Abstract
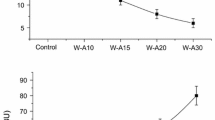
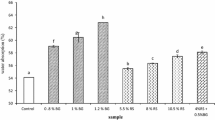
Wheat germ, a by-product of the milling industry, has interesting nutritional properties. However, it has limited use due to a high risk of rancidity, which could be reduced by using certain thermal treatments such as extrusion. The aim of this study was to investigate how wheat germ extrusion affects the changes induced by its addition to bread dough. For this purpose, different quantities of extruded or raw wheat germ (2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 20 g/100 g flour) were added to bread dough. Rheological characteristics of the dough and final quality characteristics of the bread were analysed from both the physical and the sensory points of view. Wheat germ addition increased water absorption and development time but decreased stability after over-kneading, dough tenacity, extensibility, and dough alveographic strength. The addition of extruded wheat dough improved stability and decreased extensibility and strength. Bread made from dough with added wheat germ presented decreased volume, cohesiveness, and elasticity and increased firmness. However, extrusion increased the volume of breads with added wheat germ and improver and decreased firmness. All breads obtained positive acceptability scores in sensory analysis, although wheat germ addition (10 g/100 g flour) slightly decreased texture, appearance, and overall acceptability scores of breads. Germ extrusion therefore improves dough rheology and bread quality and constitutes a suitable treatment to stabilise wheat germ in bread dough.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000). Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, Methods 44-15A (moisture), 08-01(ash), 30-10(fat), 76-12(starch), 46-08 (protein), 32-05 (total fibre); 54-30 (alveographic analysis) (10th ed.). St. Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists.
Al-Hooti, S. N., Sidhu, J. S., Al-Saqer, J. M., & Al-Othman, A. (2002). Effect of raw wheat germ addition on the physical texture and objective color of a designer food (pan bread). Nahrung-Food, 46(2), 68–72.
Arrigoni, E., Jorger, F., Kolloffel, B., Roulet, I., Herensperger, M., Meile, L., et al. (2002). In vitro fermentability of a commercial wheat germ preparation and its impact on the growth of bifidobacteria. Food Research International, 35(5), 475–481.
Axford, D. W. E., Colwell, K. H., Cornford, S. J., & Elton, G. A. H. (1968). Effect of loaf specific volume on rate and extent of staling in bread. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 19(2), 95–101.
Barnes, P. J. (1982). Composition of cereal germ preparations. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung, 174(6), 467–471.
Camire, M. E., Camire, A., & Krumhar, K. (1990). Chemical and nutritional changes in foods during extrusion. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 29(1), 35–57.
Czuchajowska, Z., & Pomeranz, Y. (1993). Gas formation and gas retention. I. The system and methodology. Cereal Foods World, 38(7), 499–503.
Defloor, I., Degeest, C., Schellekens, M., Martens, A., & Delcour, J. A. (1991). Emulsifiers and or extruded starch in the production of breads from cassava. Cereal Chemistry, 68(4), 323–327.
Engelsen, M. M., & Hansen, A. (2009). Tocopherol and tocotrienol content in commercial wheat mill streams. Cereal Chemistry, 86(5), 499–502.
Every, D., Morrison, S. C., Simmons, L. D., & Ross, M. P. (2006a). Distribution of glutathione in millstreams and relationships to chemical and baking properties of flour. Cereal Chemistry, 83(1), 57–61.
Every, D., Simmons, L. D., & Ross, M. P. (2006b). Distribution of redox enzymes in millstreams and relationships to chemical and baking properties of flour. Cereal Chemistry, 83(3), 62–68.
Galliard, T. (1986). Hydrolytic and oxidative-degradation of lipids during storage of wholemeal flour—effects of bran and germ components. Journal of Cereal Science, 4(2), 179–192.
Gomez, M., Ronda, F., Caballero, P., Blanco, C., & Rosell, C. M. (2007). Functionality of different hydrocolloids on the quality and shelf-life of yellow layer cakes. Food Hydrocolloids, 21(2), 167–173.
Gomez, M., Oliete, B., Pando, V., Ronda, F., & Caballero, P. A. (2008). Effect of fermentation conditions on bread staling kinetics. European Food Research and Technology, 226(6), 1379–1387.
Ibanoglu, E. (2002). Kinetic study on colour changes in wheat germ due to heat. Journal of Food Engineering, 51(3), 209–213.
Kermasha, S., Bisakowski, B., Ramaswamy, H., & Vandevoort, F. (1993). Comparison of microwave, conventional and combination heat-treatments on wheat-germ lipase activity. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 28(6), 617–623.
