Abstract
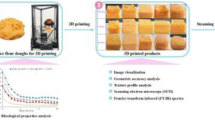
This study focused on developing nutritious 3D-printed snacks from composite flour prepared from barnyard millet, green gram, fried gram, and ajwain seeds. The work evaluated extrusion printability of the high-fibre, high-protein composite flour. Optimised process parameters that gave best resolution and stability are nozzle diameter of 0.84 mm, nozzle height of 0.63 mm, printing speed of 2400 mm/min, extruder motor speed of 300 rpm, and movement speed of X/Y and Z axis of 6000 mm/min and 1000 mm/min, respectively. 3D-printed objects were post-processed by deep frying, hot-air drying followed by deep frying and microwave drying. With proximate analysis of the post-processed 3D-printed foods, we conclude that microwave drying could better retain nutrients, while ensuring minimal changes in colour and textural properties, as compared with other post-processing methods. All post-processed samples were acceptable in terms of sensory attributes; the developed snack has the potential to be commercialised. This work explains the successful development of nutritious 3D-printed snacks from diverse plant sources, importantly, with emphasis on the development of high-fibre foods with good consumer acceptance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anukiruthika, T., Moses, J. A., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2019). 3D printing of egg yolk and white with rice flour blends. Journal of Food Engineering., 265, 109691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.109691.
AOAC International (2016). Official Methods of Analysis, 20th edn. (On-line). Rockville, MD: AOAC International.
Berman, B., Zarb, F. G., & Hall, W. (2012). 3-D printing: the new industrial revolution. Business Horizons, 55(2), 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2011.11.003.
Caballero, B., Trugo, L. C., & Finglas, P. M. (2003). Encyclopedia of food sciences and nutrition. Cambridge: Academic.
Dadali, G., Kiliç Apar, D., & Özbek, B. (2007). Microwave drying kinetics of okra. Drying Technology, 25(5), 917–924.
Dankar, I., Haddarah, A., Omar, F. E. L., Sepulcre, F., & Pujolà, M. (2018a). 3D printing technology: the new era for food customization and elaboration. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 75, 231–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.018.
Dankar, I., Pujolà, M., El Omar, F., Sepulcre, F., & Haddarah, A. (2018b). Impact of mechanical and microstructural properties of potato puree-food additive complexes on extrusion-based 3D printing. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(11), 2021–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2159-5.
Ding, S., & Yang, J. (2013). The influence of emulsifiers on the rheological properties of wheat flour dough and quality of fried instant noodles. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 53(1), 61–69.
El-Adawy, T. A., Rahma, E. H., El-Bedawey, A. A., & El-Beltagy, A. E. (2003). Nutritional potential and functional properties of germinated mung bean, pea and lentil seeds. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 58(3), 1–13.
Frary, C. D., Johnson, R. K., & Wang, M. Q. (2005). Food sources and intakes of caffeine in the diets of persons in the United States. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 105(1), 110–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2004.10.027.
Gamble, M. H., & Rice, P. (1987). Effect of pre-fry drying of oil uptake and distribution in potato crisp manufacture. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 22(5), 535–548. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1987.tb00519.x.
Godoi, F. C., Bhandari, B. R., Prakash, S., & Zhang, M. (2018). Fundamentals of 3D food printing and applications. Cambridge: Academic Press.
Guo, C., Zhang, M., & Bhandari, B. (2019). Model building and slicing in food 3D printing processes: a review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety., 18(4), 1052–1069.
Hadde, E. K., & Chen, J. (2019). Shear and extensional rheological characterization of thickened fluid for dysphagia management. Journal of Food Engineering, 245, 18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.10.007.
Huang, M., Zhang, M., & Bhandari, B. (2019). Assessing the 3D printing precision and texture properties of brown rice induced by infill levels and printing variables. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02287-x.
Içöz, D., Sumnu, G., & Sahin, S. (2004). Color and texture development during microwave and conventional baking of breads. International Journal of Food Properties, 7(2), 201–213. https://doi.org/10.1081/JFP-120025396.
Jackson, D. S., & Ratnayake, W. S. (2006). Gelatinization and solubility of corn starch during heating in excess water: new insights. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(10), 3712–3716.
Jozinović, A., Panak Balentić, J., Ačkar, D. J., Babić, J., Pajin, B., Miličević, B., et al. (2019). Cocoa husk application in the enrichment of extruded snack products. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 43(2), e13866.
Kietzmann, J., Pitt, L., & Berthon, P. (2015). Disruptions, decisions, and destinations: enter the age of 3-D printing and additive manufacturing. Business Horizons, 58(2), 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.11.005.
Lee, J. H., Won, D. J., Kim, H. W., & Park, H. J. (2019). Effect of particle size on 3D printing performance of the food-ink system with cellular food materials. Journal of Food Engineering, 256, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.03.014.
Li, W., Shu, C., Zhang, P., & Shen, Q. (2011). Properties of starch separated from ten mung bean varieties and seeds processing characteristics. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(5), 814–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0421-6.
Lille, M., Nurmela, A., Nordlund, E., Metsä-Kortelainen, S., & Sozer, N. (2018). Applicability of protein and fiber-rich food materials in extrusion-based 3D printing. Journal of Food Engineering, 220, 20–27.
Liu, Z., Zhang, M., Bhandari, B., & Wang, Y. (2017). 3D printing: printing precision and application in food sector. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 69, 83–94.
Liu, L., Meng, Y., Dai, X., Chen, K., & Zhu, Y. (2019). 3D printing complex egg white protein objects: properties and optimization. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(2), 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2209-z.
