Abstract
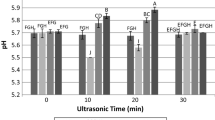
Low-frequency and high-power ultrasound (40 kHz, 1,500 W) was tested for its effects on the characteristics of intramuscular heat-insoluble collagen and meat quality and textural properties of beef semitendinosus muscle. Meat steaks (2.5 × 5.0 × 5.0 cm, 100 ± 5 g) were sonicated for 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min, respectively. Characteristics changes of collagen and meat quality and texture were estimated. The results indicated that ultrasound treatment had no significant (P > 0.05) effects on L* (lightness) and a* (redness) values but decreased b* (yellowness) value significantly when sonicated for 30 min (minimum 6.98). Ultrasound treatment significantly (P < 0.01) reduced the muscle fiber diameter and filtering residues but had no significant effects on the content of heat-insoluble collagen. Significant differences (P < 0.05) in β-galactosidase and β-glucuronidase activity were found between ultrasound treated for 10 min (reached the minimum were 5.2 × 10−3 and 1.6 × 10−3 umol∙ml−1∙min−1, respectively) and control samples. Thermal characteristics analysis of collagen suggested that ultrasound treatment weaken the average stability of collagen. After ultrasound treatment, collagenous fibers were disordered and staggered significantly; fiber arrangement became loose; and the denaturing, granulation, and aggregation of collagen fiber appeared in the extracellular space. Those changes on collagen characteristics had significant effects on meat textural properties. The results suggested that low-frequency and high-power sonication had a significant effect on collagen characters and meat textural properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktas, N., & Kaya, M. (2001). Influence of weak organic acids and salts on the denaturation characteristics of intramuscular connective tissue. A differential scanning calorimetry study. Meat Science, 58, 413–419.
Arvanitoyannis, I. S., & Houwelingen-Koukaliaroglou, M. (2003). Implementation of chemometrics for quality control and authentication of meat and meat products. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 43(2), 173–218.
Bailey, A. J., & Light, N. D. (1989). Connective tissue in meat and meat products. London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Caner, C., Aday, M. S., & Demir, M. (2008). Extending the quality of fresh strawberries by equilibrium modified atmosphere packaging. European Food Research and Technology, 227, 1575–1583.
Cheng, C. S., & Parrish, F. C., Jr. (1979). Heat-induced changes in myofibrillar proteins of bovine longissimus muscle. Journal of Food Science, 44, 22–24.
Delgado, A. E., Zheng, L., & Sun, D.-W. (2009). Influence of ultrasound on freezing rate of immersion-frozen apples. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2, 263–270.
Dutson, T. R., & Lawrie, R. A. (1974). Release of lysosomal enzymes during postmortem conditioning and their relationship to tenderness. Journal of Food Technology, 9, 43–50.
Fernandes, F. A. N., Oliveira, F. I. P., & Rodrigues, S. (2008). Use of ultrasound for dehydration of papayas. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1, 339–345.
Flint, F. O., & Pickering, K. (1984). Demonstration of collagen in meat products by an improved picro-sirius red polarization method. Analyst (London), 109, 1505–1508. doi:10.1039/an9840901505.
Frizzell, L. A. (1988). Biological effects of acoustic cavitation. In K. S. Suslick (Ed.), Ultrasound: It’s chemical, physical, and biological effects (pp. 287–301). New York: VCH.
Got, F., Culioli, J., Berge, P., Vignon, X., Astruc, T., Quideau, J. M., et al. (1999). Effects of high-intensity high-frequency ultrasound on ageing rate, ultrastructure and some physico-chemical properties of beef. Meat Science, 51, 35–42.
Guan, Y.-G., Zhang, B.-S., Yu, S.-J., Wang, X.-R., Xu, X.-B., Wang, J., et al. (2009). Effects of ultrasound on a glycin-glucose model system—A means of promoting maillard reaction. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0251-6.
Herrero, A. M., de la Hoz, L., Ordóñez, J. A., Herranz, B., Romero de Ávila, M. D., & Cambero, M. I. (2008). Tensile properties of cooked meat sausages and their correlation with texture profile analysis (TPA) parameters and physico-chemical characteristics. Meat Science, 80(3), 690–696.
Jayasooriya, S. D., Bhandari, B. R., Torley, P., & D’Arcy, B. R. (2004). Effect of high power ultrasound waves on properties of meat: A review. International Journal of Food Properties, 2, 301–319.
Jayasooriya, S. D., Torley, P. J., D’Arcy, B. R., & Bhandari, B. R. (2007). Effect of high power ultrasound and ageing on the physical properties of bovine semitendinosus and longissimus muscles. Meat Science, 75, 628–639.
Kijowski, J. M., & Mast, M. G. (1988). Thermal properties of proteins in chicken broiler tissues. Journal of Food Science, 53, 363–366.
King, N. L. (1987). Thermal transition of collagen in ovine connective tissues. Meat Science, 20, 25–37.
Li, C. B., Zhou, G. H., & Xu, X. L. (2008a). Dynamical changes of beef intramuscular connective tissue and muscle fiber during heating and their effects on beef shear force. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-008-0117-3.
Li, C. B., Zhou, G. H., & Xu, X. L. (2008b). Changes of meat quality characteristics and intramuscular connective tissue of beef semitendinosus muscle during postmortem aging for Chinese Yellow bulls. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 43, 838–845.
