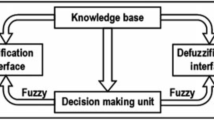
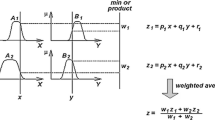
Abstract
Release modeling is an important issue in designing controlled release systems for food bioactive compounds and nutraceuticals in order to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. Adequate knowledge about such mechanisms leads to designing optimal controlled delivery vehicles. The conventional modeling approaches such as mathematical and mechanistic modeling represent considerable information about the release phenomena but the limiting factor in their applicability is the poor possibility of generalization of the curve fitting results. In this study, intelligent and probabilistic models for evaluating the release of food bioactive ingredients from carriers/nanocarriers are reviewed. Stochastic methods such as Monte Carlo (MC) and cellular automata (CA) are developed based on the idea of existing random fluctuations in the release process that can be an alternative to overcome the limitations of the conventional methods. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are also very efficient when a nonlinear relationship exists between release profiles and formulation and process factors. The release process can be optimized using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANFIS) and genetic algorithms (GAs). In this study, theoretical background and fundamental operating principles of probabilistic methods (MC and CA) and artificial intelligence-based methods (ANNs, ANFIS, GAs) in the field of food bioactive release from carriers/nanocarriers are introduced. Also, some application examples for utilization of such methods are briefly discussed to preset a state of the art for practical application of these models in future food-related applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article because no database was generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abad, F. Y., & M., Rajabzadeh, G., Taghvaei Ganjali, S., & Tavakoli, R. (2016). Preparing allicin nanocapsules and determining the factors controlling their particle size through artificial intelligence. International Journal of Food Engineering, 12(3), 257–264. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2015-0251
Abuiziah, I., & Nidal, S. (2013). A review of genetic algorithm optimization: operations and applications to water pipeline systems.
Aliakbarian, B., Sampaio, F. C., de Faria, J. T., Pitangui, C. G., Lovaglio, F., Casazza, A. A., Converti, A., & Perego, P. (2018). Optimization of spray drying microencapsulation of olive pomace polyphenols using response surface methodology and artificial neural network. LWT, 93, 220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.03.048
Baghaei, B., Saeb, M. R., Jafari, S. H., Khonakdar, H. A., Rezaee, B., Goodarzi, V., & Mohammadi, Y. (2017). Modeling and closed-loop control of particle size and initial burst of PLGA biodegradable nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 134(33), 45145. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45145
Barat, A. (2006). Probabilistic models for drug dissolution Dublin City University].
Barat, A., Ruskin, H. J., & Crane, M. (2006a). Probabilistic methods for drug dissolution. Part 2. Modelling a soluble binary drug delivery system dissolving in vitro. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 14(7), 857–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2006a.03.003
Barat, A., Ruskin, H. J., & Crane, M. (2006b). Probabilistic models for drug dissolution. Part 1. Review of Monte Carlo and stochastic cellular automata approaches. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 14(7), 843–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2006b.01.004
Barmpalexis, P., Kachrimanis, K., Tsakonas, A., & Georgarakis, E. (2011). Symbolic regression via genetic programming in the optimization of a controlled release pharmaceutical formulation. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 107(1), 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2011.01.012
Belščak-Cvitanović, A., Jurić, S., Đorđević, V., Barišić, L., Komes, D., Ježek, D., Bugarski, B., & Nedović, V. (2016). Chemometric evaluation of binary mixtures of alginate and polysaccharide biopolymers as carriers for microencapsulation of green tea polyphenols. International Journal of Food Properties, 20(9), 1971–1986. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1225762
Bezbradica, M., Crane, M., & Ruskin, H. J. (2012, 2012/07). Parallelisation strategies for large scale cellular automata frameworks in pharmaceutical modelling 2012 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation (HPCS). https://doi.org/10.1109/hpcsim.2012.6266916
Binder, K., Ceperley, D. M., Hansen, J.-P., Kalos, M., Landau, D., Levesque, D., Mueller-Krumbhaar, H., Stauffer, D., & Weis, J.-J. (2012). Monte Carlo methods in statistical physics (Vol. 7). Springer Science & Business Media.