Mantihal, S., Prakash, S., Godoi, F. C., & Bhandari, B. (2017). Optimization of chocolate 3D printing by correlating thermal and flow properties with 3D structure modeling. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 44, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.09.012.
Maskan, M. (2001). Drying, shrinkage and rehydration characteristics of kiwifruits during hot air and microwave drying. Journal of Food Engineering, 48(2), 177–182.
Mondal, A., & Datta, A. K. (2008). Bread baking - a review. Journal of Food Engineering, 86(4), 465–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.11.014.
Moses, J. A., Karthickumar, P., Sinija, V. R., Alagusundaram, K., & Tiwari, B. K. (2013). Effect of microwave treatment on drying characteristics and quality parameters of thin layer drying of coconut. Asian Journal of Food and Agro Industry, 6(02), 72–85.
Nachal, N., Moses, J., Karthik, K., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2019). Applications of 3D printing in food industry: a review. Food Engineering Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-019-09199-8.
Ngo, T. D., Kashani, A., Imbalzano, G., Nguyen, K. T. Q., & Hui, D. (2018). Additive manufacturing (3D printing): a review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering, 143, 172–196.
Oyedeji, A. B., Sobukola, O. P., Henshaw, F., Adegunwa, M. O., Ijabadeniyi, O. A., Sanni, L. O., & Tomlins, K. I. (2017). Effect of frying treatments on texture and colour parameters of deep fat fried yellow fleshed cassava chips. Journal of Food Quality, 2017.
Pallottino, F., Hakola, L., Costa, C., Antonucci, F., Figorilli, S., Seisto, A., & Menesatti, P. (2016). Printing on food or food printing: a review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(5), 725–733.
Pathare, P. B., Opara, U. L., & Al-Said, F. A. J. (2013). Colour measurement and analysis in fresh and processed foods: a review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(1), 36–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0867-9.
Paula, A. M., & Conti-Silva, A. C. (2014). Texture profile and correlation between sensory and instrumental analyses on extruded snacks. Journal of Food Engineering, 121(1), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.08.007.
Pongpichaiudom, A., & Songsermpong, S. (2018). Characterization of frying, microwave-drying, infrared-drying, and hot-air drying on protein-enriched, instant noodle microstructure, and qualities. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 42(3), e13560.
Prabhakaran, B., & Moses, J. A. (2016). Pasting characteristics of raw rice flour obtained from various mill types. Advances in Life Sciences, 5(5), 1605–1609.
Severini, C., Azzollini, D., Albenzio, M., & Derossi, A. (2018a). On printability, quality and nutritional properties of 3D printed cereal based snacks enriched with edible insects. Food Research International, 106(November 2017), 666–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.034.
Severini, C., Derossi, A., Ricci, I., Caporizzi, R., & Fiore, A. (2018b). Printing a blend of fruit and vegetables. New advances on critical variables and shelf life of 3D edible objects. Journal of Food Engineering, 220, 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.08.025.
Shaw, R. (1968). Reducing the oil content of potato chips by controlling their temperature after frying.
Sun, J., Zhou, W., Huang, D., Fuh, J. Y. H., & Hong, G. S. (2015). An overview of 3D printing technologies for food fabrication. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(8), 1605–1615.
Theagarajan, R., Malur Narayanaswamy, L., Dutta, S., Moses, J. A., & Chinnaswamy, A. (2019). Valorisation of grape pomace (cv. Muscat) for development of functional cookies. International Journal of Food Science & Technology.
Trumbo, P., Schlicker, S., Yates, A. A., Poos, M., & Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine, The National Academies. (2002). Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein and amino acids. Journal of the American Dietetic Association., 102(11), 1621–1630.
Ugare, R., Chimmad, B., Naik, R., Bharati, P., & Itagi, S. (2014). Glycemic index and significance of barnyard millet (Echinochloa frumentacae) in type II diabetics. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(2), 392–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0516-8.
Wang, L., Zhang, M., Bhandari, B., & Yang, C. (2018). Investigation on fish surimi gel as promising food material for 3D printing. Journal of Food Engineering, 220, 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.02.029.
Wu, J., Aluko, R. E., & Corke, H. (2006). Partial least-squares regression study of the effects of wheat flour composition, protein and starch quality characteristics on oil content of steamed-and-fried instant noodles. Journal of Cereal Science, 44(2), 117–126.
Wu, Y., Lin, Q., Cui, T., & Xiao, H. (2014). Structural and physical properties of starches isolated from six varieties of millet grown in China. International Journal of Food Properties, 17(10), 2344–2360. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2013.803119.
Yang, F., Zhang, M., Bhandari, B., & Liu, Y. (2018). Investigation on lemon juice gel as food material for 3D printing and optimization of printing parameters. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 87, 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.054.
Zavadlav, S., Janči, T., Lacković, I., Karlović, S., Rogulj, I., & Vidaček, S. (2016). Assessment of storage shelf life of European squid (cephalopod: Loliginidae, Loligo vulgaris) by bioelectrical impedance measurements. Journal of Food Engineering, 184, 44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.03.022.
Ziaiifar, A. M., Courtois, F., & Trystram, G. (2010). Porosity development and its effect on oil uptake during frying process. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 33(2), 191–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4530.2008.00267.x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnaraj, P., Anukiruthika, T., Choudhary, P. et al. 3D Extrusion Printing and Post-Processing of Fibre-Rich Snack from Indigenous Composite Flour. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 1776–1786 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02336-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02336-5