization of bacterial type 3 secretion system components down to the molecular level by MINFLUX nanoscopy. bioRxiv.
Castello, M., Tortarolo, G., Coto Hernández, I., Deguchi, T., Diaspro, A., & Vicidomini, G. (2017). Removal of anti-Stokes emission background in STED microscopy by FPGA-based synchronous detection. Review of Scientific Instruments, 88(5), 053701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4983082
Chang, M., Oh, J., Kim, Y., Hohng, S., & Lee, J.-B. (2017). Extended depth of field for single biomolecule optical imaging-force spectroscopy. Optics Express, 25(25), 32189. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.25.032189
Chen, B., Gong, W., Yang, Z., Pan, W., Verwilst, P., Shin, J., Yan, W., Liu, L., Qu, J., & Kim, J. S. (2020). STORM imaging of mitochondrial dynamics using a vicinal-dithiol-proteins-targeted probe. Biomaterials, 243, 119938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119938
Chen, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, Z., Zheng, C., Huang, Y., Cao, R., Zhu, D., Xu, L., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y. H., Fan, J., Jin, L., Xu, Y., Kuang, C., & Liu, X. (2018). Multi-color live-cell super-resolution volume imaging with multi-angle interference microscopy. Nature Communications, 9(1), 4818. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07244-4
Codron, P., Letournel, F., Marty, S., Renaud, L., Bodin, A., Duchesne, M., Verny, C., Lenaers, G., Duyckaerts, C., Julien, J.-P., Cassereau, J., & Chevrollier, A. (2021). STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM) reveals the nanoscale organization of pathological aggregates in human brain. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 47(1), 127–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12646
Coltharp, C., & Xiao, J. (2012). Superresolution microscopy for microbiology. Cellular Microbiology, 14(12), 1808–1818. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.12024
Culley, S., Tosheva, K. L., Matos Pereira, P., & Henriques, R. (2018). SRRF: Universal live-cell super-resolution microscopy. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 101, 74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2018.05.014
D’Incecco, P., Ong, L., Gras, S., & Pellegrino, L. (2018). A fluorescence in situ staining method for investigating spores and vegetative cells of Clostridia by confocal laser scanning microscopy and structured illuminated microscopy. Micron, 110, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2018.04.005
De Zitter, E., Ridard, J., Thédié, D., Adam, V., Lévy, B., Byrdin, M., Gotthard, G., Van Meervelt, L., Dedecker, P., Demachy, I., & Bourgeois, D. (2020). Mechanistic Investigations of Green mEos4b Reveal a Dynamic Long-Lived Dark State. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(25), 10978–10988. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c01880
Dumbović, G., Sanjuan, X., Perucho, M., & Forcales, S. V. (2021). Stimulated emission depletion (STED) super resolution imaging of RNA- and protein-containing domains in fixed cells. Methods, 187, 68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.04.009
Dunst, S., & Tomancak, P. (2019). Imaging flies by fluorescence microscopy: Principles, technologies, and applications. Genetics, 211, 15–34. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.118.300227
Dürrenberger, M. B., Handschin, S., Conde-Petit, B., & Escher, F. (2001). Visualization of food structure by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). LWT - Food Science and Technology, 34(1), 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1006/fstl.2000.0739
Ellefsen, K. L., Dynes, J. L., Parker, I., & Waigh, T. (2015). Spinning-spot shadowless TIRF microscopy. PLoS ONE, 10(8), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136055
Feiner-Gracia, N., Pujals, S., Delcanale, P., & Albertazzi, L. (2018). 15 - Advanced optical microscopy techniques for the investigation of cell-nanoparticle interactions. In G. Ciofani (Ed.), Micro and Nano Technologies (pp. 219–236). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814156-4.00015-X
Ferrand, A., Schleicher, K. D., Ehrenfeuchter, N., Heusermann, W., & Biehlmaier, O. (2019). Using the NoiSee workflow to measure signal-to-noise ratios of confocal microscopes. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37781-3
Fomby, P., & Cherlin, A. J. (2011). Photocontrolable Flourecent proteins for superresulution imaging. Annual Review of Biophysics, 72(2), 181–204. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-051013-022836