Calo, R. (2017). Artificial intelligence policy: A roadmap. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3015350
Chansanroj, K., Petrović, J., Ibrić, S., & Betz, G. (2011). Drug release control and system understanding of sucrose esters matrix tablets by artificial neural networks. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 44(3), 321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2011.08.012
Chiroma, H., Abdulkareem, S., Abubakar, A., & Herawan, T. (2017). Neural networks optimization through genetic algorithm searches: A review. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci, 11(6), 1543–1564.
Colbourn, E., & Rowe, R. (2005). Neural computing and pharmaceutical formulation. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology. In: New York, USA: Marcel Dekker.
Colbourn, E. A., Roskilly, S. J., Rowe, R. C., & York, P. (2011). Modelling formulations using gene expression programming – a comparative analysis with artificial neural networks. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 44(3), 366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2011.08.021
Dan, N. (2014). Nanostructured lipid carriers: Effect of solid phase fraction and distribution on the release of encapsulated materials. Langmuir, 30(46), 13809–13814. https://doi.org/10.1021/la5030197
Dan, N. (2016). Compound release from nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). Journal of Food Engineering, 171, 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.10.005
Das, S., Dey, A., Pal, A., & Roy, N. (2015). Applications of artificial intelligence in machine learning: Review and prospect. International Journal of Computer Applications, 115(9), 31–41. https://doi.org/10.5120/20182-2402
Djuris, J., Ibric, S., & Djuric, Z. (2013). Neural computing in pharmaceutical products and process development. In Computer-Aided Applications in Pharmaceutical Technology (pp. 91–175): Elsevier.
Espinosa-Sandoval, L., Cerqueira, M., Ochoa-Martínez, C., & Ayala-Aponte, A. (2019). Phenolic compound–loaded nanosystems: Artificial neural network modeling to predict particle size, polydispersity index, and encapsulation efficiency. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(8), 1395–1408.
Espinosa-Sandoval, L. A., Ochoa-Martínez, C. I., & Ayala-Aponte, A. A. (2020). Prediction of in vitro release of nanoencapsulated phenolic compounds using artificial neural networks. DYNA, 87, 244–250. http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0012-73532020000100244&nrm=iso
Fathi, M., Mohebbi, M., Varshosaz, J., & Shahidi, F. (2013). Cellular automata modeling of hesperetin release phenomenon from lipid nanocarriers. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(11), 3134–3142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0995-2
Ganje, M., Jafari, S. M., Tamadon, A. M., Niakosari, M., & Maghsoudlou, Y. (2019). Mathematical and fuzzy modeling of limonene release from amylose nanostructures and evaluation of its release kinetics. Food Hydrocolloids, 95, 186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.045
Gharibzahedi, S. M. T., & Jafari, S. M. (2017). The importance of minerals in human nutrition: Bioavailability, food fortification, processing effects and nanoencapsulation. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 62, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.02.017
Ghosh, M., Srivastava, S., Raigar, R. K., & Mishra, H. N. (2020). Multilayer perceptron neural networking for prediction of quality attributes of spray-dried vegetable oil powder. Soft Computing, 24(13), 9821–9833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04494-2
Goonoo, N., Bhaw-Luximon, A., Ujoodha, R., Jhugroo, A., Hulse, G. K., & Jhurry, D. (2014). Naltrexone: A review of existing sustained drug delivery systems and emerging nano-based systems. Journal of Controlled Release, 183, 154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.046
Gurikov, P., Kolnoochenko, A., Golubchikov, M., Menshutina, N., & Smirnova, I. (2016). A synchronous cellular automaton model of mass transport in porous media. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 84, 446–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2015.10.001
Hezaveh, H., Muhamad, I. I., Noshadi, I., Shu Fen, L., & Ngadi, N. (2012). Swelling behaviour and controlled drug release from cross-linked κ-carrageenan/NaCMC hydrogel by diffusion mechanism. Journal of Microencapsulation, 29(4), 368–379. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2011.651501
Huang, S.-M., Kuo, C.-H., Chen, C.-A., Liu, Y.-C., & Shieh, C.-J. (2017). RSM and ANN modeling-based optimization approach for the development of ultrasound-assisted liposome encapsulation of piceid. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 36, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.11.016
Huang, Y., Kangas, L. J., & Rasco, B. A. (2007). Applications of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in food science. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 47(2), 113–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390600626453
Jafari, S. M., Ganje, M., Dehnad, D., & Ghanbari, V. (2016). Mathematical, fuzzy logic and artificial neural network modeling techniques to predict drying kinetics of onion. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 40(2), 329–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12610
Kaunisto, E., Marucci, M., Borgquist, P., & Axelsson, A. (2011). Mechanistic modelling of drug release from polymer-coated and swelling and dissolving polymer matrix systems. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 418(1), 54–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.01.021
Kosmidis, K., & Dassios, G. (2019). Monte Carlo simulations in drug release. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, 46(2), 165–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-019-09625-8
Laaksonen, H., Hirvonen, J., & Laaksonen, T. (2009a). Cellular automata model for swelling-controlled drug release. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 380(1–2), 25–32.