Miladi, S., Hegsted, D. M., Saunders, R. M., & Kohler, G. O. (1972). The relative nutritive value, amino acid content, and digestibility of the proteins of wheat mill fractions. Cereal Chemistry, 49(1), 119–126.
Miyazaki, M., & Morita, N. (2005). Effect of heat-moisture treated maize starch on the properties of dough and bread. Food Research International, 38(4), 369–376.
Nystrom, L., Paasonen, A., Lampi, A. M., & Piironen, V. (2007). Total plant sterols, steryl ferulates and steryl glycosides in milling fractions of wheat and rye. Journal of Cereal Science, 45(1), 106–115.
Pomeranz, Y. (1970). Phosphatides in baking wheat germ bread. Food Technology, 24(8), 927–928.
Pomeranz, Y. (1988). Chemical composition of kernel structures. In Y. Pomeranz (Ed.), Wheat Chemistry and Technology. St. Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists.
Pomeranz, Y., Carvajal, M. J., Shogren, M. D., Hoseney, R. C., & Finney, K. F. (1970). Wheat germ in breadmaking.2. Improving breadmaking properties by physical and chemical methods. Cereal Chemistry, 47(4), 429–437.
Purlis, E. (2010). Browning development in bakery products—a review. Journal of Food Engineering, 99(3), 239–249.
Rao, P. H., Kumar, G. V., Rao, G. C. P. R., & Shurpalekar, S. R. (1980a). Studies on stabilization of wheat-germ. LWT Food Science and Technology, 13(6), 302–307.
Rao, G. C. P. R., Rao, P. H., Kumar, G. V., & Shurpalekar, S. R. (1980b). Utilization of wheat-germ in the preparation of bread and biscuits. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore, 17(4), 171–175.
Rogers, D. E., Zeleznak, K. J., Lai, C. S., & Hoseney, R. C. (1988). Effect of native lipids, shortening, and bread moisture on bread firming. Cereal Chemistry, 65(5), 398–401.
Sidhu, J. S., Al-Hooti, S. N., Al-Saqer, J. M., & Al-Othman, A. (2001). Studies on the development of pan bread using raw wheat germ. Journal of Food Quality, 24(3), 235–247.
Sidhu, J. S., Kabir, Y., & Huffman, F. G. (2007). Functional foods from cereal grains. International Journal of Food Properties, 10(2), 231–244.
Singh, S., Gamlath, S., & Wakeling, L. (2007). Nutritional aspects of food extrusion: A review. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 42(8), 916–929.
Sjovall, O., Virtalaine, T., Lapvetelainen, A., & Kallio, H. (2000). Development of rancidity in wheat germ analyzed by headspace gas chromatography and sensory analysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(8), 3522–3527.
Srivastava, A. K., Sudha, M. L., Baskaran, V., & Leelavathi, K. (2007). Studies on heat stabilized wheat germ and its influence on rheological characteristics of dough. European Food Research and Technology, 224(3), 365–372.
Sudha, M. L., Srivastava, A. K., & Leelavathi, K. (2007). Studies on pasting and structural characteristics of thermally treated wheat germ. European Food Research and Technology, 225(3–4), 351–357.
Tsen, C. C. (1975). Defatted corn germ flour: a nutritive ingredient for breadmaking. Baker’s Digest, 49(5), 42–44. 55.
Vetrimani, R., Jyothirmayi, N., Rao, P. H., & Ramadoss, C. S. (1992). Inactivation of lipase and lipoxygenase in cereal bran, germ and soybean by microwave treatment. LWT Food Science and Technology, 25(6), 532–535.
Zhokhov, S. S., Broberg, A., Kenne, L., & Jastrebova, J. (2010). Content of antioxidant hydroquinones substituted by beta-1, 6-linked oligosaccharides in wheat milled fractions, flours and breads. Food Chemistry, 121(3), 645–652.
Zhu, K. X., Zhou, H. M., & Qian, H. F. (2006). Proteins extracted from defatted wheat germ: nutritional and structural properties. Cereal Chemistry, 83(1), 69–75.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología Proyects (AGL2005-05192-C04-02/ALI), Spain. Authors are also grateful to Harinera Los Pisones for supplying raw materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, M., González, J. & Oliete, B. Effect of Extruded Wheat Germ on Dough Rheology and Bread Quality. Food Bioprocess Technol 5, 2409–2418 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0519-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0519-5