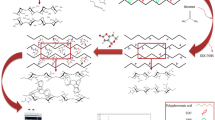
Abstract
NaOH-HCl-modified apple pomace was prepared in order to increase the adsorption capacity for epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg). The modified apple pomace contained 408.2 mg g−1 dietary fiber, 57.7 mg g−1 lignin, 23.2 mg g−1 protein, and 9.0 mg g−1 pectin, and the features of the apple pomace materials were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The adsorption of EGCg onto modified apple pomace showed excellent fitness with the pseudo-second-order model, suggesting that chemisorption was the rate-controlling step. The isothermal adsorption studies were carried out over a range of concentrations (25–1000 mg L−1) and temperatures (20, 30, and 40 °C). Low temperature advanced the adsorption capacity for EGCg. Both the Langmuir and Freundlich models precisely described the isothermal adsorption of EGCg onto modified apple pomace. Thermodynamics showed that this adsorption process was endothermic and spontaneous. Our study highlights that NaOH-HCl-modified apple pomace has good adsorption characteristics for EGCg, which could be a promising candidate for EGCg delivery in functional food and dietary supplement applications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananingsih, V. K., Sharma, A., & Zhou, W. B. (2013). Green tea catechins during food processing and storage: a review on stability and detection. Food Research International, 50(2), 469–479.
Benshitrit, R. C., Levi, C. S., Tal, S. L., Shimoni, E., & Lesmes, U. (2012). Development of oral food-grade delivery systems: current knowledge and future challenges. Food & Function, 3(1), 10–21.
Diñeiro García, Y., Valles, B. S., & Picinelli Lobo, A. (2009). Phenolic and antioxidant composition of by-products from the cider industry: apple pomace. Food Chemistry, 117(4), 731–738.
Dong, Z., Liang, Y., Fan, F., Ye, J., Zheng, X., & Lu, J. (2011). Adsorption behavior of the catechins and caffeine onto polyvinylpolypyrrolidone. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(8), 4238–4247.
Dube, A., Nicolazzo, J. A., & Larson, I. (2010). Chitosan nanoparticles enhance the intestinal absorption of the green tea catechins (+)-catechin and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 41(2), 219–225.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57, 385–470.
Gadkari, P. V., & Balaraman, M. (2015). Catechins: Sources, extraction and encapsulation: a review. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 93, 122–138.
Gao, R., Liu, H., Peng, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., & Zhao, G. (2012). Adsorption of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) onto oat β-glucan. Food Chemistry, 132(4), 1936–1943.
Gao, Z. P., Yu, Z. F., Yue, T. L., & Quek, S. Y. (2013). Adsorption isotherm, thermodynamics and kinetics studies of polyphenols separation from kiwifruit juice using adsorbent resin. Journal of Food Engineering, 116(1), 195–201.
Han, R., Zhang, L., Song, C., Zhang, M., Zhu, H., & Zhang, L. (2010). Characterization of modified wheat straw, kinetic and equilibrium study about copper ion and methylene blue adsorption in batch mode. Carbohydrate Polymers, 79(4), 1140–1149.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465.
Jaycock, M. J., & Parfitt, G. D. (1981). Chemistry of interfaces. Horwood: Chichester, U.K.
Kang, N., Lee, D. S., & Yoon, J. (2002). Kinetic modeling of fenton oxidation of phenol and monochlorophenols. Chemosphere, 47(9), 915–924.
Khan, N., Bharali, D. J., Adhami, V. M., Siddiqui, I. A., Cui, H. D., Shabana, S. M., et al. (2014). Oral administration of naturally occurring chitosan-based nanoformulated green tea polyphenol EGCG effectively inhibits prostate cancer cell growth in a xenograft model. Carcinogenesis, 35(2), 415–423.
Kuroda, Y., & Hara, Y. (1999). Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic activity of tea polyphenols. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research, 436(1), 69–97.
Kusic, H., Koprivanac, N., Bozic, A. L., & Selanec, I. (2006). Photo-assisted Fenton type processes for the degradation of phenol: a kinetic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 632–644.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38(11), 2221–2295.