Foroutanparsa, S., Brüls, M., Tas, R. P., Elizabeth, C., & Voets, I. K. (2021). Super resolution microscopy imaging of pH induced changes in the microstructure of casein micelles. Food Structure, 30, 100231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100231
Fu, Y., & Finney, N. S. (2018). Small-molecule fluorescent probes and their design. RSC Advances, 8(51), 29051–29061. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra02297f
Gagnon, L. (2020). Imaging the genome in 3D at super resolution. Microscopy Today, 28(6), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1551929520001546
Ganjkhani, Y., Charsooghi, M. A., Akhlaghi, E. A., & Moradi, A. R. (2017). Super-resolved Mirau digital holography by structured illumination. Optics Communications, 404, 110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.05.061
Gevaux, D. (2014). Seeing the Nanoscale. Nature Nanotechnology, 9, 878. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(06)70079-2
Glover, Z. J., Bisgaard, A. H., Andersen, U., Povey, M. J., Brewer, J. R., & Simonsen, A. C. (2019). Cross-correlation analysis to quantify relative spatial distributions of fat and protein in super-resolution microscopy images of dairy gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 97, 105225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105225
Glover, Z. J., Francis, M. J., Bisgaard, A. H., Andersen, U., Johansen, L. B., Povey, M. J., Holmes, M. J., Brewer, J. R., & Simonsen, A. C. (2020). Dynamic moisture loss explored through quantitative super-resolution microscopy, spatial micro-viscosity and macroscopic analyses in acid milk gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 101, 105501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105501
Görlitz, F., Guldbrand, S., Runcorn, T. H., Murray, R. T., Jaso-Tamame, A. L., Sinclair, H. G., Martinez-Perez, E., Taylor, J. R., Neil, M. A. A., Dunsby, C., & French, P. M. W. (2018). easySLM-STED: Stimulated emission depletion microscopy with aberration correction, extended field of view and multiple beam scanning. Journal of Biophotonics, 11(11), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201800087
Göttfert, F., Wurm, C. A., Mueller, V., Berning, S., Cordes, V. C., Honigmann, A., & Hell, S. W. (2013). Coaligned dual-channel STED nanoscopy and molecular diffusion analysis at 20 nm resolution. Biophysical Journal, 105(1), 6–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2013.05.029
Gustafsson, M. G. L. (2005). Nonlinear structured-illumination microscopy: Wide-field fluorescence imaging with theoretically unlimited resolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(37), 13081–13086. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0406877102
Gwosch, K. C., Pape, J. K., Balzarotti, F., Hoess, P., Ellenberg, J., Ries, J., & Hell, S. W. (2020). MINFLUX nanoscopy delivers 3D multicolor nanometer resolution in cells. Nature Methods, 17(2), 217–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0688-0
Halabi, E. A., Thiel, Z., Trapp, N., Pinotsi, D., & Rivera-Fuentes, P. (2017). A photoactivatable probe for super-resolution imaging of enzymatic activity in live cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 139(37), 13200–13207. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b07748
Heintzmann, R., & Huser, T. (2017). Super-Resolution structured illumination microscopy. Chemical Reviews, 117(23), 13890–13908. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00218
Henriques, R., Griffiths, C., Rego, E. H., & Mhlanga, M. M. (2011). PALM and STORM: Unlocking live-cell super-resolution. Biopolymers, 95(5), 322–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.21586
Hernández-Varela, J. D., Chanona-Pérez, J. J., Calderón Benavides, H. A., Cervantes Sodi, F., & Vicente-Flores, M. (2021a). Effect of ball milling on cellulose nanoparticles structure obtained from garlic and agave waste. Carbohydrate Polymers, 255, 117347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117347
Hernández-Varela, J. D., Chanona-Pérez, J. J., Calderón Benavides, H. A., Gallegos Cerda, S. D., Gonzalez Victoriano, L., Perea Flores, M. D. J., Campos López, M., Rojas Candelas, L. E., & Arrendondo Tamayo, B. (2021b). CLSM and TIRF images from lignocellulosic materials: Garlic skin and agave fibers study. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 27(1), 1730–1734. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1431927621006334
