Abstract
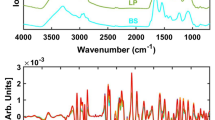
Attenuated total reflectance infrared microspectroscopy combined with soft independent modeling of class analogy (SIMCA) multivariate technique was used to differentiate between alive, dead, and injured Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells. E. coli O157:H7 cells were suspended in citrate phosphate buffer at pH 4.0 and 7.0 and treated by heat at 54 °C for 5, 10, 20, and 90 min or pulsed electric field (PEF) at 35 kV/cm for 10, 25, 50, and 60 pulses. The SIMCA analysis confirmed that major contribution to the discrimination of the untreated and treated E. coli cells were (1) the amide I band at 1,638 and 1,618 cm−1 corresponding to changes in β-pleated secondary protein structure (heat-treated cells at pH 7.0 and 4.0, and PEF-treated cells at pH 4.0), and (2) the bands at 1,078 and 993 cm−1 corresponding to changes in P = O (PO −2 ) stretching of phosphodiesters or lipopolysaccharides and C–O–C or C–O stretching of different polysaccharides (PEF-treated cells at pH 7.0). The use of partial least squares regression analysis allowed for correctly predicting the survivors of the thermal treatment. Injured cells could be estimated from the comparison of cell counts predicted in nonselective and selective plating media with sodium chloride and bile salts. The prediction results yielded inactivation values with a coefficient of determination (R 2) of 0.83 or higher and a standard error of cross validation between 0.11 and 0.37 log cycles of inactivation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Ouazzou, A., Espina, L., Gelaw, T. G., de Lamo-Castellví, S., Pagán, R., & García-Gonzalo, D. (2013). New insights in mechanisms of bacterial inactivation by carvacrol. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114, 173–185.
Al-Qadiri, H. M., Lin, M., Al-Holy, M. A., Cavinato, A. G., & Rasco, B. A. (2008). Detection of sublethal thermal injury in Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (4,000 to 600 cm−1). Journal of Food Science, 73, M54–M61.
Alvarez-Ordónez, A., Mouwen, D. J. M., López, M., & Prieto, M. (2011). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterize molecular composition and stress response in foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 84, 369–378.
Baldauf, N. A., Rodriguez-Romo, L. A., Männig, A., Yousef, A. E., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. E. (2007). Effect of selective growth media on the differentiation of Salmonella enterica serovars by Fourier-transform mid-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 68, 106–114.
Barrett, T. J., Lior, H., Green, J. H., Khakhria, R., Wells, J. G., Bell, B. P., et al. (1994). Laboratory investigation of a multistate food-borne outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by using pulsed field gel-electrophoresis and phage typing. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 32, 3013–3017.
Beekes, M., Lasch, P., & Naumann, D. (2007). Analytical applications of Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy in microbiology and prion research. Veterinary Microbiology, 123, 305–319.
Busch, S. V., & Donnelly, C. W. (1992). Development of a repair-enrichment broth for resuscitation of heat-injured Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 14–20.
Chapman, P. A., Wright, D. J., Norman, P., Fox, J., & Crick, E. (1993). Cattle as a possible source of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 infections in man. Epidemiology and Infection, 111, 439–447.
De Maesschalck, R., Candolfi, A., Massart, D. L., & Heuerding, S. (1999). Decision criteria for soft independent modelling of class analogy applied to near infrared data. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 47, 65–77.
De Maesschalck, R., Jouan-Rimbaud, D., & Massart, D. L. (2000). The Mahalanobis distance. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 50, 1–18.
De Nardo, T., Shiroma-Kian, C., Halim, Y., Francis, D., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. E. (2009). Rapid and simultaneous determination of lycopene and beta-carotene contents in tomato juice by infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 1105–1112.
Dunn, W. J., & Wold, S. (1995). SIMCA pattern recognition and classification. In H. van de Waterbeemd (Ed.), Chemometric methods in molecular design (pp. 179–193). New York: EUA:VCH.
Espina, L., Somolinos, M., Pagán, R., & García-Gonzalo, D. (2010). Effect of citral on the thermal inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in citrate phosphate buffer and apple juice. Journal of Food Protection, 73, 2189–2196.
Espina, L., Gelaw, T. K., de Lamo-Castellví, S., Pagán, R., & García-Gonzalo, D. (2013). Mechanism of bacterial inactivation by (+)-limonene and its potential use in food preservation combined processes. PloS one, 8, e56769.
García, D., Gómez, N., Condón, S., Raso, J., & Pagán, R. (2003). Pulsed electric fields cause sublethal injury in Escherichia coli. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 36, 140–144.
García, D., Hassani, M., Mañas, P., Condón, S., & Pagán, R. (2005a). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during the storage under refrigeration of apple juice treated by pulsed electric fields. Journal of Food Safety, 25, 30–42.
García, D., Gomez, N., Mañas, P., Condón, S., Raso, J., & Pagán, R. (2005b). Occurrence of sublethal injury after pulsed electric fields depending on the micro-organism, the treatment medium pH and the intensity of the treatment investigated. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99, 94–104.
García, D., Gómez, N., Raso, J., & Pagán, R. (2005c). Bacterial resistance after pulsed electric fields depending on the treatment medium pH. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 6, 388–395.
García, D., Gómez, N., Mañas, P., Raso, J., & Pagán, R. (2007). Pulsed electric fields cause bacterial envelopes permeabilization depending on the treatment intensity, the treatment medium pH and the microorganism investigated. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 113, 219–227.
Gmeiner, J., & Schlecht, S. (1980). Molecular composition of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and the importance of protein–lipopolysaccharide interactions. Archives of Microbiology, 127, 81–86.