Lavelli, V., & Kerr, W. (2012). Apple pomace is a good matrix for phytochemical retention. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(22), 5660–5666.
Liu, Y. (2009). Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 54(7), 1981–1985.
Nanjo, F., Mori, M., Goto, K., & HARA, Y. (1999). Radical scavenging activity of tea catechins and their related compounds. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 63(9), 1621–1623.
Neilson, A. P., Hopf, A. S., Cooper, B. R., Pereira, M. A., Bomser, J. A., & Ferruzzi, M. G. (2007). Catechin degradation with concurrent formation of homo- and heterocatechin dimers during in Vitro digestion. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(22), 8941–8949.
Parra, A. F. P., Ribotta, P. D., & Ferrero, C. (2015). Starch–apple pomace mixtures: pasting properties and microstructure. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(9), 1854–1863.
Shi, X. Y., Xiao, B., Yang, X. Y., Zhou, X. P., & Li, J. F. (2007). Batch study of dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on NaOH-treated firry sawdust. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 16(12A), 1583–1587.
Shihabi, Z. K., & Rauck, R. (1991). Plasma phenol determination by HPLC. Journal of Liquid Chromatography, 14(9), 1691–1697.
Sun-Waterhouse, D. X., Luberriaga, C., Jin, D., Wibisono, R., Wadhwa, S. S., & Waterhouse, G. I. N. (2013). Juices, fibres and skin waste extracts from white, pink or red-fleshed apple genotypes as potential food ingredients. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(2), 377–390.
Vendruscolo, F., Albuquerque, P. M., Streit, F., Esposito, E., & Ninow, J. L. (2008). Apple pomace: a versatile substrate for biotechnological applications. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 28(1), 1–12.
Wu, Z., Li, H., Ming, J., & Zhao, G. (2011). Optimization of adsorption of tea polyphenols into oat beta-glucan using response surface methodology. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(1), 378–385.
Wu, L., Melton, L. D., Sanguansri, L., & Augustin, M. A. (2014a). The batch adsorption of the epigallocatechin gallate onto apple pomace. Food Chemistry, 160, 260–265.
Wu, L., Sanguansri, L., & Augustin, M. A. (2014b). Protection of epigallocatechin gallate against degradation during in vitro digestion using apple pomace as a carrier. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(50), 12265–12270.
Wu, L., Sanguansri, L., & Augustin, M. A. (2015). Processing treatments enhance the adsorption characteristics of epigallocatechin-3-gallate onto apple pomace. Journal of Food Engineering, 150, 75–81.
Yang, B., Jiang, Y., Zhao, M., Chen, F., Wang, R., Chen, Y., et al. (2009a). Structural characterisation of polysaccharides purified from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) fruit pericarp. Food Chemistry, 115(2), 609–614.
Yang, F., Li, G., He, Y. G., Ren, F. X., & Wang, G. X. (2009b). Synthesis, characterization, and applied properties of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carbohydrate Polymers, 78(1), 95–99.
Ye, J., Jin, J., Liang, H., Lu, J., Du, Y., Zheng, X., et al. (2009). Using tea stalk lignocellulose as an adsorbent for separating decaffeinated tea catechins. Bioresource Technology, 100(2), 622–628.
Ye, J., Dong, J., Lu, J., Zheng, X., Jin, J., Chen, H., et al. (2010). Effect of graft copolymerization of fir sawdust lignocellulose with N-vinylpyrrolidone on adsorption capacity to tea catechins. Carbohydrate Polymers, 81(2), 441–447.
Zou, W., Bai, H., Gao, S., Zhao, X., & Han, R. (2012). Investigations on the batch performance of cationic dyes adsorption by citric acid modified peanut husk. Desalination and Water Treatment, 49(1–3), 41–56.
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by the “Fuzhou Jasmine Industry Promotion Project” and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2014J01082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, LY., Guo, YL., Cao, LL. et al. Application of NaOH-HCl-Modified Apple Pomace to Binding Epigallocatechin Gallate. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 917–923 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1683-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1683-4