Hohlbein, J. (2021). Single-molecule localization microscopy as an emerging tool to probe multiscale food structures. Food Structure, 30, 100236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100236
Huff, J. (2015). The Airyscan detector from ZEISS: Confocal imaging with improved signal-to-noise ratio and super-resolution. Nature Methods, 12(12), i–ii. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.388
Huszka, G., & Gijs, M. A. M. (2019). Super-resolution optical imaging: A comparison. Micro and Nano Engineering, 2, 7–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mne.2018.11.005
Ishitsuka, Y., Nienhaus, K., & Nienhaus, G. U. (2014). Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins for super-resolution microscopy. In S. Cambridge (Ed.), Photoswitching Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology (Vol. 1148). New York: Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0470-9
Jeong, D., & Kim, D. (2022). Recent developments in correlative super-resolution fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy. Molecules and Cells, 45(1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2021.5011
Jonkman, J., Brown, C. M., Wright, G. D., Anderson, K. I., & North, A. J. (2020). Tutorial: Guidance for quantitative confocal microscopy. Nature Protocols, 15(5), 1585–1611. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0313-9
Jost, A., & Heintzmann, R. (2013). Superresolution Multidimensional Imaging with Structured Illumination Microscopy Keynote Topic. Annual Review of Materials Research, 43, 261–282. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-071312-121648
Jradi, F. M., & Lavis, L. D. (2019). Chemistry of photosensitive fluorophores for single-molecule localization microscopy [Review-article]. ACS Chemical Biology, 14(6), 1077–1090. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00197
Klar, T. A., Jakobs, S., Dyba, M., Egner, A., & Hell, S. W. (2000). Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(15), 8206–8210. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.15.8206
Klementieva, N. V., Pavlikov, A. I., Moiseev, A. A., Bozhanova, N. G., Mishina, N. M., Lukyanov, S. A., Zagaynova, E. V., Lukyanov, K. A., & Mishin, A. S. (2017). Intrinsic blinking of red fluorescent proteins for super-resolution microscopy. Chemical Communications, 53(5), 949–951. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cc09200d
Klevanski, M., Herrmannsdoerfer, F., Sass, S., Venkataramani, V., Heilemann, M., & Kuner, T. (2020). Automated highly multiplexed super-resolution imaging of protein nano-architecture in cells and tissues. Nature Communications, 11(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15362-1
Klötzner, D. P., Klehs, K., Heilemann, M., & Heckel, A. (2017). A new photoactivatable near-infrared-emitting QCy7 fluorophore for single-molecule super-resolution microscopy. Chemical Communications, 53(71), 9874–9877. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc04996j
Ko, S., & Gunasekaran, S. (2007). Error correction of confocal microscopy images for in situ food microstructure evaluation. Journal of Food Engineering, 79(3), 935–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.03.014
Kozma, E., & Kele, P. (2019). Fluorogenic probes for super-resolution microscopy. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 17(2), 215–233. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ob02711k
Kudalkar, E. M., Davis, T. N., & Asbury, C. L. (2016a). Preparation of reactions for imaging with total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2016(5), 466–470. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot085563
Kudalkar, E. M., Deng, Y., Davis, T. N., & Asbury, C. L. (2016b). Coverslip cleaning and functionalization for total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2016(5), pdb.prot085548. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot085548
Leménager, G., De Luca, E., Sun, Y. P., & Pompa, P. P. (2014). Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of biocompatible carbon dots. Nanoscale, 6(15), 8617–8623. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr01970a
Li, M., & Huang, Z. L. (2020). Rethinking resolution estimation in fluorescence microscopy: From theoretical resolution criteria to super-resolution microscopy. Science China Life Sciences, 63(12), 1776–1785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1785-4
Liesche, J., Ziomkiewicz, I., & Schulz, A. (2013). Super-resolution imaging with Pontamine Fast Scarlet 4BS enables direct visualization of cellulose orientation and cell connection architecture in onion epidermis cells. BMC Plant Biology, 13, 226.
