Abstract
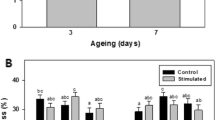
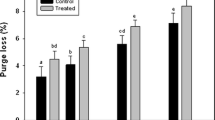
The present research investigated the effects of pulsed electric fields (PEF), low PEF (LPEF, 2.5 kV, 200 Hz and 20 μs) and high PEF (HPEF, 10 kV, 200 Hz and 20 μs), on the quality of chicken breast at 1 and 4 days post-treatment and on the concentrations of minerals (phosphorus, iron, zinc and potassium) in raw and cooked samples. HPEF increased (P < 0.001) the temperature of the chicken breasts. The shear force of chicken breasts was not affected by treatment and post-treatment storage time and their interaction (P > 0.05). The concentrations of P, K, and Zn were decreased by cooking (P < 0.001) only. The concentration of Fe was not affected by treatment, storage time, or cooking. Both LPEF and HPEF treatments did not have negative effects on the quality of chicken breast, indicating that PEF processing of chicken breast does not have a negative impact on the quality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abugroun, H. A., Forrest, J. C., Marks, J. S., & Judge, M. D. (1985). Effect of heating rate on shortening of prerigor chicken breast muscle. Poultry Science, 64, 1315–1321.
Arroyo, C., Lascorz, D., O’Dowd, L., Noci, F., Arimi, J. M., & Lyng, J. G. (2015). Effect of pulsed electric field treatments at various stages during conditioning on quality attributes of beef longissimus thoracis et lumborum muscle. Meat Science, 99, 52–59.
Barsotti, L., & Cheftel, J. (1999). Food processing by pulsed electric fields. II. Biological aspects. Food Reviews International, 15, 181–213.
Bekhit, A. E. D., Hopkins, D. L., Fahri, F. T., & Ponnampalam, E. N. (2013). Oxidative processes in muscle systems and fresh meat: sources, markers and remedies. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 12, 565–597.
Bekhit, A. E. D., Hopkins, D. L., Geesink, G., Bekhit, A. A., & Franks, P. (2014). Exogenous proteases for meat tenderization. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 54, 1012–1031.
Bekhit, A. E. D., van de Ven, R., Hopkins, D. L., Suwandy, V., & Fahri, F. (2015). Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on cold boned muscles of different potential tenderness. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 3136–3146.
Bekhit, A. E. D., Suwandy, V., Carne, A., van de Ven, R., & Hopkins, D. L. (2016). Effect of repeated pulsed electric field treatment on the quality of hot boned beef loins and topsides. Meat Science, 111, 139–146.
Bodakian, B., & Hart, F. X. (1994). The dielectric properties of meat. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 1, 181–187.
Chrystall, B. B., & Devine, C. E. (1991). Quality assurance for tenderness. Publication No. 872. Meat Industries Research Institute of New Zealand.
Del Olmo, A., Morales, P., Ávila, M., Calzada, J., & Nuñez, M. (2010). Effect of single-cycle and multiple-cycle high-pressure treatments on the colour and texture of chicken breast fillets. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 11, 441–444.
Du, M., Nam, K., & Ahn, D. (2001). Cholesterol and lipid oxidation products in cooked meat as affected by raw meat packaging and irradiation and by cooked meat packaging and storage time. Journal of Food Science, 66(9), 1396–1401.
Farouk, M. M., Bekhit, A. E. D., Dobbie, P. M., & Waller, J. (2007). Towards benchmarking beef loin steak colour acceptability using Minolta and Hunter colorimeters. 53rd International Conference of Meat Science and Technology (ICoMST), Beijing, August 5–11; 405–406.
Feidt, C., Brun-Bellut, J., & Dransfield, E. (1998). Liberation of peptides during meat storage and their interaction with proteinase activity. Meat Science, 49, 223–231.
Gudmundsson, M., & Hafsteinsson, H. (2001). Effect of electric field pulses on microstructure of muscle foods and roes. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 122–128.
Haughton, P. N., Lyng, J. G., Cronin, D. A., Morgan, D. J., Fanning, S., & Whyte, P. (2012). Efficacy of pulsed electric fields for the inactivation of indicator microorganisms and foodborne pathogens in liquids and raw chicken. Food Control, 25, 131–135.
Khan, A. A., Randhawa, M. A., Carne, A., Barr, D., Reid, M., & Bekhit, A. E. D. A. (2017). Effect of low and high pulsed electric field on the quality and nutritional minerals in cold boned beef M. Longissimus et lumborum. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 41, 135–143.