Lyng, J. G., Allen, P., & McKenna, B. M. (1997). The influence of high intensity ultrasound baths on aspects of beef tenderness. Journal of Muscle Foods, 78, 237–249.
Lyng, J. G., Allen, P., & McKenna, B. M. (1998a). The effect on aspects of beef tenderness of pre-and post-rigor exposure to a high intensity ultrasound probe. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 78, 308–314.
Lyng, J. G., Allen, P., & McKenna, B. M. (1998b). The effects of pre-and post-rigor high-intensity ultrasound treatment on aspects of lamb tenderness. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und -Technologie, 31, 334–338.
Mason, T. J., Paniwnyk, L., & Lorimer, J. P. (1996). The uses of ultrasound in food technology. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 3, S253–S260.
McClements, D. J. (1995). Advances in the application of ultrasound in food analysis and processing. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 6, 293–299.
Nishimura, T., Hattori, A., & Takahashi, K. (1999). Structural changes in intramuscular connective tissue during the fattening of Japanese Black Cattle, effect of marbling on beef tenderization. Journal of Animal Science, 77, 93–104.
Palka, K. (2003). The influence of post-mortem ageing and roasting on the microstructure, texture and collagen solubility of bovine semitendinosus muscle. Meat Science, 64, 191–198.
Palka, K., & Daun, H. (1999). Changes in texture, cooking losses, and myofibrillar structure of bovine m. semitendinosus during heating. Meat Science, 51, 237–243.
Papadima, S. N., Arvanitoyannis, I. S., Bloukas, J. G., & Fournitzis, G. C. (1999). Chemometric model for describing traditional sausages. Meat Science, 51, 271–277.
Pohlman, F. W., Dikeman, M. E., & Kropf, D. H. (1997a). Effects of high intensity ultrasound treatment, storage time and cooking method on shear, sensory, instrumental color and cooking properties of packaged and unpackaged beef pectoralis muscle. Meat Science, 46, 89–100.
Pohlman, F. W., Dikeman, M. E., & Zayas, J. F. (1997b). The effect of low-intensity ultrasound treatment on shear properties, color stability and shelf-life of vacuum-packaged beef semitendinosus and biceps femoris muscles. Meat Science, 45, 329–337.
Pohlman, F. W., Dikeman, M. E., Zayas, J. F., & Unruh, J. A. (1997c). Effects of ultrasound and convection cooking to different end point temperatures on cooking characteristics, shear force and sensory properties, composition, and microscopic morphology of beef longissimus and pectoralis muscles. Journal of Animal Science, 2, 386–401.
Povey, M. J. W. (1989). Ultrasonics in food engineering. Part II: applications. Journal of Food Engineering, 9, 1–20.
Povey, M. J. W., & McClements, D. J. (1988). Ultrasonics in food engineering. Part 1: Introduction and experimental methods. Journal of Food Engineering, 8, 217–245.
Probola, G., & Zander, L. (2007). Application of PCA method for characterisation of textural properties of selected ready-to-eat meat products. Journal of Food Engineering, 83(1), 93–98.
Roncales, P., Ceña, P., Beltran, J. A., & Jaime, I. (1992). Ultrasonication of lamb skeletal muscle fibers enhances post mortem proteolysis. In: 38th International Congress of Meat Science and Technology (pp. 411–414). Clermont-Ferrand.
Smith, N. B., Cannon, J. E., Novakofski, J. E., McKeith, F. K., & O’Brien, W. D. (1991). Tenderisation of semitendinosus muscle using high intensity ultrasound. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium (pp. 1371–1373). Orlando.
Stadnik, J., Dolatowski, Z. J., & Baranowska, H. M. (2008). Effect of ultrasound treatment on water properties and microstructure of beef (m. semimembranosus) during ageing. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41, 2151–2158.
Torrescano, G., Sanchez-escalante, A., Gimenez, B., Roncales, P., & Beltran, J. A. (2003). Shear values of raw samples of 14 bovine muscles and their relation to muscle collagen characteristics. Meat Science, 64, 85–91.
Wu, J. J. (1978). Characteristics of bovine intramuscular collagen under various postmortem conditions. PhD Thesis. Texas A & M University, London.
Wu, J. J., Dutson, T. R., & Carpenter, Z. L. (1982). Effect of post-mortem time and temperature on bovine intramuscular collagen. Meat Science, 7, 161–168.
Yang, Z., Zheng, Y., Cao, S., Tang, S., Ma, S., & Li, N. (2007). Effects of storage temperature on textural properties of Chinese bayberry fruit. Journal of Texture Studies, 38, 166–177.
Zayas, J. F. (1986). Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the extraction of chymosin. Journal of Dairy Science, 69, 1767–1775.
Zhong, S. Y., Jiang, M., Wang, S. R., Dai, F., & Chen, H. Y. (2007). Effects of combined ultrasonic and calcium chloride treatment on beef quality. Food Science, 11, 124–146. (in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the project grant 2006G35(2) (“948” Project of Chinese Ministry of Agriculture: Introduction, innovation and industrialization of meat quality controlling techniques). We would like to express our gratitude to Mr. Yibing Tan in Jiangnan University for providing the DSC instrument. The authors are grateful to Mr. Jian Xu for assistance in the sampling of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, HJ., Xu, XL., Zhou, GH. et al. Effects of Characteristics Changes of Collagen on Meat Physicochemical Properties of Beef Semitendinosus Muscle during Ultrasonic Processing. Food Bioprocess Technol 5, 285–297 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0269-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0269-9