Liu, J., Li, Q., Li, M., Gao, S., Liu, C., Zou, L., & Tan, J. (2017). Elliptical mirror-based TIRF microscopy with shadowless illumination and adjustable penetration depth. Optics Letters, 42(13), 2587. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.42.002587
Liu, W., Liu, Q., Zhang, Z., Han, Y., Kuang, C., Xu, L., Yang, H., & Liu, X. (2019). Three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live whole cells using galvanometer-based structured illumination microscopy. Optics Express, 27(5), 7237. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.27.007237
Lu, K., Vu, C. Q., Matsuda, T., & Nagai, T. (2019). Fluorescent protein-based indicators for functional super-resolution imaging of biomolecular activities in living cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225784
MacDonald, P. J., Gayda, S., Haack, R. A., Ruan, Q., Himmelsbach, R. J., & Tetin, S. Y. (2018). Rhodamine-derived fluorescent dye with inherent blinking behavior for super-resolution imaging. Analytical Chemistry, 90(15), 9165–9173. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01645
Manley, S., Gillette, J. M., Patterson, G. H., Shroff, H., Hess, H. F., Betzig, E., & Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (2008). High-density mapping of single-molecule trajectories with photoactivated localization microscopy. Nature Methods, 5(2), 155–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1176
Markwirth, A., Lachetta, M., Mönkemöller, V., Heintzmann, R., Hübner, W., Huser, T., & Müller, M. (2019). Video-rate multi-color structured illumination microscopy with simultaneous real-time reconstruction. Nature Communications, 10(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12165-x
Martens, K. J. A., Van Duynhoven, J., & Hohlbein, J. (2020). Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of κ-carrageenan gels investigated via single-particle-tracking fluorescence microscopy. Langmuir, 36(20), 5502–5509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00393
Martin-Fernandez, M. L., Tynan, C. J., & Webb, S. E. D. (2013). A “pocket guide” to total internal reflection fluorescence. Journal of Microscopy, 252(1), 16–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12070
Mattheyses, A. L., Simon, S. M., & Rappoport, J. Z. (2010). Imaging with total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy for the cell biologist. Journal of Cell Science, 123(21), 3621–3628. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.056218
Mau, A., Friedl, K., Leterrier, C., Bourg, N., & Lévêque-Fort, S. (2021). Fast widefield scan provides tunable and uniform illumination optimizing super-resolution microscopy on large fields. Nature Communications, 12(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23405-4
McEvoy, A. L., Hoi, H., Bates, M., Platonova, E., Cranfill, P. J., Baird, M. A., Davidson, M. W., Ewers, H., Liphardt, J., & Campbell, R. E. (2012). mMaple: A photoconvertible fluorescent protein for use in multiple imaging modalities. PLoS ONE, 7(12), e51314. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051314
Minoshima, M., & Kikuchi, K. (2017). Photostable and photoswitching fluorescent dyes for super-resolution imaging. Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 22(5), 639–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-016-1435-y
Möckl, L., & Moerner, W. E. (2020). Super-resolution microscopy with single molecules in biology and beyond-essentials, current trends, and future challenges. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(42), 17828–17844. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c08178
Morozova, K. S., Piatkevich, K. D., Gould, T. J., Zhang, J., Bewersdorf, J., & Verkhusha, V. V. (2010). Far-red fluorescent protein excitable with red lasers for flow cytometry and superresolution STED nanoscopy. Biophysical Journal, 99(2), L13–L15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.025
Nevskyi, O., Sysoiev, D., Dreier, J., Stein, S. C., Oppermann, A., Lemken, F., Janke, T., Enderlein, J., Testa, I., Huhn, T., & Wöll, D. (2018). Fluorescent diarylethene photoswitches–A universal tool for super-resolution microscopy in nanostructured materials. Small (weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 14(10), 1703333. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703333
Nollmann, M., & Georgieva, M. (2015). Superresolution microscopy for bioimaging at the nanoscale: From concepts to applications in the nucleus. Research and Reports in Biology. https://doi.org/10.2147/rrb.s60501