Laaksonen, T. J., Laaksonen, H. M., Hirvonen, J. T., & Murtomäki, L. (2009b). Cellular automata model for drug release from binary matrix and reservoir polymeric devices. Biomaterials, 30(10), 1978–1987.
Lai, K., Twine, N., O’Brien, A., Guo, Y., & Bauer, D. (2019). Artificial intelligence and machine learning in bioinformatics. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (pp. 272–286): Elsevier.
Landin, M., & Rowe, R. C. (2013). Artificial neural networks technology to model, understand, and optimize drug formulations. In Formulation Tools for Pharmaceutical Development (pp. 7–37): Elsevier.
Langley, P. (2011). The changing science of machine learning. Machine Learning, 82(3), 275–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-011-5242-y
Leon, P. A., Basurto, R., Martinez, G. J., & Seck-Tuoh-Mora, J. C. (2011, 2011/07). Complex dynamics in a hexagonal cellular automaton 2011 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation. https://doi.org/10.1109/hpcsim.2011.5999904
Li, Y., Abbaspour, M. R., Grootendorst, P. V., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2015). Optimization of controlled release nanoparticle formulation of verapamil hydrochloride using artificial neural networks with genetic algorithm and response surface methodology. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 94, 170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.04.028
Looney, C. G. (1996). Advances in feedforward neural networks: Demystifying knowledge acquiring black boxes. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 8(2), 211–226.
Malekjani, N., Jafari Seid, M., Rahmati Mohammad, H., Zadeh Ebrahim, E., & Mirzaee, H. (2013). Evaluation of thin-layer drying models and artificial neural networks for describing drying kinetics of canola seed in a heat pump assisted fluidized bed dryer. In International Journal of Food Engineering (Vol. 9, pp. 375).
Malekjani, N., & Jafari, S. M. (2020). Release modeling of nanoencapsulated food ingredients by mechanistic models. In Release and Bioavailability of Nanoencapsulated Food Ingredients (pp. 247–271). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815665-0.00007-2
Malekjani, N., & Jafari, S. M. (2021). Modeling the release of food bioactive ingredients from carriers/nanocarriers by the empirical, semiempirical, and mechanistic models. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(1), 3–47.
Mamdani, E. H. (1976). Advances in the linguistic synthesis of fuzzy controllers. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 8(6), 669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7373(76)80028-4
Margenstern, M. (2011). Bacteria inspired patterns grown with hyperbolic cellular automata 2011 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation. https://doi.org/10.1109/hpcsim.2011.5999905
McClements, D. J. (2018). Recent developments in encapsulation and release of functional food ingredients: Delivery by design. Current Opinion in Food Science, 23, 80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2018.06.008
McClements, D. J. (2019). Nanoparticle-and microparticle-based delivery systems: Encapsulation, protection and release of active compounds. CRC Press.
