Abstract
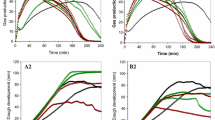
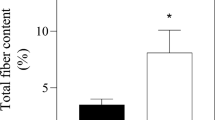
The saltiness enhancer effect of hydrolyzed animal protein (HAP) and the quality characteristics of white pan bread were evaluated through physicochemical and sensory analyses. HAP was efficiently hydrolyzed using commercial enzymes (0.20% w/w Alcalase® 2.4 L FG and 1.00% w/w FlavourzymeTM 500 MG) under high pressurization (100 MPa) and confirmed by molecular weight distribution and amino acid composition analysis. Most HAP molecules (94.18%) comprised low molecular weight peptides < 1300 Da, or free amino acids. Amino acid composition analysis of HAP also detected highly increased glutamic acid concentration. Compared with the control, the fermentation rates of doughs and loaf volumes of breads were maintained over 89.27% and 100%, respectively, with an exception of samples containing 11.70 HAP. In sensory testing, HAP concentration increases led to concomitant saltiness increases. These results suggest promising technological options for reducing salt intake from white pan bread consumption by utilizing HAP, although further study is necessary to improve bread quality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC. (1990). Approved methods, Method 10-10b. In Optimized-straight bread-making method.
Bolhuis, D. P., Temme, E. H. M., Koeman, F. T., Noort, M. W. J., Kremer, S., & Janssen, A. M. (2011). A salt reduction of 50% in bread does not decrease bread consumption or increase sodium intake by the choice of sandwich fillings. Journal of Nutrition, 141(12), 2249–2255.
Brandsma, I. (2006). Reducing sodium - a European perspective. Food Technology, 60(3), 24–29.
Brown, I. J., Tzoulaki, I., Candeias, V., & Elliott, P. (2009). Salt intakes around the world: implications for public health. International Journal of Epidemiology, 38(3), 791–813.
Chen, D. W., & Zhang, M. (2007). Non-volatile taste active compounds in the meat of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chemistry, 104(3), 1200–1205.
Desmond, E. (2006). Reducing salt: a challenge for the meat industry. Meat Science, 74(1), 188–196.
Doyle, M. E., & Glass, K. A. (2010). Sodium reduction and its effect on food safety, food quality, and human health. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 9(1), 44–56.
Emorine, M., Septier, C., Thomas-Danguin, T., & Salles, C. (2013). Heterogeneous salt distribution in hot snacks enhances saltiness without loss of acceptability. Food Research International, 51(2), 641–647.
FitzGerald, R. J., & O’Cuinn, G. (2006). Enzymatic debittering of food protein hydrolysates. Biotechnology Advances, 24(2), 234–237.
Gabriel, A. S., & Uneyama, H. (2013). Amino acid sensing in the gastrointestinal tract. Amino acids, 45(3), 451–461.
Gelabert, J., Gou, P., Guerrero, L., & Arnau, J. (2003). Effect of sodium chloride replacement on some characteristics of fermented sausages. Meat Science, 65(2), 833–839.
Gunlu, A., & Gunlu, N. (2013). Taste activity value, free amino acid content and proximate composition of Mountain trout (Salmo trutta macrostigma Dumeril, 1858) muscles. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 13(1), 58–72.
Heidolph, B. B., Ray, D. K., Roller, S., Koehler, P., Weber, J., Slocum, S., & Noort, M. W. J. (2011). Looking for my lost shaker of salt. Replacer: flavor, function, future. Cereal Foods World, 56(1), 5–19.
Imm, J. Y., & Lee, C. M. (1999). Production of seafood flavor from Red Hake (Urophycis chuss) by enzymatic hydrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47(6), 2360–2366.
In, Y. W., Yun, H. S., Bang, E., Lee, H. J., Lee, M. Y., & Cho, H. Y. (2016). Selection of commercial proteolytic enzymes for the preparation of anchovy protein hydrolysates under pressurization. Food Engineering Progress, 20(2), 89–97.
Jimenez-Maroto, L. A., Sato, T., & Rankin, S. A. (2013). Saltiness potentiation in white bread by substituting sodium chloride with a fermented soy ingredient. Journal of Cereal Science, 58(2), 313–317.
Jinap, S., & Hajeb, P. (2010). Glutamate. Its applications in food and contribution to health. Appetite, 55(1), 1–10.
Kaewka, K., Therakulkait, C., & Cadwallader, K. R. (2009). Effect of preparation conditions on composition and sensory aroma characteristics of acid hydrolyzed rice bran protein concentrate. Journal of Cereal Science, 50(1), 56–60.