Gould, G. W. (1996). Methods for preservation and extension of shelf life. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 33, 51–64.
Gould, G. W. (2001). New processing technologies: an overview. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 60, 463–474.
Grasso, E. M., Yousef, A. E., De Lamo-Castellvi, S., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. E. (2009). Rapid detection and differentiation of Alicyclobacillus species in fruit juice using hydrophobic grid membranes and attenuated total reflectance infrared microspectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 10670–10674.
Kansiz, M., Heraud, P., Wood, B., Burden, F., Beardall, J., & McNaughton, D. (1999). Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy and chemometrics as a tool for the discrimination of cyanobacterial strains. Phytochemistry, 52, 407–417.
Kobayashi, H., Miyamoto, T., Hashimoto, Y., Kiriki, M., Motomatsu, A., Honjoh, K., et al. (2005). Identification of factors involved in recovery of heat-injured Salmonella enteritidis. Journal of Food Protection, 68, 932–941.
Koutchma, T. (2009). Advances in ultraviolet light technology for non-thermal processing of liquid foods. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2, 138–155.
Lin, M. S., Al-Holy, M., Al-Qadiri, H., Kang, D. H., Cavinato, A. G., Huang, Y. Q., et al. (2004). Discrimination of intact and injured Listeria monocytogenes by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52, 5769–5772.
Mackey, B. M. (2000). Injured bacteria. In B. M. Lund, T. C. Baird-Parker, & G. W. Gould (Eds.), The microbiological safety and quality of food (Vol. I, pp. 315–341). Gaithersburg: Aspen.
Mañas, P., & Pagán, R. (2005). Microbial inactivation by new technologies of food preservation. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98, 1387–1399.
Mead, P. S., Slutsker, L., Dietz, V., McCaig, L. F., Bresee, J. S., Shapiro, C., et al. (1999). Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 15, 607–625.
Naumann, D. (2006) Infrared spectroscopy in microbiology. In: Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Chichester: Wiley
Neil, K. P., Biggerstaff, G., MacDonald, J. K., Trees, E., Medus, C., Musser, K. A., Stroika, S. G., Zink, D., & Sotir, M. J. (2009). A novel vehicle for transmission of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to humans: multistate outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 infections associated with consumption of ready-to-bake commercial prepackaged cookie dough-United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 54, 511–518.
O’Bryan, C. A., Crandall, P. G., Martin, E. M., Griffis, C. L., & Johnson, M. G. (2006). Heat resistance of Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria innocua M1, a potential surrogate for Listeria monocytogenes, in meat and poultry: a review. Journal of Food Science, 71, R23–R30.
Osaili, T., Griffis, C. L., Martin, E. M., Beard, B. L., Keener, A., & Marcy, J. A. (2006). Thermal inactivation studies of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat chicken-fried beef patties. Journal of Food Protection, 69, 1080–1086.
Osaili, T. M., Griffis, C. L., Martin, E. M., Beard, B. L., Keener, A. E., & Marcy, J. A. (2007). Thermal inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes in breaded pork patties. Journal of Food Science, 72, M56–M61.
Peng, H., Ford, V., Frampton, E. W., Restaino, L., Shelef, L. A., & Spitz, H. (2001). Isolation and enumeration of Bacillus cereus from foods on a novel chromogenic plating medium. Food Microbiology, 18, 231–238.
Rajkovic, A., Smigic, N., & Devlieghere, F. (2010). Contemporary strategies in combating microbial contamination in food chain. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 141, S29–42.
Reiss, G., Kunz, P., Koin, D., & Keeffe, E. B. (2006). Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in nursing homes: review of literature and report of recent outbreak. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 54, 680–684.
Restaino, L., Frampton, E. W., & Spitz, H. (2001). Repair and growth of heat- and freeze-injured Escherichia coli O157:H7 in selective enrichment broths. Food Microbiology, 18, 617–629.
Rodriguez-Saona, L. E., Khambaty, F. M., Fry, F. S., & Calvey, E. M. (2001). Rapid detection and identification of bacterial strains by Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49, 574–579.
Silhavy, T. J., Kahne, D., & Walker, S. (2010). The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2, a000414.
Subramanian, A., Ahn, J., Balasubramaniam, V. M., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. (2006). Determination of spore inactivation during thermal and pressure-assisted thermal processing using FT-IR spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 10300–10306.
Subramanian, A., Ahn, J., Balasubramaniam, V. M., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. (2007). Monitoring biochemical changes in bacterial spore during thermal and pressure-assisted thermal processing using FT-IR spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 9311–9317.
Tamm, L. K., Hong, H., & Liang, B. (2004). Folding and assembly of β-barrel membrane proteins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta/Biomembranes, 1666, 250–263.
Wan, J., Coventry, J., Swiergon, P., Sanguansri, P., & Versteeg, C. (2009). Advances in innovative processing technologies for microbial inactivation and enhancement of food safety—pulsed electric field and low-temperature plasma. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20, 414–424.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dirección General de Investigación, project CTQ2007-63002/PPQ, the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (Projects AGL2009-11660 and AGL2012-32165), and Universitat Rovira i Virgili, project 2009AIRE-06 for providing financial support. T. K. Gelaw is supported by a FI scholarship (Agència de Gestió d'Ajuts Universitaris I de Recerca).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelaw, T.K., Espina, L., Pagán, R. et al. Prediction of Injured and Dead Inactivated Escherichia coli O157:H7 Cells after Heat and Pulsed Electric Field Treatment with Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared Microspectroscopy Combined with Multivariate Analysis Technique. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 2084–2092 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1195-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1195-4