Kruk, Z. A., Yun, H., Rutley, D. L., Lee, E. J., Kim, Y. J., & Jo, C. (2011). The effect of high pressure on microbial population, meat quality and sensory characteristics of chicken breast fillet. Food Control, 22, 6–12.
Lombardi-Boccia, G., Lanzi, S., & Aguzzi, A. (2005). Aspects of meat quality: trace elements and B vitamins in raw and cooked meats. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 18, 39–46.
Mahapatra, A. K., Jones, B. L., Nguyen, C. N., & Kannan, G. (2010). Experimental determination of the electrical resistivity of beef. Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal, 12, 124–128.
McDonnell, C. K., Allen, P., Chardonnereau, F. S., Arimi, J. M., & Lyng, J. G. (2014). The use of pulsed electric fields for accelerating the salting of pork. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 59, 1054–1060.
Mok, J. H., Her, J.-Y., Kang, T., Hoptowit, R., & Jun, S. (2017). Effects of pulsed electric field (PEF) and oscillating magnetic field (OMF) combination technology on the extension of supercooling for chicken breasts. Journal of Food Engineering, 196, 27–35.
Montgomery, D. C. (2013). Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th Edition, Wiley.
Morrissey, P. A., Sheehy, P. J. A., Galvin, K., Kerry, J. P., & Buckley, D. J. (1998). Lipid stability in meat and meat products. Meat Science, 49(1), 73–86.
Murphy, R. Y., & Marks, B. P. (2000). Effect of meat temperature on proteins, texture, and cook loss for ground chicken breast patties. Poultry Science, 79, 99–104.
O’Dowd, L. P., Arimi, J. M., Noci, F., Cronin, D. A. & Lyng, J. G. (2013). An assessment of the effect of pulsed electrical fields on tenderness and selected quality attributes of post rigor beef muscle. Meat Science, 93, 303–309.
Pizato, S., Cortez-Vega, W. R., & Prentice, C. (2015). Quality assessment of cooked chicken breast meat at different storage temperatures. International Food Research Journal, 22(1), 143–154.
Rahman, R. S. (1999). Preserving foods with electricity: ohmic heating. In R. S. Rahman (Ed.), Handbook of Food preservation (pp 524). New York: CRC publishing.
Sipahioglu, O., Barringer, S. A., & Bircan, C. (2003). The dielectric properties of meats as a function of temperature and composition. Journal of Microwave Power & Electromagnetic Energy, 38, 161–169.
Suwandy, V., Carne, A., van de Ven, R., Bekhit, A. E. D., & Hopkins, D. L. (2015a). Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on the eating and keeping qualities of cold boned beef loins: impact of initial pH and fibre orientation. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1355–1365.
Suwandy, V., Carne, A., van de Ven, R., Bekhit, A. E. D., & Hopkins, D. L. (2015b). Effect of repeated pulsed electric field treatment on the eating and keeping qualities of cold boned beef loins and topsides. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1218–1228.
Suwandy, V., Carne, A., van de Ven, R., Bekhit, A. E. D., & Hopkins, D. L. (2015c). Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on hot-boned muscles of different potential tenderness. Meat Science, 105, 25–31.
Suwandy, V., Carne, A., van de Ven, R., Bekhit, A. E. D., & Hopkins, D. L. (2015d). Effect of pulsed electric field on the proteolysis of cold boned beef M. Longissimus lumborum and M. Semimembranosus. Meat Science, 100, 222–226.
Töpfl, S. (2006). Pulsed electric fields (PEF) for permeabilization of cell membranes in food-and bioprocessing: applications, process and equipment design and cost analysis. PhD thesis, Universität Berlin, Germany.
Yu, L.-H., Lee, E.-S., Jeong, J.-Y., Choi, J.-H., & Kim, C.-J. (2009). Effects of post-mortem temperature on the physicochemical properties of hot-boned chicken breast muscles. Korean Journal of Food Science and Animal Resources, 29, 55–61.
Zamri, A. I., Ledward, D., & Frazier, R. A. (2006). Effect of combined heat and high-pressure treatments on the texture of chicken breast muscle (Pectoralis Fundus). Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 54, 2992–2996.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and the International Scientific Partnership Program ISPP at King Saud University for funding this research work through ISPP# 0073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A.A., Randhawa, M.A., Carne, A. et al. Quality and Nutritional Minerals in Chicken Breast Muscle Treated with Low and High Pulsed Electric Fields. Food Bioprocess Technol 11, 122–131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1997-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1997-x