Abstract
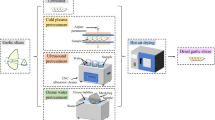
In this study, response surface methodology was used to optimize parameters of short- and medium-wave infrared drying processing for producing jujube powder. Optimization factors were power input (675–1,575 W), drying temperature (70–90 °C) and drying time (2.5–3.5 h), and responses were moisture content, L value, b value and vitamin C content of the jujube powder. Box–Benhnken center design was applied to the optimized the processing conditions. The optimal conditions for the production of jujube powder by the short- and medium-wave infrared drying method were power input of 1,125 W, drying temperature at 85.4 °C and drying time for 3.5 h. Under the optimal conditions, the values of moisture content, L, b and vitamin C content of jujube powder were 4.59 %, 64.46, 19.87 and 441.56 mg/100 g, respectively. Quality evaluation of the jujube powder was also investigated. The results were: hygroscopicity of 28.83 %, rehydration of 236.44 %, solubility of 53.59 %, bulk density of 0.70 g/ml, particle size of 154.2 μm, soluble solids content of 82.29 %, total sugar content of 46.87 %, reducing sugar content of 32.09 %, total acid content of 2.03 %, total flavonoids content of 1.45 % and cyclic adenosine monophosphate content of 75.32 mg/kg. The microstructure of jujube powder was irregular and 38 kinds of aroma components were generated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC. (1984). Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemist (14th ed.). Washington, DC: AOAC.
Cai, Y. Z., & Croke, H. (2000). Production and propertied of spray-dried Amaranthus betacyanin pigments. Journal of Food Science, 65(6), 1248–1252.
Caparino, O. A., Tang, J., Nindo, C. I., Sablani, S. S., Powers, J. R., & Fellman, J. K. (2012). Effect of drying methods on the physical properties and microstructures of mango (Philippine ‘carabao’ var.) powder. Journal of Food Engineering, 11, 135–148.
Cui, Z. Q., Meng, X. J., & Wang, C. J. (2006). Research on HPLC method for checking CAMP in winter-date. Food Research and Development, 27(7), 158–159.
Dorofejeva, K., Rakcejeva, T., Galoburda, R., Dukalska, L. J., & Kviesis, J. (2011). Vitamin C content in Latvian cranberries dried in convective and microwave vacuum driers. Procedia Food Science, 1, 433–440.
Erbay, Z., & Icier, F. (2009). Optimization of hot air drying of olive leaves using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 91, 533–541.
Fang, S. Z., Wang, Z. F., & Hu, X. S. (2009a). Hot-air drying of whole fruit Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Miller): thin-layer mathematical modeling. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 44, 1818–1824.
Fang, S. Z., Wang, Z. F., Hu, X. S., & Datta, A. K. (2009b). Hot-air drying of whole fruit Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Miller): physicochemical properties of dried products. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 44, 1415–1421.
Fang, S. Z., Wang, Z. F., Hu, X. S., Li, H., Long, W. R., & Wang, R. (2010). Shrinkage and quality characteristics of whole fruit of Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Miller) in microwave drying. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 45, 2463–2469.
Fang, S. Z., Wang, Z. F., Hu, X. S., Chen, F., Zhao, G. H., Liao, X. J., Wu, J. H., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Energy requirement and quality aspects of Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Miller) in hot air drying followed by microwave drying. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 34, 491–510.
Ferrari, C. C., Germer, S. P. M., & De Aguirre, J. M. (2012). Effects of spray-drying conditions on the physicochemical properties of blackberry powder. Drying Technology, 30, 154–163.
Gong, Z. Q., Zhang, M., Mujumdar, A. S., & Sun, J. (2008). Spray drying and agglomeration of instant bayberry powder. Drying Technology, 26, 116–121.
Guil-Guerrero, J. L., Delgado, A. D., González, M. C. M., & Isasa, M. E. T. (2004). Fatty acids and carotenes in some ber (Ziziphus jujuba Mill) varieties. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 59(1), 23–27.
Kaya, A., Aydin, O., & Kolayh, S. (2010). Effect of different drying conditions on the vitamin C (ascorbic acid) content of Hayward kiwifruits (Actinidia deliciosa Planch). Food and Bioproducts Processing, 88, 165–173.
Kim, S. H., Choi, Y. J., Lee, H., Lee, S. H., Ahn, J., Noh, B., & Min, S. C. (2012). Physicochemical properties of jujube powder from air, vacuum, and freeze drying and their correlations. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 55, 271–279.
Li, J. W., Ding, S. D., & Ding, X. L. (2005). Comparison of antioxidant capacities of extracts from five cultivars of Chinese jujube. Process Biochemistry, 40(11), 3607–3613.
Li, J. W., Fan, L. P., & Ding, S. D. (2007). Nutritional composition of five cultivars of Chinese jujube. Food Chemistry, 103, 454–460.
Lindsay, H. (1973). A colorimetric estimation of reducing sugars in potatoes with 3,5- dinitrosalicylic acid. Potato Research, 16, 176–179.
Mclaughlin, C. P., & Magee, T. R. A. (1998). The effect of shrinkage during drying of potato spheres and the effect of drying temperature on vitamin C retention. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 76, 138–142.
Nowak, D., & Lewicki, P. P. (2004). Infrared drying of apple slices. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 5, 353–360.
Sun, L. J., Zhang, J. B., Lu, X. Y., Zhang, L. Y., & Zhang, Y. L. (2011). Evaluation to the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids extract from persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49, 2689–2696.
Timoumi, S., Mihoubi, D., & Zagrouba, F. (2007). Shrinkage, vitamin C degradation and aroma losses during infra-red drying of apple slices. Food Science and Technology, 40, 1648–1654.
Togrul, H. (2005). Simple modeling of infrared drying of fresh apple slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 71, 311–323.
Tsami, E., Krokida, M. K., & Drouzas, A. E. (1999). Effect of drying method on the sorption characteristics model fruit powders. Journal of Food Engineering, 38, 381–392.
Vahedi, F., Najafi, M. F., & Bozari, K. (2008). Evaluation of inhibitory effect and apoptosis induction of Zizyphus Jujuba on tumor cell lines, an in vitro preliminary study. Cytotechnology, 56, 105–111.
Vega-Galvez, A., Scala, K. D., Rodriguez, K., Mondaca, R. L., Miranda, M., Lopez, J., & Perez-Won, M. (2009). Effect of air-drying temperature on physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacity, colour and total phenolic content of red pepper (Capsicum annuum, L. var. Hungarian). Food Chemistry, 117, 647–653.
Zhang, X., Jiang, Y. M., Peng, F. T., He, N. B., Li, Y. J., & Zhao, D. C. (2007). Changes of aroma components in Hongdeng sweet cherry during fruit development. Agricultural Sciences in China, 6(11), 1376–1382.
Zhang, L. H., Xu, H. D., & Li, S. F. (2009). Effects of micronization on properties of Chaenomeles sinensis (Thouin) Koehne fruit powder. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 10, 633–637.
Zhao, X. Y., Yang, Z. B., Gai, G. S., & Yang, Y. F. (2009). Effect of superfine grinding on properties of ginger powder. Journal of Food Engineering, 91, 217–222.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the 12th Five-year Plan Period (No. 2012BAD31B06) and Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201303073) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Incremental Project Budget of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (No. 2013ZL014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Bi and Q. Chen contributed equally to the present paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, J., Chen, Q., Zhou, Y. et al. Optimization of Short- and Medium-Wave Infrared Drying and Quality Evaluation of Jujube Powder. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 2375–2387 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1245-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1245-y