Abstract
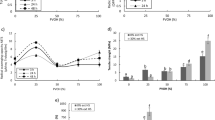
Microbial lipases constitute an important group of enzymes with high biotechnological potential, but their application is limited due to production costs. The present study aimed to evaluate the extraction conditions, concentration with ammonium sulfate, and the partial characterization of the enzyme extracts (in terms of the optimum temperature and pH and their stability at low temperatures). It was shown that the optimal extraction conditions were established at 37 °C and pH of 7.0 and that the best conditions for precipitation with ammonium sulfate were with 60% saturation for 5 h. In the partial characterization of the concentrated extract, the optima conditions were obtained at 42 °C and pH of 8.5. In a study carried out with the concentrated enzymatic extract, the hydrolytic activity was shown to be practically the same as the initial value after 91 days of storage at both 4 and −10 °C.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacha, A. B., Gargouri, Y., Ali, Y. B., Miled, N., Reinbolt, J., & Mejdoub, H. (2005). Purification and biochemical characterization of ostrich pancreatic lipase. Enzyme Microbial and Technology, 37, 309–317.
Bender, J. P., Mazutti, M. A., Oliveira, D., Di Luccio, M., & Treichel, H. (2006). Inulinase production by Kluyveromyces marxianus NRRL Y-7571 using solid state fermentation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 129, 951–958.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram of protein utilizing the principle of protein-drye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Castilho, L. R., Alves, T. L. M., & Medronho, R. A. (1999). Recovery of pectolytic enzymes produced by solid state culture of Aspergillus niger. Process Biochemistry, 34, 181–186.
Castilho, L. R., Medronho, R. A., & Alves, T. L. M. (2000). Production and extraction of pectinases obtained by solid state fermentation of agroindustrial residues with Aspergillus niger. Bioresource Technology, 71, 45–50.
Cavalcanti, E. C., Gutarra, M. L. E., Freire, D. M. G., Castilho, L. R., & Sant’Anna Jr., G. L. (2005). Lipase production by solid-state fermentation in fixed-bed bioreactors. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 48, 79–84.
Cazetta, M. L., Celligoi, M. A. P. C., Buzato, J. B., Scarmino, I. S., & da Silva, R. S. F. (2005). Optimization study for sorbitol production by Zymomonas mobilis in sugar cane molasses. Process Biochemistry, 40, 747–751.
Ceni, G. C., Baldissera, E. M., Antunes, O. A. C., Oliveira, J. V., Dariva, C., & Oliveira, D. (2008). Oxidases from mate tea leaves (Ilex paragueriensis): Extraction optimization and stability at low and high temperatures. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering. doi:10.1007/s00449-0196-y.
Chen, X., Li, Y., & Du, G. (2005). Application of response surface methodology in medium optimization for spore production of Coniothyrium minitans in solid-state fermentation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 593–599.
Fatibello-Filho, O., & Vieira, I. C. (2002). Uso analítico de tecidos e de extratos brutos vegetais como fonte enzimática. Química Nova, 25, 455–464.
Freire, D. M. G., Teles, E. M. F., Bon, E. P. S., & Sant’Anna Jr., G. L. (1997). Lipase production by Penicillium restrictum in a laboratory scale fermentor: Media composition, agitation and aeration. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 63, 409–421.
Gombert, A. K., Pinto, A. L., Castilho, L. R., & Freire, D. M. G. (2000). Lipase production by Penicillium restrictum in solid state fermentation using babassu oil cake as substrate. Process Biochemistry, 35, 85–90.
Heck, J. X., Hertz, P. F., & Ayub, M. A. Z. (2005). Extraction optimization of xylanases obtained by solid-state cultivation of Bacillus circulans BL53. Process Biochemistry, 40, 2891–2895.
Kanwar, L., Kumar, B., & Goswami, P. (2002). Production of a Pseudomonas in n-alkane substrate and its isolation using and improved ammonium sulfate precipitation technique. Bioresource Technology, 84, 207–211.
Kempka, A. P., Lipke, N. L., Pinheiro, T. L. F., Menoncin, S., Treichel, H., Freire, D. M. G., et al. (2008). Response surface method to optimize the production and characterization of lipase from Penicillium verrucosum in solid state fermentation. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 31, 119–125.
Lutz, S. (2004). Engineering lipase B from Candida antarctica. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 15, 2743–2748.
Mahadik, N. D., Puntambekar, U. S., Bastawde, K. B., Khire, J. M., & Gokhale, D. V. (2002). Production of acidic lipase by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation. Process Biochemistry, 38, 715–721.
Mazutti, M., Ceni, G., Di Luccio, M., & Treichel, H. (2007). Production of inulinase by solid state fermentation: Effect of process parameters on production and preliminary characterization of enzyme preparations. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 30, 297–394.
Mazutti, M. A., Bender, J. P., Treichel, H., & Di Luccio, M. (2006). Optimization of inulinase production by solid state fermentation using sugarcane bagasse as substrate. Enzyme Microbial and Technology, 39, 56–59.
Oliveira, D., Di Luccio, M., Freire, D. M. G., Vargas, G. D., Capra, F., & Ribeiro, N. (2004). Effect of temperature, moisture and carbon supplementation on lipase production by solid state fermentation of soy cake by Penicillium simplicissimum. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 113, 173–180.
Oliveira, D., Feihrmann, A. C., Oliveira, J. V., Dariva, C., Rubira, A. F., & Kunita, M. H. (2006a). Assessment of two immobilized lipases activity treated in compressed fluids. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 38, 373–382.
Oliveira, D., Freire, D. M. G., Oliveira, J. V., Dariva, C., Feihrmann, A. C., Cunha, A. G., et al. (2006b). Influence of compressed fluids treatment on the activity of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase. Journal of Molecular Catalysis: B, 39, 117–123.
Palma, M. B., Pinto, A. L., Gombert, A. K., Seitz, K. H., Kivatinitz, S. C., Castilho, L. R., et al. (2000). Lipase production by Penicillium restrictum using solid waste of industrial babassu oil production as substrate. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 84, 1137–1145.
Pandey, A., & Soccol, C. R. (2001). Solid state fermentation in biotechnology: Fundamentals and applications. London: Asiatec.
Pandey, A. (2003). Solid-state fermentation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 13, 81–84.
Sharma, R., Chisti, Y., & Banerjee, U. C. (2001). Production, purification, characterization, and applications of lipases. Biotechnology Advances, 19, 627–662.
Sharma, R., Soni, S. K., Vohra, R. M., Gupta, L. K., & Gupta, J. K. (2002). Purification and characterization of a thermostable alkaline lipase from a new thermophilic Bacillus sp RSJ-1. Process Biochemistry, 37, 1075–1084.
Shibata, H., Kato, H., & Oda, J. (1998). Calcium ion-dependent reactivation of a Pseudomonas lipase by its specific modulating protein, LipB. Journal of Biochemistry, 123, 136–141.
Shu, C., Xu, C., & Lin, G. (2006). Purification and partial characterization of a lipase from Antrodia cinnamomea. Process Biochemistry, 41, 734–738.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CNPq, CAPES/PROCAD, and Intecnial SA for the financial support and scholarships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menoncin, S., Domingues, N.M., Freire, D.M.G. et al. Study of the Extraction, Concentration, and Partial Characterization of Lipases Obtained from Penicillium verrucosum using Solid-State Fermentation of Soybean Bran. Food Bioprocess Technol 3, 537–544 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0104-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0104-8