Oheim, M., Salomon, A., Weissman, A., Brunstein, M., & Becherer, U. (2019). Calibrating evanescent-wave penetration depths for biological TIRF microscopy. Biophysical Journal, 117(5), 795–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2019.07.048
Oracz, J., Adolfsson, K., Westphal, V., Radzewicz, C., Borgström, M. T., Sahl, S. J., Prinz, C. N., & Hell, S. W. (2017). Ground State depletion nanoscopy resolves semiconductor nanowire barcode segments at room temperature. Nano Letters, 17(4), 2652–2659. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b00468
Pape, J. K., Stephan, T., Balzarotti, F., Büchner, R., Lange, F., Riedel, D., Jakobs, S., & Hell, S. W. (2020). Multicolor 3D MINFLUX nanoscopy of mitochondrial MICOS proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(34), 20607–20614. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2009364117
Peddie, C. J., Domart, M.-C., Snetkov, X., O’Toole, P., Larijani, B., Way, M., Cox, S., & Collinson, L. M. (2017). Correlative super-resolution fluorescence and electron microscopy using conventional fluorescent proteins in vacuo. Journal of Structural Biology, 199(2), 120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2017.05.013
Pennacchietti, F., Gould, T., & Hess, S. (2017). The Role of probe photophysics in localization-based superresolution microscopy. Biophysical Journal, 113(9), 2037–2054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.08.054
Pereira, P. M., Almada, P., & Henriques, R. (2015). High-content 3D multicolor super-resolution localization microscopy. Methods in Cell Biology, 125, 95–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2014.10.004
Poulter, N. S., Pitkeathly, W. T. E., Smith, P. J., & Rappoport, J. Z. (2015). The Physical basis of total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy and its cellular applications. In P. J. Verveer (Ed.), Advanced Fluorescence Microscopy: Methods and Protocols (pp. 1–23). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2080-8_1
Prakash, K. (2021). Laser-free super-resolution microscopy. Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0144
Price, R. L., & Jerome, W. G. (2003). More basic confocal microscopy: A tutorial. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 9, 1568–1569. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1431927603447843
Pujals, S., Feiner-Gracia, N., Delcanale, P., Voets, I., & Albertazzi, L. (2019). Super-resolution microscopy as a powerful tool to study complex synthetic materials. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 3(2), 68–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-018-0070-2
Rahlves, M., Roth, B., & Reithmeier, E. (2017). Confocal signal evaluation algorithms for surface metrology: Uncertainty and numerical efficiency. Applied Optics, 56(21), 5920. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.56.005920
Reymond, L., Ziegler, J., Knapp, C., Wang, F.-C., Huser, T., Ruprecht, V., & Wieser, S. (2019). SIMPLE: Structured illumination based point localization estimator with enhanced precision. Optics Express, 27(17), 24578. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.27.024578
Schermelleh, L., Heintzmann, R., & Leonhardt, H. (2010). A guide to super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Journal of Cell Biology, 190(2), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201002018
Schloetel, J.-G., Heine, J., Cowman, A. F., & Pasternak, M. (2019). Guided STED nanoscopy enables super-resolution imaging of blood stage malaria parasites. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 4674. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40718-z
Schmidt, R., Weihs, T., Wurm, C. A., Jansen, I., Rehman, J., Sahl, S. J., & Hell, S. W. (2021). MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope. Nature Communications, 12(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21652-z
Schubert, V. (2017). Super-resolution microscopy - Applications in plant cell research. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00531
Schubert, V., & Weisshart, K. (2015). Abundance and distribution of RNA polymerase II in Arabidopsis interphase nuclei. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(6), 1687–1698. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv091
Sehayek, S., Gidi, Y., Glembockyte, V., Brandaõ, H. B., François, P., Cosa, G., & Wiseman, P. W. (2019). A high-throughput image correlation method for rapid analysis of fluorophore photoblinking and photobleaching rates. ACS Nano, 13(10), 11955–11966. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b06033
