Abstract
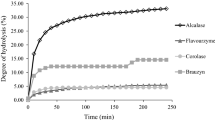
A fish protein hydrolysate (FPH) from Pacific whiting (Merluccius productus) muscle was produced by autolysis of a minced homogenate (8% protein) at pH 7.0 and 60°C, where maximum endogenous proteolytic activity was detected. FPH production was controlled by the pH stat method, yielding a 4.43% degree of hydrolysis after 1 h of autolysis. Upon autolytic processing, 28.9 ± 0.7% of the total protein was found in the soluble fraction. FPH was 100% soluble at pH 7.0 and 10.0 and was less soluble at pH 4 (82.5%, P ≤ 0.05). FPH showed better emulsifying properties than sodium caseinate (SCA) at pH 4.0 (P ≤ 0.05), but had a lower foaming capacity (P ≤ 0.05) than bovine albumin (BSA) at all evaluated pHs. FPH foaming capacity was not affected by pH, however, foam stability was equal or better than that of BSA, especially at pH 4.0 (P ≤ 0.05). These results suggest the possibility of producing FPH with similar or better functional properties than those of functional ingredients, such as SCA and BSA. Furthermore, the data presented support our hypothesis that the high proteolytic activity in Pacific whiting could be used as an advantage in fish protein hydrolysate production or as a processing aid where protein hydrolysis is required.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Nissen, J. (1979). Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 27(6), 1256–1262.
Adler-Nissen, J. (1986). Enzymatic hydrolysis of food proteins (pp. 132–169). London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Adler-Nissen, J., & Olsen, H. S. (1979). The influence of peptide chain length on taste and functional properties of enzymatically modified soy protein. In A. Pour-El (Ed.), Functionality and protein structure (pp. 125–146). Washington: American Chemical Society.
Adlerstein, S. A., & Dorn, M. W. (1998). The effect of Kudoa paniformis infection on the reproductive effort of female Pacific hake. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 76(12), 2285–2289.
Althea-Ann, T., & Nakai, S. (1983). Relationships between hydrophobicity and foaming characteristics of food proteins. Journal of Food Science, 48(2), 588–594.
AOAC. (1993). Official methods of analysis, vol II (14th ed.). Harlington: Association of Official Analytical Chemistry.
Casas-Valdez, M. (2004). La región marina del noroeste de México: oportunidades, su potencial y necesidades de investigación científica y tecnológica. In: 3a Reunión sobre legislación y política en ciencia, tecnología y educación superior en la región noroeste. Foro Consultivo Científico y Tecnológico. Available at: www.foroconsultivo.org.mx/eventos_realizados/10_agosto/presentaciones/casas.pdf. Accessed 20 March 2009.
Chobert, J. M., Bertrand-Hard, C., & Nicholas, M. G. (1988). Solubility and emulsifying properties of caseins and whey proteins modified enzimatically by trypsin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 36(5), 883–892.
Cudennec, B., Ravallec-Plé, R., Courois, E., & Fouchereau-Peron, M. (2008). Peptides from fish and crustacean by-products hydrolysates stimulate cholecystokinin release in STC-1 cells. Food Chemistry, 111(4), 970–975.
Damodaran, S. (1997). Protein-stabilized foams and emulsions. In S. Damodaran & A. Paraf (Eds.), Food proteins and their applications (pp. 57–110). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Dickinson, E., & McClements, D. J. (1996). Molecular basis of protein functionality. In: Advances in Food Colloids (pp. 27-80). Blackie Academic & Professional. Glasgow, UK.
Erickson, M. C., Gordon, D. T., & Anglemier, A. F. (1983). Proteolytic activity in the sarcoplasmatic fluids of parasited Pacific whiting (Merluccius productus) and unparasited true cod (Gadus macrocephalus). Journal of Food Science, 48(4), 1315–1319.
Fligner, K. L., & Mangino, M. E. (1991). Relationship of composition to protein functionality. In N. Parris & R. Barfor (Eds.), Interactions of Food Proteins (pp. 1–12). Washington: ACS American Chemical Society. Symposium series 454.
Gbogouri, G. A., Linder, M., Fanni, J., & Parmentier, M. (2004). Influence of hydrolysis degree on the functional properties of salmon byproducts hydrolysates. Journal of Food Science, 69(8), C615–C622.
Graham, D. E., & Philips, M. C. (1976). The conformation of proteins at their air-water interface in the role in stabilizing foams. In R. J. Akers (Ed.), Foams (p. 23). London: Academic.
Haard, N. F. (2001). Enzymatic modification of proteins in food systems. In Z. E. Sikorsky (Ed.), Chemical and functional properties of food proteins (pp. 155–190). New York: Technomic Publishing Co. Inc.
Hake, Z., & Kinsella, J. E. (1989). Relative emulsifying activity of bovine serum albumin and casein as assessed by three different methods. Journal Food Science, 54(5), 1341–1344.
Je, J. Y., Qian, Z. J., Byun, H. G., & Kim, S. K. (2007). Purification and characterization of an antioxidant peptide obtained from tuna backbone protein by enzymatic hydrolysis. Process Biochemistry, 42(5), 840–846.
Kato, A., Takahashi, A., Matsudomi, N., & Kobayashi, K. (1983). Determination of foaming properties of proteins by conductivity measurements. Journal of Food Science, 48(1), 62–65.
Khalil, M. E., Metwalli, S. M., & El-Sebaiy, L. A. (1987). Factors affecting the autolysis rate of crude preparations of proteolytic enzymes from bouri fish (Mugil cephalus). Food Chemistry, 24(2), 127–135.
