Abstract
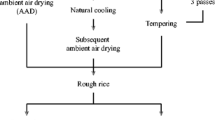
Infrared radiation heating has a promising potential in improving drying rate and food safety, but its effect on the storage stability of rough rice is not known. The objective of this study was to develop an infrared drying (IRD) method to improve the storage stability of rough rice during storage. The effects of IRD on the physicochemical properties of stored rough rice were compared with those of hot air drying (HAD) and ambient air drying (AAD). Freshly harvested M206 rice was dried to a targeted moisture content of 16 % (d.b.) by using IRD, HAD, and AAD. The dried rice samples were then stored at 35.0 ± 1.0 °C and a relative humidity of 65.0 ± 3.0 % for up to 10 months. The physicochemical and cooking properties of rice samples were periodically determined over the storage duration. Compared with AAD, the yellowness index, water uptake, and volume expansion ratio of the rough rice dried with IRD and stored for 4 months were reduced by 26.3, 76.3, and 14.5 %, respectively. After 10 months of storage, the change in hardness of cooked IR-dried rice was significantly reduced by 22 % compared to that of samples dried with AAD. IRD likely caused a slight denaturation of protein and annealing of starch that was located on the surface layer of rice kernels, resulting in decreased gelatinization temperature, enthalpy, and viscosity, and reduced the changes in microstructure, but retained cooking characteristics after storage. Therefore, IRD is recommended as a promising technique that achieves high rice drying efficiency and improved storage stability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASAE. (1995). Moisture measurements-ungrounded grain seeds (moisture relationships of grains (42nd ed., Vol. S 352.2). ASAE: Michigan.
Bei, W., Khir, R., Pan, Z., EI-Mashad, H., Atungulu, G. G., Ma, H., Qu, W., & Wu, B. (2014). Effective disinfection of rough rice using infrared radiation heating. Journal of Food Protection, 77(9), 1538–1545.
Bhardwaj, K., Raju, A., & Rajasekharan, R. (2001). Identification, purification, and characterization of a thermally stable lipase from rice bran. A new member of the (phospho) lipase family. Plant Physiology, 127(4), 1728–1738.
Blenford, D. E. (1980). Potential applications of miccronizing in food processing. Food Trade Review, 50, 6.
Champagne, E. T. (2004). Rice: chemistry and technology (3rd ed.). Eagan: Eagan Press.
Choi, B. M. (2012). Equilibrium moisture content/equilibrium relative humidity of rough rice, brown rice, white rice, and rice hull. Jeonju: Proceedings of the 6th ISMAB.
Chrastil, J., & Zarins, Z. M. (1992). Influence of storage on peptide subunit composition of rice oryzenin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 40(6), 927–930.
Cnossen, A. G., & Siebenmorgen, T. J. (2000). The glass transition temperature concept in rice drying and tempering: effect on milling quality. Transactions of the ASAE-American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 43(6), 1661–1668.
Cui, L., Pan, Z., Yue, T. L., Atungulu, G. G., & Berrios, J. (2010). Effect of ultrasonic treatment of brown rice at different temperatures on cooking properties and quality. Cereal Chemistry, 87(5), 403–408.
Dhaliwal, Y. S., Sekhon, K. S., & Nagi, H. P. S. (1991). Enzymatic activities and rheological properties of stored rice. Cereal Chemistry, 68(1), 18–21.
Ding, C., Khir, R., Pan, Z., Zhao, L., Tu, K., El-Mashad, H., & McHugh, T. H. (2015a). Improvement in shelf life of rough and brown rice using infrared radiation heating. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(5), 1149–1159.
Ding, C., Khir, R., Zhongli, P., Zhang, J., El-Mashad, H., & Tu, K. (2015b). Effect of infrared and conventional drying methods on physicochemical characteristics of stored white rice. Cereal Chemistry. doi:10.1094/CCHEM-11-14-0232-R.
Fan, J., & Marks, B. P. (1999). Effects of rough rice storage conditions on gelatinization and retrogradation properties of rice flours. Cereal Chemistry, 76(6), 894–897.
Fasina, O., Tyler, B., Pickard, M., Zheng, G. H., & Wang, N. (2001). Effect of infrared heating on the properties of legume seeds. International journal of Food Science and Technology, 36, 79–90.
Favati, F., Galgano, F., & Pace, A. M. (2007). Shelf-life evaluation of portioned Provolone cheese packaged in protective atmosphere. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 40(3), 480–488.
Guo, Y., Cai, W., Tu, K., Tu, S., Wang, S., Zhu, X., et al. (2012). Infrared and Raman spectroscopic characterization of structural changes in albumin, globulin, glutelin, and prolamin during rice aging. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(1), 185–192.
Jaiboon, P., Prachayawarakorn, S., Devahastin, S., & Soponronnarit, S. (2009). Effects of fluidized bed drying temperature and tempering time on quality of waxy rice. Journal of Food Engineering, 95(3), 517–524.