Khetra, Y., Kanawjia, S. K., Puri, R., Kumar, R., & Meena, G. S. (2019). Using taste-induced saltiness enhancement for reducing sodium in Cheddar cheese: effect on physico-chemical and sensorial attributes. International Dairy Journal, 91, 165–171.
Kramer, A., Kahan, G., Cooper, D., & Papavasiliou, A. (1974). A non-parametric ranking method for the statistical evaluation of sensory data. Chemical Senses, 1(1), 121–133.
Kristinsson, H. G., & Rasco, B. (2000). Kinetics of the hydrolysis of Atlantic salmon (Salmon salar) muscle proteins by alkaline proteases and a visceral serine protease mixture. Process Biochemistry, 36(1-2), 131–139.
Lee, M. J., Popkin, B. M., & Kim, S. (2002). The unique aspects of the nutrition transition in South Korea: the retention of healthful elements in their traditional diet. Public Health Nutrition, 5(1A), 197–203.
Lee, J., Cho, H. Y., & Choi, M. J. (2016a). Effect of hydrolyzed anchovy oligopeptide under 5kDa on dried noodle as salty taste enhancer. Food Engineering Progress, 20(3), 183–189.
Lee, J., Lee, M. Y., Cho, H. Y., & Choi, M. J. (2016b). Effect of liposome-coated salt on salty taste intensity of noodle. Food Engineering Progress, 20(2), 98–104.
Lynch, E. J., Dal Bello, F., Sheehan, E. M., Cashman, K. D., & Arendt, E. K. (2009). Fundamental studies on the reduction of salt on dough and bread characteristics. Food Research International, 42(7), 885–891.
McCann, T. H., & Day, L. (2013). Effect of sodium chloride on gluten network formation, dough microstructure and rheology in relation to breadmaking. Journal of Cereal Science, 57(3), 444–452.
Nilsang, S., Lertsiri, S., Suphantharika, M., & Assavanig, A. (2005). Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of fish soluble concentrate by commercial proteases. Journal of Food Engineering, 70(4), 571–578.
Park, J. N., Watanabe, T., Endoh, K. I., Watanabe, K., & Abe, H. (2002). Taste-active components in a Vietnamese fish sauce. Fisheries Science, 68(4), 913–920.
Pietrasik, Z., & Gaudette, N. J. (2014). The impact of salt replacers and flavor enhancer on the processing characteristics and consumer acceptance of restructured cooked hams. Meat Science, 96(3), 1165–1170.
Raksakulthai, R., & Haard, N. F. (2003). Exopeptidases and their application to reduce bitterness in food: a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 43(4), 401–445.
Samapundo, S., Deschuyffeleer, N., Van Laere, D., De Leyn, I., & Devlieghere, F. (2010). Effect of NaCl reduction and replacement on the growth of fungi important to the spoilage of bread. Food Microbiology, 27(6), 749–756.
Schindler, A., Dunkel, A., Stähler, F., Backes, M., Ley, J., Meyerhof, W., & Hofmann, T. (2011). Discovery of salt taste enhancing arginyl dipeptides in protein digests and fermented fish sauces by means of a sensomics approach. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(23), 12578–12588.
Shimono, M., & Sugiyama, K. (2015). Salty taste enhancer and food or drink containing same. US Patent No. US8,932,661 B2.
World Health Organization. (2007). Reducing Salt Intake in Populations: report of a WHO Forum and Technical Meeting, 5–7 October 2006, Paris, France. URL (www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/Salt_Report_VC_april07.pdf) (2018.06.12).
Youn, S. J., Cha, G. H., & Shin, J. K. (2015). Salty taste enhancing effect of enzymatically hydrolyzed anchovy protein. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 47(6), 751–756.
Yun, H.-S., Park, H.-S., Lee, M.-Y., Shin, J.-K., & Cho, H.-Y. (2015). A feasibility study on producing salt taste enhancer in the commercial fermented fish and soy sauces. Food Engineering Progress, 19(2), 139–147.
Zanardi, E., Ghidini, S., Conter, M., & Ianieri, A. (2010). Mineral composition of Italian salami and effect NaCl partial replacement on compositional, physico-chemical and sensory parameters. Meat Science, 86(3), 742–747.
Zhang, S., Zhang, C., Qiao, Y., Xing, L., Kang, D., Khan, I. A., Huang, M., & Zhou, G. (2017). Effect of Flavourzyme on proteolysis, antioxidant activity and sensory qualities of Cantonese bacon. Food Chemistry, 237, 779–785.
Funding
This research was supported by a high value-added food technology development program [312010043HD030], Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Korea. This paper was also supported by the KU Research Professor Program of Konkuk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, Y., Lee, J., Lee, MY. et al. Effects of Hydrolyzed Animal Protein on the Enhancement of Saltiness and Quality Characteristics of White Pan Bread. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 1832–1841 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02332-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02332-9