Abstract
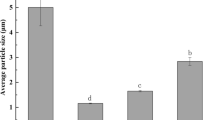
Foamability and foam stability of dairy-based emulsions, as a function of emulsion droplet size ranging from micron- to nanometre-scale, were investigated. Fat phase (10 % w/w of anhydrous milk fat, stearin or olein fraction) was mixed with 2 % w/w protein solution (sodium caseinate or whey protein concentrate) and homogenised at 3, 10 and 35 MPa to obtain emulsions having particle sizes of about 1.20, 0.60 and 0.20 μm, respectively. The emulsions were cooled down and aged at 4 °C for 48 h to promote crystallisation. No fat coalescence was observed in any of the emulsions, as particle size distribution remained the same upon aging and whipping. It was shown that the smaller the particle size, the higher was the apparent viscosity and the lower was the solid fat content. Higher solid fat content tended to yield better foamability and foam stability. Destabilisation of air cells happened fastest with nanosized fat particles, resulting in shorter half-life of foam.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, K. E., Dickinson, E., & Murray, B. (2006). Acidified sodium caseinate emulsion foams containing liquid fat: a comparison with whipped cream. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 39(3), 225–234.
Allen, K. E., Murray, B. S., & Dickinson, E. (2008). Development of a model whipped cream: effects of emulsion droplet liquid/solid character and added hydrocolloid. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(4), 690–699.
Barfod, N. M., & Krog, N. (1985). Lipid-protein interactions and fat crystallization in whippable emulsions. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 62(4), 628–629.
Barfod, N. M., Krog, N., Larsen, G., & Buchheim, W. (1991). Effects of emulsifiers on protein-fat interaction in ice-cream mix during aging. 1. Quantitative analyses. Fett Wissenschaft Technologie-Fat Science Technology, 93(1), 24–29.
Bazmi, A., & Relkin, P. (2009). Effects of processing conditions on structural and functional parameters of whipped dairy emulsions containing various fatty acid compositions. Journal of Dairy Science, 92(8), 3566–3574.
Bazmi, A., Launay, B., Cuvelier, G., & Relkin, P. (2008). Impact of crystalline milk fat on rheological properties of ice cream mix emulsions during aging time at 4C. Journal of Texture Studies, 39(4), 309–325.
Biasutti, M., Venir, E., Marino, M., Maifreni, M., & Innocente, N. (2013). Effects of high pressure homogenisation of ice cream mix on the physical and structural properties of ice cream. International Dairy Journal, 32(1), 40–45.
Britten, M., & Lavoie, L. (1992). Foaming properties of proteins as affected by concentration. Journal of Food Science, 57(5), 1219. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1992.tb11303.x.
Brooker, B. E. (1993). The stabilization of air in foods containing fat—a review. Food Structure, 12(1), 115–122.
Bugeat, S., Briard-Bion, V., Perez, J., Pradel, P., Martin, B., Lesieur, S., et al. (2011). Enrichment in unsaturated fatty acids and emulsion droplet size affect the crystallization behaviour of milk triacylglycerols upon storage at 4 degrees C. Food Research International, 44(5), 1314–1330.
Dickinson, E. (1989). Protein adsorption at liquid interfaces and the relationship to foam stability. In A. J. Wilson (Ed.), Foams: physics, chemistry and structure (pp. 39-53, Springer series in applied biology). London: Springer-Verlag.
Dickinson, E. (1992a). An introduction to food colloids. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Dickinson, E. (1992b). Structure and composition of adsorbed protein layers and the relationship to emulsion stability. journal of the Chemical Society-Faraday Transactions, 88(20), 2973–2983.
Dickinson, E. (2010). Food emulsions and foams: stabilization by particles. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 15(1–2), 40–49.
Dickinson, E., Radford, S. J., & Golding, M. (2003). Stability and rheology of emulsions containing sodium caseinate: combined effects of ionic calcium and non-ionic surfactant. Food Hydrocolloids, 17(2), 211–220.
Eisner, M. D., Jeelani, S. A. K., & Windhab, E. J. (2007). Stability of foams containing proteins, fat particles and nonionic surfactants. Chemical Engineering Science, 62(7), 1974–1987.
Gelin, J. L., Poyen, L., Courthaudon, J. L., Lemeste, M., & Lorient, D. (1994). Structural changes in oil-in-water emulsions during the manufacture of ice cream. Food Hydrocolloids, 8(3–4), 299–308.
Goff, H. D. (1997a). Colloidal aspects of ice cream—a review. International Dairy Journal, 7(6–7), 363–373.
Goff, H. D. (1997b). Instability and partial coalescence in whippable dairy emulsions. Journal of Dairy Science, 80(10), 2620–2630.
Goff, H. D., Verespej, E., & Smith, A. K. (1999). A study of fat and air structures in ice cream. International Dairy Journal, 9(11), 817–829.
Goh, K. K. T., Ye, A. Q., & Dale, N. (2006). Characterisation of ice cream containing flaxseed oil. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 41(8), 946–953.
Hayes, M. G., Lefrancois, A. C., Waldron, D. S., Goff, H. D., & Kelly, A. L. (2003). Influence of high pressure homogenisation on some characteristics of ice cream. Milchwissenschaft-Milk Science International, 58(9–10), 519–523.
Hotrum, N. E., Stuart, M. A. C., van Vliet, T., & van Aken, G. A. (2005). Proposing a relationship between the spreading coefficient and the whipping time of cream. Food Colloids: Interactions, Microstructure and Processing, 298, 317–325.