Jamradloedluk, J., Nathakaranakule, A., Soponronnarit, S., & Prachayawarakorn, S. (2007). Influences of drying medium and temperature on drying kinetics and quality attributes of durian chip. Journal of Food Engineering, 78(1), 198–205.
Kaminski, T. A., Brackmann, A., da Silva, L. P., Nicoletti, A. M., & Roberto, B. S. (2013). Changes in culinary, viscoamylographic and sensory characteristics during rice storage at different temperatures. Journal of Stored Products Research, 53, 37–42.
Khir, R., Pan, Z. L., Salim, A., Hartsough, B. R., & Mohamed, S. (2011). Moisture diffusivity of rough rice under infrared radiation drying. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 44(4).
Khir, R., Pan, Z., Thompson, J. F., Salim, A., Hartsough, B. R., & Salah, M. (2014). Moisture removal characteristics of thin layer rough rice under sequenced infrared radiation heating and cooling. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 38, 430–440.
Lamberts, L., Brijs, K., Mohamed, R., Verhelst, N., & Delcour, J. A. (2006). Impact of browning reactions and bran pigments on color of parboiled rice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(26), 9924–9929.
Li, X., & Pan, Z. (2013). Dry-peeling of tomato by infrared radiative heating: part I. Model development. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(7), 1996–2004.
Likitwattanasade, T., & Hongsprabhas, P. (2010). Effect of storage proteins on pasting properties and microstructure of Thai rice. Food Research International, 43(5), 1402–1409.
Pan, Z., Khir, R., Godfrey, L. D., Lewis, R., Thompson, J. F., & Salim, A. (2008). Feasibility of simultaneous rough rice drying and disinfestations by infrared radiation heating and rice milling quality. Journal of Food Engineering, 84(3), 469–479.
Pan, Z., Khir, R., Bett-Garber, K. L., Champagne, E. T., Thompson, J. F., Salim, A., et al. (2011). Drying characteristics and quality of rough rice under infrared radiation heating. Transactions of the ASABE, 54(1), 203–210.
Park, C. E., Kim, Y. S., Park, K. J., & Kim, B. K. (2012). Changes in physicochemical characteristics of rice during storage at different temperatures. Journal of Stored Products Research, 48, 25–29.
Service, F. G. I. (2009). United States standards for milled rice. Washington DC: Department of Agriculture.
Shimelis, E. A., Meaza, M., & Rakshit, S. (2006). Physico-chemical properties, pasting behavior and functional characteristics of flours and starches from improved bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties grown in East Africa. CIGR E Journal, 8, 1–18.
Sodhi, N., Singh, N., Arora, M., & Singh, J. (2003). Changes in physico-chemical, thermal, cooking and textural properties of rice during aging. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 27(5), 387–400.
Tananuwong, K., & Lertsiri, S. (2010). Changes in volatile aroma compounds of organic fragrant rice during storage under different conditions. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 90(10), 1590–1596.
Tananuwong, K., & Malila, Y. (2011). Changes in physicochemical properties of organic hulled rice during storage under different conditions. Food Chemistry, 125(1), 179–185.
Teo, C. H., Abd, A., Cheah, P. B., Norziah, M. H., & Seow, C. C. (2000). On the roles of protein and starch in the aging of non-waxy rice flour. Food Chemistry, 69(3), 229–236.
Tester, R. F., & Morrison, W. R. (1990). Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. 2. Waxy rice starches. Cereal Chemistry, 67(6), 558–563.
Wiset, L., Srzednicki, G., Wootton, M., Driscoll, R. H., & Blakeney, A. B. (2005). Effects of high-temperature drying on physicochemical properties of various cultivars of rice. Drying Technology, 23(9-11), 2227–2237.
Zhou, Z. K., Robards, K., Helliwell, S., & Blanchard, C. (2002a). Composition and functional properties of rice. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 37(8), 849–868.
Zhou, Z., Robards, K., Helliwell, S., & Blanchard, C. (2002b). Ageing of stored rice: changes in chemical and physical attributes. Journal of Cereal Science, 35(1), 65–78.
Zhou, Z. K., Robards, K., Helliwell, S., & Blanchard, C. (2003). Effect of rice storage on pasting properties of rice flour. Food Research International, 36(6), 625–634.
Zhou, Z. K., Robards, K., Helliwell, S., & Blanchard, C. (2007). Effect of storage temperature on cooking behaviour of rice. Food Chemistry, 105(2), 491–497.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Farmers’ Rice Cooperative for supplying the fresh rice samples for this research; Artur P. Klamczynski, Donald A. Olson, James Pan, and Borsen Chou in Western Regional Research Center, USDA-ARS, for providing the experimental instruments and helping with conducting the experiments of measuring pasting and thermal properties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, C., Khir, R., Pan, Z. et al. Improvement in Storage Stability of Infrared-Dried Rough Rice. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 1010–1020 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1690-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1690-5