Shterman, D., Gjonaj, B., & Bartal, G. (2018). Experimental demonstration of multi moiré structured illumination microscopy. ACS Photonics, 5(5), 1898–1902. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.8b00280
Small, A., & Stahlheber, S. (2014). Fluorophore localization algorithms for super-resolution microscopy. Nature Methods, 11(3), 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2844
Su, Y., Zhang, M., Fang, Z., & Zhang, W. (2017). Analysis of dehydration kinetics, status of water and oil distribution of microwave-assisted vacuum frying potato chips combined with NMR and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Food Research International, 101, 188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.08.067
Szabó, Á., Szendi-Szatmári, T., Ujlaky-Nagy, L., Rádi, I., Vereb, G., Szöllősi, J., & Nagy, P. (2018). The effect of fluorophore conjugation on antibody affinity and the photophysical properties of dyes. Biophysical Journal, 114(3), 688–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.12.011
Szkop, M., Kliszcz, B., & Kasprzak, A. A. (2018). A simple and reproducible protocol of glass surface silanization for TIRF microscopy imaging. Analytical Biochemistry, 549, 119–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.03.020
Tam, J., & Merino, D. (2015). Stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) in comparison with stimulated emission depletion (STED) and other imaging methods. Journal of Neurochemistry, 135(4), 643–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13257
Tang, J., Ren, J., & Han, K. Y. (2019). Fluorescence Imaging with Tailored Light. Nanophotonics, 8(12), 2111–2128. https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2019-0227
Tao, A., Zhang, R., & Yuan, J. (2020). Characterization of photophysical properties of photoactivatable fluorescent proteins for super-resolution microscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 124(10), 1892–1897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b11028
Thill, S., Schmidt, T., Wöll, D., & Gebhardt, R. (2020). Single particle tracking as a new tool to characterise the rennet coagulation process. International Dairy Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2020.104659
Thompson, M. A., Biteen, J. S., Lord, S. J., Conley, N. R., & Moerner, W. E. (2010). Molecules and methods for super-resolution imaging. Methods in Enzymology (1st ed., Vol. 475). Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(10)75002-3
Tichá, M., Hlaváčková, K., Hrbáčková, M., Ovečka, M., Šamajová, O., & Šamaj, J. (2020). Super-resolution imaging of microtubules in Medicago sativa. Methods in Cell Biology, 160, 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2020.03.004
Tortarolo, G., Sun, Y., Teng, K. W., Ishitsuka, Y., Lanzanó, L., Selvin, P. R., Barbieri, B., Diaspro, A., & Vicidomini, G. (2019). Photon-separation to enhance the spatial resolution of pulsed STED microscopy. Nanoscale, 11(4), 1754–1761. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr07485b
Upputuri, P. K., & Pramanik, M. (2017). Microsphere-aided optical microscopy and its applications for super-resolution imaging. Optics Communications, 404, 32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.05.049
van de Linde, S., Wolter, S., Heilemann, M., & Sauer, M. (2010). The effect of photoswitching kinetics and labeling densities on super-resolution fluorescence imaging. Journal of Biotechnology, 149(4), 260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.02.010
Vangindertael, J., Camacho, R., Sempels, W., Mizuno, H., Dedecker, P., & Janssen, K. P. F. (2018). An introduction to optical super-resolution microscopy for the adventurous biologist. Methods and Applications in Fluorescence, 6(2), 022003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2050-6120/aaae0c
Villegas-Hernández, L. E., Nystad, M., Ströhl, F., Basnet, P., Acharya, G., & Ahluwalia, B. S. (2020). Visualizing ultrastructural details of placental tissue with super-resolution structured illumination microscopy. Placenta, 97, 42–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2020.06.007
Vinçon, B., Geisler, C., & Egner, A. (2020). Pixel hopping enables fast STED nanoscopy at low light dose. Optics Express, 28(4), 4516–4528. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.385174
Walsh, C., Holroyd, N., Shipley, R., & Walker-Samuel, S. (2020). Asymmetric point spread function estimation and deconvolution for serial-sectioning block-face imaging. In B. W. Papież, A. I. L. Namburete, M. Yaqub, & J. A. Noble (Eds.), Medical Image Understanding and Analysis (pp. 235–249). Springer International Publishing.