Huppertz, T., Fox, P. F., de Kruif, K. G., & Kelly, A. L. (2006). High pressure-induced changes in bovine milk proteins: a review. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Proteins and Proteomics, 1764(3), 593–598.
Ibanoglu, E., & Karatas, S. (2001). High pressure effect on foaming behaviour of whey protein isolate. Journal of Food Engineering, 47(1), 31–36.
Ihara, K., Habara, K., Ozaki, Y., Nakamura, K., Ochi, H., Saito, H., et al. (2010). Influence of whipping temperature on the whipping properties and rheological characteristics of whipped cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 93(7), 2887–2895.
Innocente, N., Biasutti, M., Venir, E., Spaziani, M., & Marchesini, G. (2009). Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distribution and rheological properties of ice cream mixes. Journal of Dairy Science, 92(5), 1864–1875.
Kamath, S., Huppertz, T., Houlihan, A. V., & Deeth, H. C. (2008). The influence of temperature on the foaming of milk. International Dairy Journal, 18(10–11), 994–1002.
Koxholt, M. M. R., Eisenmann, B., & Hinrichs, J. (2001). Effect of the fat globule sizes on the meltdown of ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 84(1), 31–37.
Lim, S. Y., Swanson, B. G., & Clark, S. (2008). High hydrostatic pressure modification of whey protein concentrate for improved functional properties. Journal of Dairy Science, 91(4), 1299–1307.
Long, Z., Zhao, M. M., Zhao, Q. Z., Yang, B., & Liu, L. Y. (2012). Effect of homogenisation and storage time on surface and rheology properties of whipping cream. Food Chemistry, 131(3), 748–753.
Marinova, K. G., Basheva, E. S., Nenova, B., Temelska, M., Mirarefi, A. Y., Campbell, B., et al. (2009). Physico-chemical factors controlling the foamability and foam stability of milk proteins: Sodium caseinate and whey protein concentrates. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(7), 1864–1876.
Martin, A. H., Grolle, K., Bos, M. A., Stuart, M. A., & van Vliet, T. (2002). Network forming properties of various proteins adsorbed at the air/water interface in relation to foam stability. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 254(1), 175–183.
Mendez-Velasco, C., & Goff, H. D. (2011). Enhancement of fat colloidal interactions for the preparation of ice cream high in unsaturated fat. International Dairy Journal, 21(8), 540–547.
Montenegro, R., Antonietti, M., Mastai, Y., & Landfester, K. (2003). Crystallization in miniemulsion droplets. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 107(21), 5088–5094.
Murray, B. S., Durga, K., Yusoff, A., & Stoyanov, S. D. (2011). Stabilization of foams and emulsions by mixtures of surface active food-grade particles and proteins. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(4), 627–638.
Olson, D. W., White, C. H., & Watson, C. E. (2003). Properties of frozen dairy desserts processed by microfluidization of their mixes. Journal of Dairy Science, 86(4), 1157–1162.
Pal, R. (1996). Effect of droplet size on the rheology of emulsions. Aiche Journal, 42(11), 3181–3190.
Patino, J. M. R., Delgado, M. D. N., & Fernandez, J. A. L. (1995). Stability and mechanical strength of aqueous foams containing food proteins. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 99(1), 65–78.
Pittia, P., Wilde, P. J., Husband, F., & Clark, D. C. (1996). Functional and structural properties of beta-lactoglobulin as affected by high pressure treatment. Journal of Food Science, 61(6), 1123–1128.
Relkin, P., & Sourdet, S. (2005). Factors affecting fat droplet aggregation in whipped frozen protein-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 19(3), 503–511.
Schmidt, K. A., & Smith, D. E. (1989). Effects of varying homogenization pressure on the physical properties of vanilla ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 72(2), 378–384.
Smith, A. K., Goff, H. D., & Kakuda, Y. (2000). Microstructure and rheological properties of whipped cream as affected by heat treatment and addition of stabilizer. International Dairy Journal, 10(4), 295–301.
Sung, K. K., & Goff, H. D. (2010). Effect of solid fat content on structure in ice creams containing palm kernel oil and high-oleic sunflower oil. Journal of Food Science, 75(3), C274–C279.
Surh, J., Jeong, Y. G., & Vladisavljevic, G. T. (2008). On the preparation of lecithin-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions by multi-stage premix membrane emulsification. Journal of Food Engineering, 89(2), 164–170.
Truong, T., Bansal, N., Sharma, J., Palmer, M., & Bhandari, B. (2014). Effects of emulsion droplet sizes on the crystallisation of milk fat. Food Chemistry, 145, 725–735.
van Aken, G. A. (2001). Aeration of emulsions by whipping. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 190(3), 333–354.
Walstra, P. (2003). Physical chemistry of foods. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Walstra, P., Wouters, J. T. M., & Geurts, T. J. (2005). Dairy science and technology. Boca Raton: CRC.
Zayas, J. F. (1997). Foaming properties of proteins. In Functionality of proteins in food (pp. 260–304). New York: Springer.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by a research grant from Dairy Innovation Australia Ltd. We thank Dr. Martin Palmer for his advice during the course of this research and in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truong, T., Bansal, N. & Bhandari, B. Effect of Emulsion Droplet Size on Foaming Properties of Milk Fat Emulsions. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 3416–3428 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1352-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1352-4