Mendyk, A., Güres, S., Jachowicz, R., Szlęk, J., Polak, S., Wiśniowska, B., & Kleinebudde, P. (2015). From heuristic to mathematical modeling of drugs dissolution profiles: Application of artificial neural networks and genetic programming. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2015, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/863874
Menshutina, N. V., Kolnoochenko, A. V., & Lebedev, E. A. (2020). Cellular automata in chemistry and chemical engineering. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 11(1), 87–108. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-093019-075250
Movahedi, F., Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H., Alavi, S. E., Esfahani, K. M., & M. (2014). Release modeling and comparison of nanoarchaeosomal, nanoliposomal and pegylated nanoliposomal carriers for paclitaxel. Tumor Biology, 35(9), 8665–8672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2125-4
Mukherjee, I., & Routroy, S. (2012). Comparing the performance of neural networks developed by using Levenberg–Marquardt and quasi-Newton with the gradient descent algorithm for modelling a multiple response grinding process. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(3), 2397–2407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.08.087
Nwankpa, C., Ijomah, W., Gachagan, A., & Marshall, S. (2018). Activation functions: Comparison of trends in practice and research for deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.03378.
Onwulata, C. I. (2013). Microencapsulation and functional bioactive foods. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 37(5), 510–532. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4549.2012.00680.x
Oztop, M. H., & McCarthy, K. L. (2011). Mathematical modeling of swelling in high moisture whey protein gels. Journal of Food Engineering, 106(1), 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.04.007
Patanarapeelert, K., Frank, T. D., & Tang, I. M. (2011). From a cellular automaton model of tumor–immune interactions to its macroscopic dynamical equation: A drift–diffusion data analysis approach. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 53(1–2), 122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2010.07.025
Patel, J., & Patel, A. (2016). Chapter 10 - artificial neural networking in controlled drug delivery. In M. Puri, Y. Pathak, V. K. Sutariya, S. Tipparaju, & W. Moreno (Eds.), Artificial Neural Network for Drug Design, Delivery and Disposition (pp. 195–218). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801559-9.00010-7
Rebouh, S., Lefnaoui, S., Bouhedda, M., Yahoum, M. M., & Hanini, S. (2018). Neuro-fuzzy modeling of ibuprofen-sustained release from tablets based on different cellulose derivatives. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 9(1), 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-00592-0
Rey, S. J. (2015). Mathematical models in geography. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences: Second Edition (pp. 785–790). Elsevier Inc.
Sadollah, A. (2018). Introductory chapter: Which membership function is appropriate in fuzzy system? In Fuzzy Logic Based in Optimization Methods and Control Systems and its Applications: InTech.
Shahraki, M. H., Jafari, S. M., Mashkour, M., & Esmaeilzadeh, E. (2014). Optimization of closed-cycle fluidized bed drying of sesame seeds using response surface methodology and genetic algorithms. Journal of Food Engineering, 10, 167–181.
Siepmann, J., & Siepmann, F. (2008). Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 364(2), 328–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.09.004
Sun, Y., Peng, Y., Chen, Y., & Shukla, A. J. (2003). Application of artificial neural networks in the design of controlled release drug delivery systems. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 55(9), 1201–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(03)00119-4
Szlęk, J., Pacławski, A., Lau, R., Jachowicz, R., & Mendyk, A. (2013). Heuristic modeling of macromolecule release from PLGA microspheres. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 8, 4601–4611. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S53364
Von Neumann, J., & Burks, A. W. (1966). Theory of self-reproducing automata. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5(1), 3–14.
Wang, W., Ye, Z., Gao, H., & Ouyang, D. (2021). Computational pharmaceutics - a new paradigm of drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 338, 119–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.030
Yousefi, A. R., & Razavi, S. M. A. (2017). Modeling of glucose release from native and modified wheat starch gels during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion using artificial intelligence methods. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 97, 752–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.082
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8(3), 338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0019-9958(65)90241-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malekjani, N., Jafari, S.M. Intelligent and Probabilistic Models for Evaluating the Release of Food Bioactive Ingredients from Carriers/Nanocarriers. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 1495–1516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02791-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02791-7