Kristinsson, H. G., & Rasco, B. A. (2000). Biochemical and functional properties of atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) muscle proteins hydrolyzed with various alkaline proteases. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(3), 657–666.
Kudo, G., Barnett, H. J., & Nelson, R. W. (1987). Factors affecting cooked quality of Pacific whiting, Merluccius productus, fillets with particular emphasis on the effects of infection by the myxosporeans Kudoa paniformis and K. thyrisitis. Fisheries Bulletin, 85, 745–756.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227(5259), 680–685.
Liaset, B., & Espe, M. (2008). Nutritional composition of soluble and insoluble fractions obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of fish-raw materials. Process Biochemistry, 43(1), 42–48.
Liu, J., Alexander, M., Verespej, E., & Corredig, M. (2007). Real-time determination of structural changes of sodium caseinate-stabilized emulsions containing pectin using high resolution ultrasonic spectroscopy. Food Biophysics, 2, 67–75.
Martinez, V. G., Rodero, M., Zapatero, L., & Cuellar, C. (2002). Humoral immune responses induced by Kudoa sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) antigens in BALB/c mice. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 97, 1091–1095.
Mazorra-Manzano, M. A., Pacheco-Aguilar, R., Ramirez-Suarez, J. C., & Garcia-Sanchez, G. (2008). Pacific whiting (Merluccius productus) underutilization in the Golf of California: muscle autolytic activity characterization. Food Chemistry, 107(1), 106–111.
Milewski, S. (2001). Protein structure and physicochemical properties. In A. E. Sikorsky (Ed.), Chemical and functional properties of food proteins (pp. 35–55). Lancaster: Technomic Publishing Co., Inc.
Ovissipour, M., Safari, R., Motamedzadegan, A., & Shabanpour, B. (2009). Chemical and biochemical hydrolysis of Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) visceral protein. Food and Bioprocess Technology, doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0284-x (in press).
Pacheco-Aguilar, R., Mazorra-Manzano, M. A., & Ramirez-Suarez, J. C. (2008). Functional properties of fish protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting (Merluccius productos) muscle produced by a commercial protease. Food Chemistry, 109(4), 782–789.
Pearce, K. N., & Kinsella, J. E. (1978). Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 26(3), 716–723.
Raymundo, A., Empis, J., & Sousa, I. (2000). Effect of pH and NaCl on rheological and textrual properties of lupin protein emulsions. In P. A. Williams & G. O. Phillips (Eds.), Gums and stabilizers for the food industry (pp. 350–365). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Samaranayaka, A. G. P., & Li-Chan, E. C. Y. (2008). Autolysis-asisted production of fish protein hydrolysates with antioxidant properties from Pacific hake (Merluccius productus). Food Chemistry, 107(2), 768–776.
Safari, R., Motamedzadegan, A., Ovissipour, M., Regenstein, J. M., Gildberg, A., & Rasco, B. (2009). Use of hydrolysates from Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) heads as a complex nitrogen source for lactic acid bacteria. Food and Bioprocess Technology, doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0225-8 (in press).
Santos, S. D., Martins, V. G., Salas-Mellado, M., & Prentice, C. (2009). Evaluation of functional properties in protein hydrolysates from Bluewing searobin (Prionotus punctatus) obtained with different microbial enzymes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0301-0 (in press).
Slizyte, R., Dauksas, E., Falch, E., Storro, I., & Rustad, T. (2005). Characteristics of protein fractions generated from hydrolysed cod (Gadus morhua) by-products. Process Biochemistry, 40(6), 2021–2033.
Thiansilakul, Y., Benjakul, S., & Shahidi, F. (2007). Compositions, functional properties and antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi). Food Chemistry, 103(4), 1385–1394.
Turgeon, S. L., Gauthier, S. F., & Paquin, P. (1992). Emulsifying property of whey peptide fractions as a function of pH and ionic strength. Journal of Food Science, 57(3), 601–604. 634.
Waniska, R. D., & Kinsella, J. E. (1979). Foaming properties of proteins: evaluation of a column aeration apparatus using ovalbumin. Journal of Food Science, 44(5), 1398–1411.
Webb, N. B., Ivey, F. J., Craig, H. B., Jone, V. A., & Monroe, J. (1970). The measurement of emulsifying capacity by electrical resistance. Journal of Food Science, 35(4), 501–504.
Wilde, P. J., & Clark, D. C. (1996). Foam formation and stability. In G. M. Hall (Ed.), Methods for testing protein functionality (pp. 110–148). London: Blackie A & P.
Yin, H., Pu, J., Wan, Y., Xiang, B., Bechtel, P. J., & Sathivel, S. (2010). Rheological and functional properties of catfish skin protein hydrolysates. Journal of Food Science, 75(1), E11–E17.
Yu, M. A., & Damodaran, S. (1991). Kinetics of protein foam stabilization: evaluation of a method using bovine serum albumin. Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry, 39(9), 1555–1562.
Zhu, H. M., & Damodaran, S. (1994). Heat-induced conformational changes in whey protein isolate and its relation to foaming properties. Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry, 42(4), 846–855.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Science and Technology National Council (CONACyT) from the Republic of México for supporting this research. We are grateful to Derek Dee from the Biophysics Interdepartmental Group at the University of Guelph for his critical review to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazorra-Manzano, M.A., Pacheco-Aguilar, R., Ramírez-Suárez, J.C. et al. Endogenous Proteases in Pacific Whiting (Merluccius productus) Muscle as A Processing Aid in Functional Fish Protein Hydrolysate Production. Food Bioprocess Technol 5, 130–137 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0374-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0374-9