Wang, H., Gao, G., Ke, L., Zhou, J., Rao, P., Jin, Y., He, L., Wan, J., & Wang, Q. (2019). Isolation of colloidal particles from porcine bone soup and their interaction with murine peritoneal macrophage. Journal of Functional Foods, 54, 403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.021
Wang, S., Moffitt, J. R., Dempsey, G. T., Xie, X. S., & Zhuang, X. (2014). Characterization and development of photoactivatable fluorescent proteins for single-molecule–based superresolution imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(23), 8452–8457. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1406593111
Wang, Y., Lin, J., Zhang, Q., Chen, X., Luan, H., & Gu, M. (2021). Fluorescence nanoscopy in neuroscience. Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.11.010
Wegel, E., Göhler, A., Lagerholm, B. C., Wainman, A., Uphoff, S., Kaufmann, R., & Dobbie, I. M. (2016). Imaging cellular structures in super-resolution with SIM, STED and Localisation Microscopy: A practical comparison. Scientific Reports, 6, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27290
Wei, X., & Gu, B. (2019). Optical imaging in human disease and biological. Singapore: Springer.
Wijesooriya, C. S., Peterson, J. A., Shrestha, P., Gehrmann, E. J., Winter, A. H., & Smith, E. A. (2018). A photoactivatable BODIPY probe for localization-based super-resolution cellular imaging. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 57(39), 12685–12689. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201805827
Wurm, C. A., Kolmakov, K., Göttfert, F., Ta, H., Bossi, M., Schill, H., Berning, S., Jakobs, S., Donnert, G., Belov, V. N., & Hell, S. W. (2012). Novel red fluorophores with superior performance in STED microscopy. Optical Nanoscopy, 1(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2192-2853-1-7
Yang, Z., Sharma, A., Qi, J., Peng, X., Lee, D., Hu, R., Lin, D., Qu, J., & Kim, J. (2016). Super-Resolution fluorescent materials: An insight into design and bioimaging applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 45, 4651–4667. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00875A
Zhao, W., Zhao, S., Li, L., Huang, X., Xing, S., Zhang, Y., Qiu, G., Han, Z., Shang, Y., Sun, D., Shan, C., Wu, R., Gu, L., Zhang, S., Chen, R., Xiao, J., Mo, Y., Wang, J., Ji, W., Chen, X., Ding, B., et al. (2022). Sparse deconvolution improves the resolution of live-cell super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Nature Biotechnology, 40(4), 606–617.
Zheng, H. (2019). Introduction: Measuring rheological properties of foods. Food Engineering Series. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27134-3_1
Zhuang, X. (2009). Nano-imaging with STORM. Nature Photonics, 3(7), 365–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.101
Zobiak, B., & Failla, A. V. (2018). Advanced spinning disk-TIRF microscopy for faster imaging of the cell interior and the plasma membrane. Journal of Microscopy, 269(3), 282–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12626
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank CONACyT, BEIFI and IPN in Mexico City, Mexico.
Funding
The authors declared the financial support provided by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) with projects number 239899, 268660 and Secretaria de Investigación y Posgrado at Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN) with projects numbers 20195198, 20200506 and 20210065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SDGC: conceptualization, methodology, writing–original draft, visualization, data curation, formal analysis. JDHV: conceptualization, methodology, writing–original draft, visualization, data curation, formal analysis. JJCP: conceptualization, methodology, writing–review and editing, data curation, formal analysis, supervision. BAT: writing–review and editing. JVMM: writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gallegos-Cerda, S.D., Hernández-Varela, J.D., Chanona-Pérez, J.J. et al. Super-Resolution Microscopy and Their Applications in Food Materials: Beyond the Resolution Limits of Fluorescence Microscopy. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 268–288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02883-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02883-4